Vue
Vue
概念:Vue (读音 /vjuː/,类似于 view) 是一套 **构建用户界面 ** 的 渐进式 框架
Vue2官网:https://v2.cn.vuejs.org/
什么是构建用户界面
基于数据渲染出用户可以看到的界面
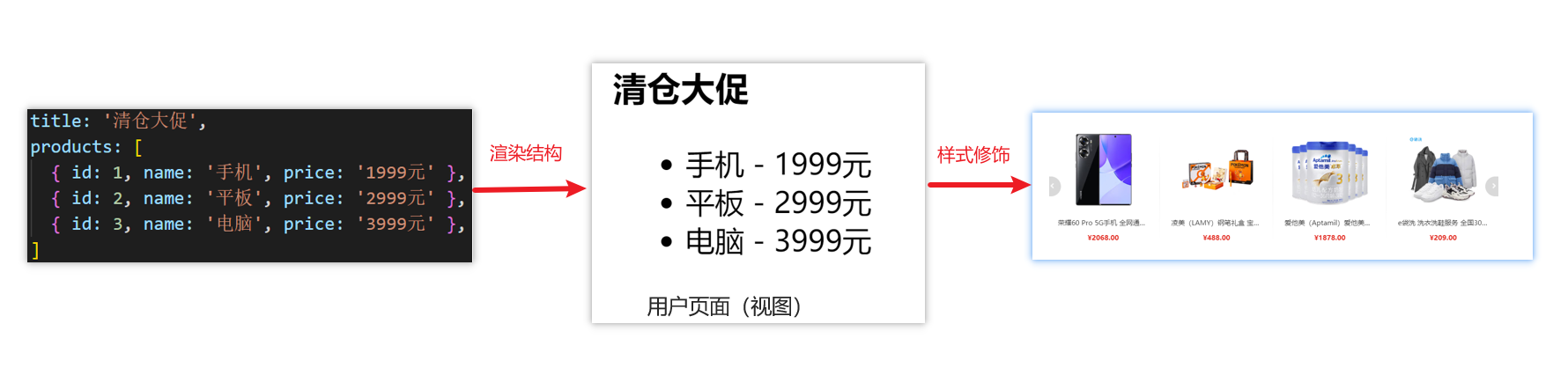
什么是渐进式
所谓渐进式就是循序渐进,不一定非得把Vue中的所有API都学完才能开发Vue,可以学一点开发一点
Vue的两种开发方式:
Vue核心包开发
场景:局部模块改造
Vue核心包&Vue插件&工程化
场景:整站开发
什么是框架
所谓框架:就是一套完整的解决方案
举个栗子
如果把一个完整的项目比喻为一个装修好的房子,那么框架就是一个毛坯房。
我们只需要在“毛坯房”的基础上,增加功能代码即可。
提到框架,不得不提一下库。
- 库,类似工具箱,是一堆方法的集合,比如 axios、lodash、echarts等
- 框架,是一套完整的解决方案,实现了大部分功能,我们只需要按照一定的规则去编码即可。
下图是 库 和 框架的对比。
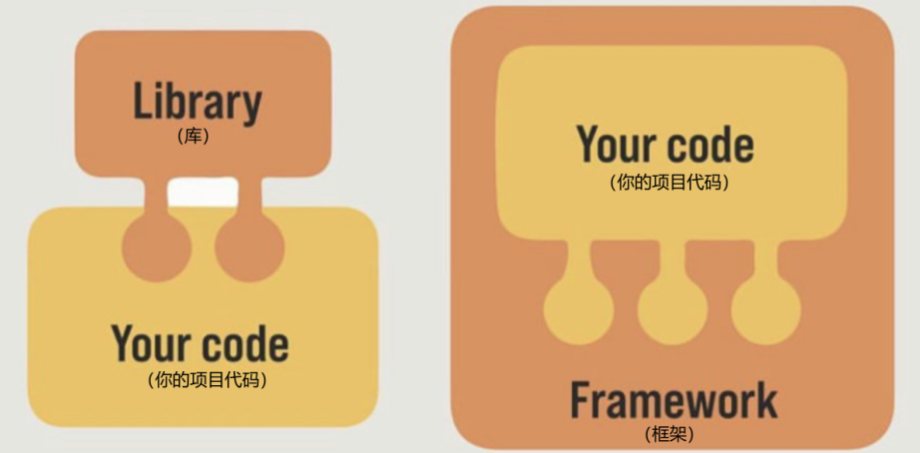
框架的特点:有一套必须让开发者遵守的规则或者约束
咱们学框架就是学习的这些规则 官网
什么是Vue?
Vue是什么:
什么是构建用户界面:
什么是渐进式:
什么是框架:
创建Vue实例
我们已经知道了Vue框架可以 基于数据帮助我们渲染出用户界面,那应该怎么做呢?
比如就上面这个数据,基于提供好的msg 怎么渲染后右侧可展示的数据呢?
核心步骤(4步):
- 准备容器
- 引包(官网) — 开发版本/生产版本
- 创建Vue实例 new Vue()
- 指定配置项,渲染数据
- el:指定挂载点
- data提供数据
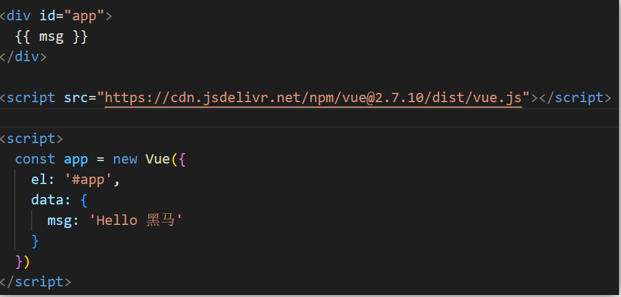
总结:创建Vue实例需要执行哪4步
插值表达式 {{}}
插值表达式是一种Vue的模板语法
我们可以用插值表达式渲染出Vue提供的数据
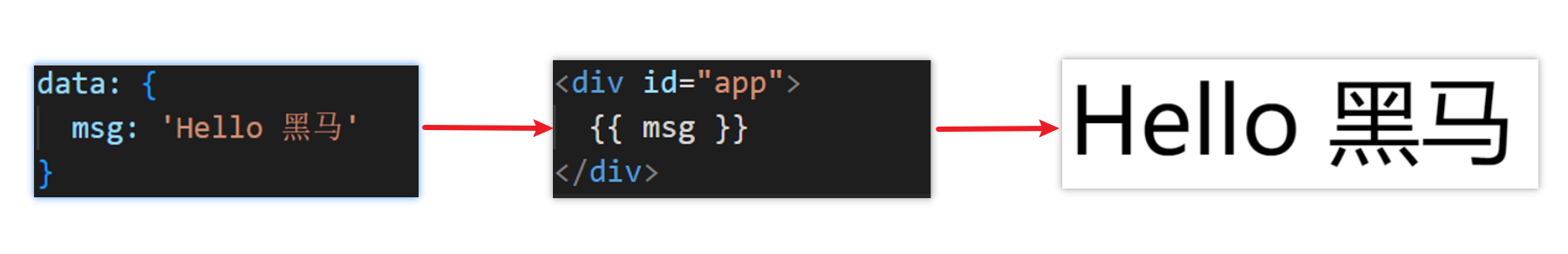
1.作用:利用表达式进行插值,渲染到页面中
表达式:是可以被求值的代码,JS引擎会讲其计算出一个结果
以下的情况都是表达式:
money + 100
money - 100
money * 10
money / 10
price >= 100 ? '真贵':'还行'
obj.name
arr[0]
fn()
obj.fn()2.语法
插值表达式语法:{{ 表达式 }}
<h3>{{title}}<h3>
<p>{{nickName.toUpperCase()}}</p>
<p>{{age >= 18 ? '成年':'未成年'}}</p>
<p>{{obj.name}}</p>
<p>{{fn()}}</p>3.错误用法
1.在插值表达式中使用的数据 必须在data中进行了提供
<p>{{hobby}}</p> //如果在data中不存在 则会报错
2.支持的是表达式,而非语句,比如:if for ...
<p>{{if}}</p>
3.不能在标签属性中使用 {{ }} 插值 (插值表达式只能标签中间使用)
<p title="{{username}}">我是P标签</p>响应式特性
1.什么是响应式?
简单理解就是数据变,视图对应变。
2.如何访问 和 修改 data中的数据(响应式演示)
data中的数据, 最终会被添加到实例上
① 访问数据: "实例.属性名"
② 修改数据: "实例.属性名"= "值"

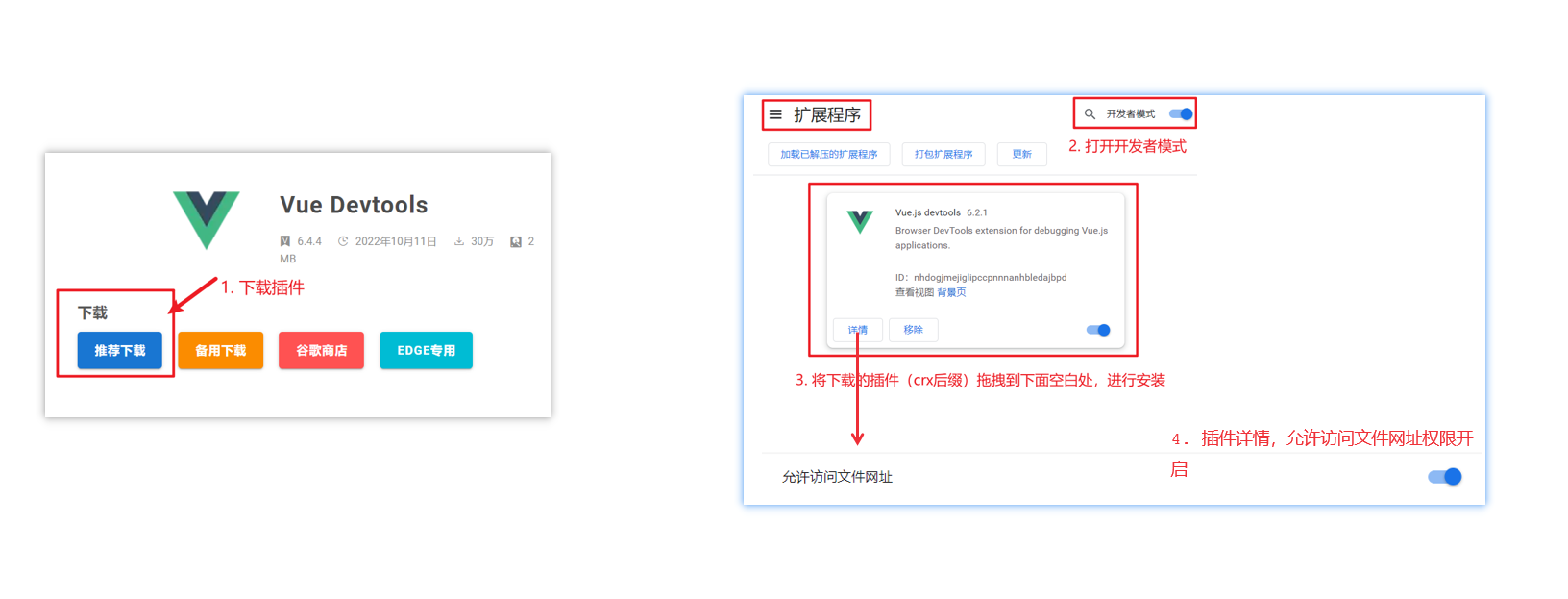
Vue开发者工具安装
- 通过谷歌应用商店安装(国外网站)
- 极简插件下载(推荐) https://chrome.zzzmh.cn/index
安装步骤:
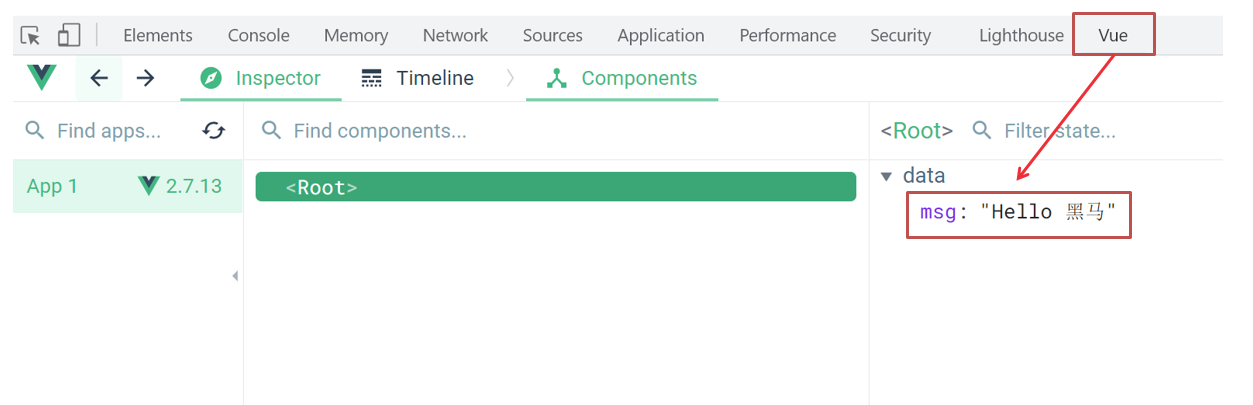
安装之后可以F12后看到多一个Vue的调试面板
Vue中的常用指令
概念:指令(Directives)是 Vue 提供的带有 v- 前缀 的 特殊 标签属性。
为啥要学:提高程序员操作 DOM 的效率。
vue 中的指令按照不同的用途可以分为如下 6 大类:
- 内容渲染指令(v-html、v-text)
- 条件渲染指令(v-show、v-if、v-else、v-else-if)
- 事件绑定指令(v-on)
- 属性绑定指令 (v-bind)
- 双向绑定指令(v-model)
- 列表渲染指令(v-for)
指令是 vue 开发中最基础、最常用、最简单的知识点。
内容渲染指令v-text
内容渲染指令用来辅助开发者渲染 DOM 元素的文本内容。常用的内容渲染指令有如下2 个:
v-text(类似innerText)
- 使用语法:
<p v-text="uname">hello</p>,意思是将 uame 值渲染到 p 标签中 - 类似 innerText,使用该语法,会覆盖 p 标签原有内容
- 使用语法:
v-html(类似 innerHTML)
- 使用语法:
<p v-html="intro">hello</p>,意思是将 intro 值渲染到 p 标签中 - 类似 innerHTML,使用该语法,会覆盖 p 标签原有内容
- 类似 innerHTML,使用该语法,能够将HTML标签的样式呈现出来。
- 使用语法:
代码演示:
<div id="app">
<h2>个人信息</h2>
// 既然指令是vue提供的特殊的html属性,所以咱们写的时候就当成属性来用即可
<p v-text="uname">姓名:</p>
<p v-html="intro">简介:</p>
</div>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
uname:'张三',
intro:'<h2>这是一个<strong>非常优秀</strong>的boy<h2>'
}
})
</script>条件渲染指令v-show v-if
条件判断指令,用来辅助开发者按需控制 DOM 的显示与隐藏。条件渲染指令有如下两个,分别是:
v-show
- 作用: 控制元素显示隐藏
- 语法: v-show = "表达式" 表达式值为 true 显示, false 隐藏
- 原理: 切换 display:none 控制显示隐藏
- 场景:频繁切换显示隐藏的场景
68189122828 v-if
- 作用: 控制元素显示隐藏(条件渲染)
- 语法: v-if= "表达式" 表达式值 true显示, false 隐藏
- 原理: 基于条件判断,是否创建 或 移除元素节点
- 场景: 要么显示,要么隐藏,不频繁切换的场景
68189123775 示例代码:
<div id="app"> <div v-show="flag" class="box">我是v-show控制的盒子</div> <div v-if="flag" class="box">我是v-if控制的盒子</div> </div> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { flag: false } }) </script>v-else 和 v-else-if
- 作用:辅助v-if进行判断渲染
- 语法:v-else v-else-if="表达式"
- 需要紧接着v-if使用
示例代码:
<div id="app">
<p v-if="gender === 1">性别:♂ 男</p>
<p v-else>性别:♀ 女</p>
<hr>
<p v-if="score >= 90">成绩评定A:奖励电脑一台</p>
<p v-else-if="score >= 70">成绩评定B:奖励周末郊游</p>
<p v-else-if="score >= 60">成绩评定C:奖励零食礼包</p>
<p v-else>成绩评定D:惩罚一周不能玩手机</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
gender: 2,
score: 95
}
})
</script>事件绑定指令v-on
使用Vue时,如需为DOM注册事件,及其的简单,语法如下:
<button v-on:事件名="内联语句">按钮</button><button v-on:事件名="处理函数">按钮</button><button v-on:事件名="处理函数(实参)">按钮</button>v-on:简写为 @
内联语句
div id="app"> <button @click="count--">-</button> <span>{{ count }}</span> <button v-on:click="count++">+</button> </div> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script> <script> const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { count: 100 } }) </script>事件处理函数
注意:
- 事件处理函数应该写到一个跟data同级的配置项(methods)中
- methods中的函数内部的this都指向Vue实例
<div id="app">
<button @click="fn">切换显示隐藏</button>
<h1 v-show="isShow">黑马程序员</h1>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app4 = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isShow: true
},
methods: {
fn () {
// 让提供的所有methods中的函数,this都指向当前实例
// console.log('执行了fn', app.isShow)
// console.log(app3 === this)
this.isShow = !this.isShow
}
}
})
</script>3.给事件处理函数传参
如果不传递任何参数,则方法无需加小括号;methods方法中可以直接使用 e 当做事件对象
如果传递了参数,则实参
$event表示事件对象,固定用法。
<style>
.box {
border: 3px solid #000000;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
margin: 20px;
width: 200px;
}
h3 {
margin: 10px 0 20px 0;
}
p {
margin: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box">
<h3>小黑自动售货机</h3>
<button @click="buy(5)">可乐5元</button>
<button @click="buy(10)">咖啡10元</button>
<button @click="buy(8)">牛奶8元</button>
</div>
<p>银行卡余额:{{ money }}元</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
money: 100
},
methods: {
buy (price) {
this.money -= price
}
}
})
</script>属性绑定指令v-bind
- **作用:**动态设置html的标签属性 比如:src、url、title
- 语法:**v-bind:**属性名=“表达式”
- **v-bind:**可以简写成 => :
比如,有一个图片,它的 src 属性值,是一个图片地址。这个地址在数据 data 中存储。
则可以这样设置属性值:
<img v-bind:src="url" /><img :src="url" />(v-bind可以省略)
<div id="app">
<!-- v-bind:src => :src -->
<img v-bind:src="imgUrl" v-bind:title="msg" alt="">
<img :src="imgUrl" :title="msg" alt="">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
imgUrl: './imgs/10-02.png',
msg: 'hello 波仔'
}
})
</script>小案例-波仔的学习之旅
需求:默认展示数组中的第一张图片,点击上一页下一页来回切换数组中的图片
实现思路:
1.数组存储图片路径 ['url1','url2','url3',...]
2.可以准备个下标index 去数组中取图片地址。
3.通过v-bind给src绑定当前的图片地址
4.点击上一页下一页只需要修改下标的值即可
5.当展示第一张的时候,上一页按钮应该隐藏。展示最后一张的时候,下一页按钮应该隐藏
<div id="app">
<button v-show="index > 0" @click="index--">上一页</button>
<div>
<img :src="list[index]" alt="">
</div>
<button v-show="index < list.length - 1" @click="index++">下一页</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
index: 0,
list: [
'./imgs/11-00.gif',
'./imgs/11-01.gif',
'./imgs/11-02.gif',
'./imgs/11-03.gif',
'./imgs/11-04.png',
'./imgs/11-05.png',
]
}
})
</script>列表渲染指令 v-for
Vue 提供了 v-for 列表渲染指令,用来辅助开发者基于一个数组来循环渲染一个列表结构。
v-for 指令需要使用 (item, index) in arr 形式的特殊语法,其中:
- item 是数组中的每一项
- index 是每一项的索引,不需要可以省略
- arr 是被遍历的数组
此语法也可以遍历对象和数字
//遍历对象
<div v-for="(value, key, index) in object">{{value}}</div>
value:对象中的值
key:对象中的键
index:遍历索引从0开始
//遍历数字
<p v-for="item in 10">{{item}}</p>
item从1 开始小案例-小黑的书架
需求:
1.根据左侧数据渲染出右侧列表(v-for)
2.点击删除按钮时,应该把当前行从列表中删除(获取当前行的id,利用filter进行过滤)
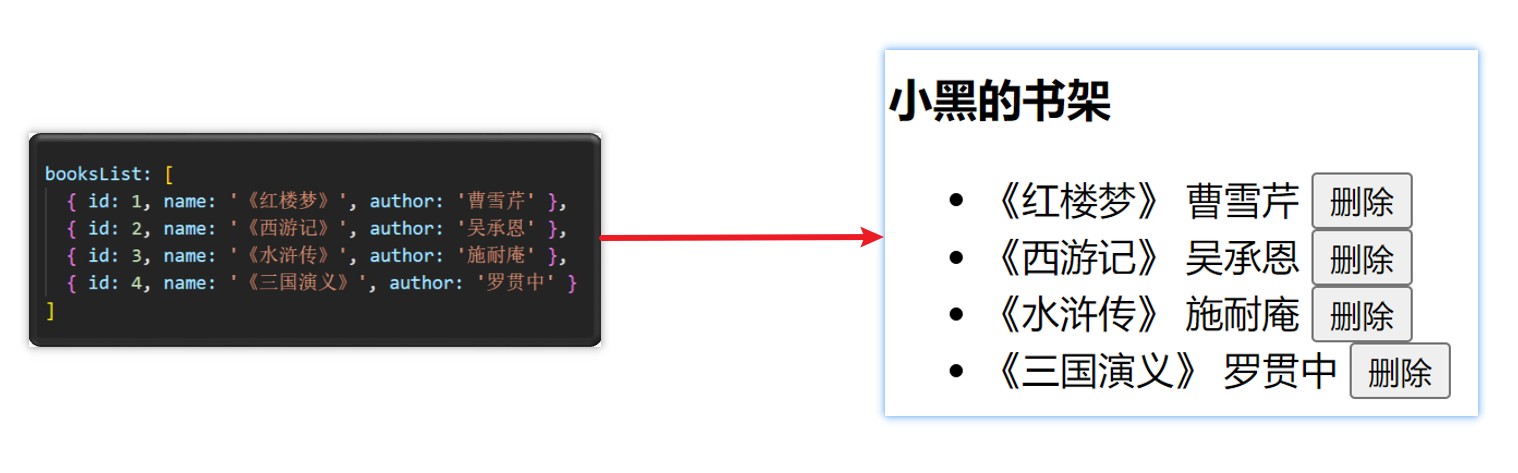
准备代码:
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑的书架</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in booksList" :key="item.id">
<span>{{ item.name }}</span>
<span>{{ item.author }}</span>
<!-- 注册点击事件 → 通过 id 进行删除数组中的 对应项 -->
<button @click="del(item.id)">删除</button>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
booksList: [
{ id: 1, name: '《红楼梦》', author: '曹雪芹' },
{ id: 2, name: '《西游记》', author: '吴承恩' },
{ id: 3, name: '《水浒传》', author: '施耐庵' },
{ id: 4, name: '《三国演义》', author: '罗贯中' }
]
},
methods: {
del (id) {
// console.log('删除', id)
// 通过 id 进行删除数组中的 对应项 → filter(不会改变原数组)
// filter: 根据条件,保留满足条件的对应项,得到一个新数组。
// console.log(this.booksList.filter(item => item.id !== id))
this.booksList = this.booksList.filter(item => item.id !== id)
}
}
})
</script>v-for中的key
语法: key="唯一值"
作用:给列表项添加的唯一标识。便于Vue进行列表项的正确排序复用。
**为什么加key:**Vue 的默认行为会尝试原地修改元素(就地复用)
实例代码:
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in booksList" :key="item.id">
<span>{{ item.name }}</span>
<span>{{ item.author }}</span>
<button @click="del(item.id)">删除</button>
</li>
</ul>注意:
- key 的值只能是字符串 或 数字类型
- key 的值必须具有唯一性
- 推荐使用 id 作为 key(唯一),不推荐使用 index 作为 key(会变化,不对应)
双向绑定指令v-model
所谓双向绑定就是:
- 数据改变后,呈现的页面结果会更新
- 页面结果更新后,数据也会随之而变
作用: 给表单元素(input、radio、select)使用,双向绑定数据,可以快速 获取 或 设置 表单元素内容
**语法:**v-model="变量"
**需求:**使用双向绑定实现以下需求
- 点击登录按钮获取表单中的内容
- 点击重置按钮清空表单中的内容

<div id="app">
<!--
v-model 可以让数据和视图,形成双向数据绑定
(1) 数据变化,视图自动更新
(2) 视图变化,数据自动更新
可以快速[获取]或[设置]表单元素的内容
-->
账户:<input type="text" v-model="username"> <br><br>
密码:<input type="password" v-model="password"> <br><br>
<button @click="login">登录</button>
<button @click="reset">重置</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: '',
password: ''
},
methods: {
login () {
console.log(this.username, this.password)
},
reset () {
this.username = ''
this.password = ''
}
}
})
</script>指令修饰符
1.什么是指令修饰符?
所谓指令修饰符就是通过“.”指明一些指令后缀 不同的后缀封装了不同的处理操作 —> 简化代码
2.按键修饰符
- @keyup.enter —>当点击enter键的时候才触发
代码演示:
<div id="app">
<h3>@keyup.enter → 监听键盘回车事件</h3>
<input @keyup.enter="fn" v-model="username" type="text">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: ''
},
methods: {
fn (e) {
// if (e.key === 'Enter') {
// console.log('键盘回车的时候触发', this.username)
// }
console.log('键盘回车的时候触发', this.username)
}
}
})
</script>3.v-model修饰符
- v-model.trim —>去除首位空格
- v-model.number —>转数字
4.事件修饰符
- @事件名.stop —> 阻止冒泡
- @事件名.prevent —>阻止默认行为
- @事件名.stop.prevent —>可以连用 即阻止事件冒泡也阻止默认行为
<style>
.father {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
margin-top: 20px;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>v-model修饰符 .trim .number</h3>
姓名:<input v-model.trim="username" type="text"><br>
年纪:<input v-model.number="age" type="text"><br>
<h3>@事件名.stop → 阻止冒泡</h3>
<div @click="fatherFn" class="father">
<div @click.stop="sonFn" class="son">儿子</div>
</div>
<h3>@事件名.prevent → 阻止默认行为</h3>
<a @click.prevent href="http://www.baidu.com">阻止默认行为</a>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: '',
age: '',
},
methods: {
fatherFn () {
alert('老父亲被点击了')
},
sonFn (e) {
// e.stopPropagation()
alert('儿子被点击了')
}
}
})
</script>v-bind对样式控制的增强-操作class
为了方便开发者进行样式控制, Vue 扩展了 v-bind 的语法,可以针对 class 类名 和 style 行内样式 进行控制 。
1.语法:
<div> :class = "对象/数组">这是一个div</div>2.对象语法
当class动态绑定的是对象时,键就是类名,值就是布尔值,如果值是true,就有这个类,否则没有这个类
<div class="box" :class="{ 类名1: 布尔值, 类名2: 布尔值 }"></div> 适用场景:一个类名,来回切换
3.数组语法
当class动态绑定的是数组时 → 数组中所有的类,都会添加到盒子上,本质就是一个 class 列表
<div class="box" :class="[ 类名1, 类名2, 类名3 ]"></div>使用场景:批量添加或删除类
4.代码
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid #000;
font-size: 30px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.pink {
background-color: pink;
}
.big {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box" :class="{ pink: true, big: true }">黑马程序员</div>
<div class="box" :class="['pink', 'big']">黑马程序员</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
}
})
</script>京东秒杀-tab栏切换导航高亮
1.需求:
当我们点击哪个tab页签时,哪个tab页签就高亮
2.代码:
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul {
display: flex;
border-bottom: 2px solid #e01222;
padding: 0 10px;
}
li {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
list-style: none;
text-align: center;
}
li a {
display: block;
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
color: #333333;
}
li a.active {
background-color: #e01222;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id" @click="activeIndex = index">
<a :class="{ active: index === activeIndex }" href="#">{{ item.name }}</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
activeIndex: 2, // 记录高亮
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '京东秒杀' },
{ id: 2, name: '每日特价' },
{ id: 3, name: '品类秒杀' }
]
}
})
</script>3.思路:
1.基于数据,动态渲染tab(v-for)
2.准备一个下标 记录高亮的是哪一个 tab
3.基于下标动态切换class的类名
v-bind对有样式控制的增强-操作style
1.语法
<div class="box" :style="{ CSS属性名1: CSS属性值, CSS属性名2: CSS属性值 }"></div>2.代码
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(187, 150, 156);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box" :style="{ width: '400px', height: '400px', backgroundColor: 'green' }"></div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
}
})
</script>3.进度条案例
<style>
.progress {
height: 25px;
width: 400px;
border-radius: 15px;
background-color: #272425;
border: 3px solid #272425;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.inner {
width: 50%;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
text-align: right;
position: relative;
background-color: #409eff;
background-size: 20px 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
transition: all 1s;
}
.inner span {
position: absolute;
right: -20px;
bottom: -25px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 外层盒子底色 (黑色) -->
<div class="progress">
<!-- 内层盒子 - 进度(蓝色) -->
<div class="inner" :style="{ width: percent + '%' }">
<span>{{ percent }}%</span>
</div>
</div>
<button @click="percent = 25">设置25%</button>
<button @click="percent = 50">设置50%</button>
<button @click="percent = 75">设置75%</button>
<button @click="percent = 100">设置100%</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
percent: 30
}
})
</script>v-model在其他表单元素的使用
1.讲解内容:
常见的表单元素都可以用 v-model 绑定关联 → 快速 获取 或 设置 表单元素的值
它会根据 控件类型 自动选取 正确的方法 来更新元素
输入框 input:text ——> value
文本域 textarea ——> value
复选框 input:checkbox ——> checked
单选框 input:radio ——> checked
下拉菜单 select ——> value
...2.代码
<style>
textarea {
display: block;
width: 240px;
height: 100px;
margin: 10px 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑学习网</h3>
姓名:
<input type="text" v-model="username">
<br><br>
是否单身:
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isSingle">
<br><br>
<!--
前置理解:
1. name: 给单选框加上 name 属性 可以分组 → 同一组互相会互斥
2. value: 给单选框加上 value 属性,用于提交给后台的数据
结合 Vue 使用 → v-model
-->
性别:
<input v-model="gender" type="radio" name="gender" value="1">男
<input v-model="gender" type="radio" name="gender" value="2">女
<br><br>
<!--
前置理解:
1. option 需要设置 value 值,提交给后台
2. select 的 value 值,关联了选中的 option 的 value 值
结合 Vue 使用 → v-model
-->
所在城市:
<select v-model="cityId">
<option value="101">北京</option>
<option value="102">上海</option>
<option value="103">成都</option>
<option value="104">南京</option>
</select>
<br><br>
自我描述:
<textarea v-model="desc"></textarea>
<button>立即注册</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
username: '',
isSingle: false,
gender: "2",
cityId: '102',
desc: ""
}
})
</script>computed计算属性
1.概念
基于现有的数据,计算出来的新属性。 依赖的数据变化,自动重新计算。
2.语法
- 声明在 computed 配置项中,一个计算属性对应一个函数
- 使用起来和普通属性一样使用
{{ 计算属性名}}
3.注意
- computed配置项和data配置项是同级的
- computed中的计算属性虽然是函数的写法,但他依然是个属性
- computed中的计算属性不能和data中的属性同名
- 使用computed中的计算属性和使用data中的属性是一样的用法
- computed中计算属性内部的this依然指向的是Vue实例
4.案例
比如我们可以使用计算属性实现下面这个业务场景

5.代码
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid #000;
text-align: center;
width: 240px;
}
th,td {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
h3 {
position: relative;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑的礼物清单</h3>
<table>
<tr>
<th>名字</th>
<th>数量</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.num }}个</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- 目标:统计求和,求得礼物总数 -->
<p>礼物总数:{{ totalCount }} 个</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 现有的数据
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '篮球', num: 1 },
{ id: 2, name: '玩具', num: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '铅笔', num: 5 },
]
},
computed: {
totalCount () {
// 基于现有的数据,编写求值逻辑
// 计算属性函数内部,可以直接通过 this 访问到 app 实例
// console.log(this.list)
// 需求:对 this.list 数组里面的 num 进行求和 → reduce
// sum: 求和得来的数
// item: 该list
// 0:sum初始值是0
let total = this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.num, 0)
return total
}
}
})
</script>computed计算属性 VS methods方法
1.computed计算属性
作用:封装了一段对于数据的处理,求得一个结果
语法:
- 写在computed配置项中
- 作为属性,直接使用
- js中使用计算属性: this.计算属性
- 模板中使用计算属性:
{{计算属性}}
2.methods计算属性
作用:给Vue实例提供一个方法,调用以处理业务逻辑。
语法:
- 写在methods配置项中
- 作为方法调用
- js中调用:this.方法名()
- 模板中调用
{{方法名()}}或者 @事件名=“方法名”
3.计算属性的优势
缓存特性(提升性能)
计算属性会对计算出来的结果缓存,再次使用直接读取缓存,
依赖项变化了,会自动重新计算 → 并再次缓存
methods没有缓存特性
通过代码比较
<style>
table {
border: 1px solid #000;
text-align: center;
width: 300px;
}
th,td {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
h3 {
position: relative;
}
span {
position: absolute;
left: 145px;
top: -4px;
width: 16px;
height: 16px;
color: white;
font-size: 12px;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: #e63f32;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>小黑的礼物清单🛒<span>{{ totalCountFn() }}</span></h3>
<h3>小黑的礼物清单🛒<span>{{ totalCountFn() }}</span></h3>
<h3>小黑的礼物清单🛒<span>{{ totalCountFn() }}</span></h3>
<h3>小黑的礼物清单🛒<span>{{ totalCountFn() }}</span></h3>
<table>
<tr>
<th>名字</th>
<th>数量</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.num }}个</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>礼物总数:{{ totalCountFn() }} 个</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 现有的数据
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '篮球', num: 3 },
{ id: 2, name: '玩具', num: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '铅笔', num: 5 },
]
},
methods: {
totalCountFn () {
console.log('methods方法执行了')
let total = this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.num, 0)
return total
}
},
computed: {
// 计算属性:有缓存的,一旦计算出来结果,就会立刻缓存
// 下一次读取 → 直接读缓存就行 → 性能特别高
// totalCount () {
// console.log('计算属性执行了')
// let total = this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.num, 0)
// return total
// }
}
})
</script>4.总结
1.computed有缓存特性,methods没有缓存
2.当一个结果依赖其他多个值时,推荐使用计算属性
3.当处理业务逻辑时,推荐使用methods方法,比如事件的处理函数
计算属性的完整写法
既然计算属性也是属性,能访问,应该也能修改了?
- 计算属性默认的简写,只能读取访问,不能 "修改"
- 如果要 "修改" → 需要写计算属性的完整写法
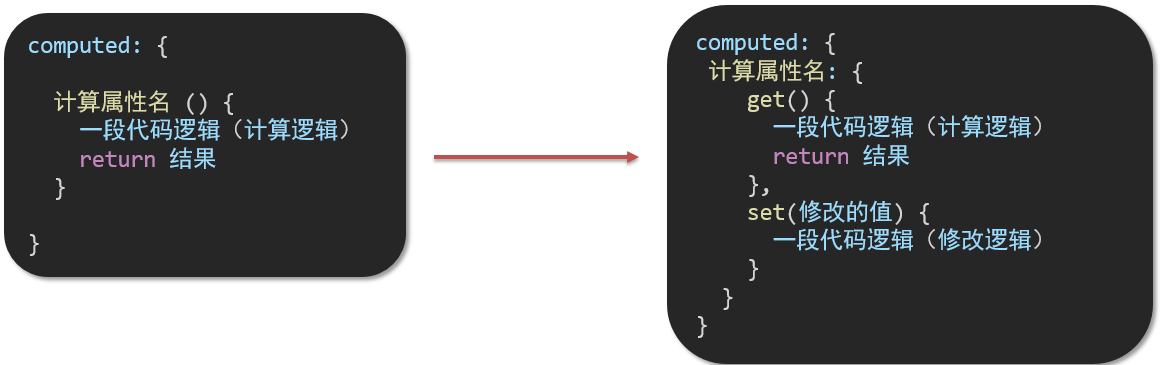
完整写法代码演示
<style>
input {
width: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> +
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> =
<span>{{ fullName }}</span><br><br>
<button @click="changeName">改名卡</button>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: '刘',
lastName: '备',
},
methods: {
changeName () {
this.fullName = '黄忠'
}
},
computed: {
// 简写 → 获取,没有配置设置的逻辑
// fullName () {
// return this.firstName + this.lastName
// }
// 完整写法 → 获取 + 设置
fullName: {
// (1) 当fullName计算属性,被获取求值时,执行get(有缓存,优先读缓存)
// 会将返回值作为,求值的结果
get () {
return this.firstName + this.lastName
},
// (2) 当fullName计算属性,被修改赋值时,执行set
// 修改的值,传递给set方法的形参
set (value) {
// console.log(value.slice(0, 1))
// console.log(value.slice(1))
this.firstName = value.slice(0, 1)
this.lastName = value.slice(1)
}
}
}
})
</script>综合案例-成绩案例
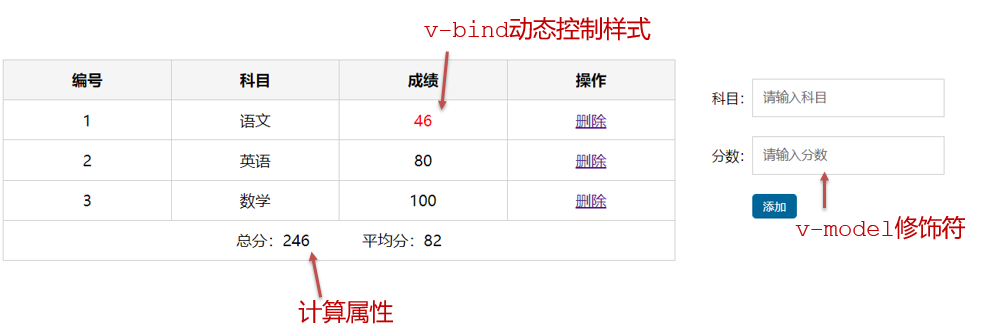
功能描述:
1.渲染功能
2.删除功能
3.添加功能
4.统计总分,求平均分
思路分析:
1.渲染功能 v-for :key v-bind:动态绑定class的样式
2.删除功能 v-on绑定事件, 阻止a标签的默认行为
3.v-model的修饰符 .trim、 .number、 判断数据是否为空后 再添加、添加后清空文本框的数据
4.使用计算属性computed 计算总分和平均分的值
watch侦听器(监视器)
1.作用:
监视数据变化,执行一些业务逻辑或异步操作
2.语法:
watch同样声明在跟data同级的配置项中
简单写法: 简单类型数据直接监视
完整写法:添加额外配置项
data: { words: '苹果', obj: { words: '苹果' } }, watch: { // 该方法会在数据变化时,触发执行 数据属性名 (newValue, oldValue) { 一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。 }, '对象.属性名' (newValue, oldValue) { 一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。 } }
3.侦听器代码准备
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 18px;
}
#app {
padding: 10px 20px;
}
.query {
margin: 10px 0;
}
.box {
display: flex;
}
textarea {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
font-size: 18px;
border: 1px solid #dedede;
outline: none;
resize: none;
padding: 10px;
}
textarea:hover {
border: 1px solid #1589f5;
}
.transbox {
width: 300px;
height: 160px;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
padding: 10px;
border: none;
}
.tip-box {
width: 300px;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
display: flex;
}
.tip-box span {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
}
.query span {
font-size: 18px;
}
.input-wrap {
position: relative;
}
.input-wrap span {
position: absolute;
right: 15px;
bottom: 15px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.input-wrap i {
font-size: 20px;
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 条件选择框 -->
<div class="query">
<span>翻译成的语言:</span>
<select>
<option value="italy">意大利</option>
<option value="english">英语</option>
<option value="german">德语</option>
</select>
</div>
<!-- 翻译框 -->
<div class="box">
<div class="input-wrap">
<textarea v-model="obj.words"></textarea>
<span><i>⌨️</i>文档翻译</span>
</div>
<div class="output-wrap">
<div class="transbox">mela</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 接口地址:https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate
// 请求方式:get
// 请求参数:
// (1)words:需要被翻译的文本(必传)
// (2)lang: 需要被翻译成的语言(可选)默认值-意大利
// -----------------------------------------------
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// words: ''
obj: {
words: ''
}
},
// 具体讲解:(1) watch语法 (2) 具体业务实现
watch: {
// 该方法会在数据变化时调用执行
// newValue新值, oldValue老值(一般不用)
// words (newValue) {
// console.log('变化了', newValue)
// }
'obj.words' (newValue) {
console.log('变化了', newValue)
}
}
})
</script>翻译案例-代码实现
<script>
// 接口地址:https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate
// 请求方式:get
// 请求参数:
// (1)words:需要被翻译的文本(必传)
// (2)lang: 需要被翻译成的语言(可选)默认值-意大利
// -----------------------------------------------
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
//words: ''
obj: {
words: ''
},
result: '', // 翻译结果
// timer: null // 延时器id
},
// 具体讲解:(1) watch语法 (2) 具体业务实现
watch: {
// 该方法会在数据变化时调用执行
// newValue新值, oldValue老值(一般不用)
// words (newValue) {
// console.log('变化了', newValue)
// }
'obj.words' (newValue) {
// console.log('变化了', newValue)
// 防抖: 延迟执行 → 干啥事先等一等,延迟一会,一段时间内没有再次触发,才执行
clearTimeout(this.timer)
this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
const res = await axios({
url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
params: {
words: newValue
}
})
this.result = res.data.data
console.log(res.data.data)
}, 300)
}
}
})
</script>watch侦听器完整写法
1.语法
完整写法 —>添加额外的配置项
- deep:true 对复杂类型进行深度监听
- immdiate:true 初始化 立刻执行一次
data: {
obj: {
words: '苹果',
lang: 'italy'
},
},
watch: {// watch 完整写法
对象: {
deep: true, // 深度监视
immdiate:true,//立即执行handler函数
handler (newValue) {
console.log(newValue)
}
}
}2.需求
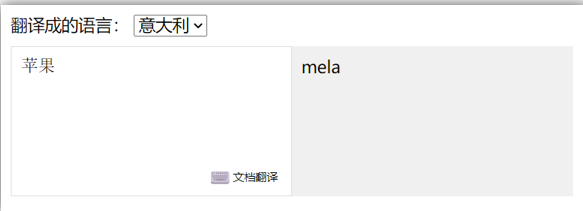
- 当文本框输入的时候 右侧翻译内容要时时变化
- 当下拉框中的语言发生变化的时候 右侧翻译的内容依然要时时变化
- 如果文本框中有默认值的话要立即翻译
3.代码实现
<script>
// 需求:输入内容,修改语言,都实时翻译
// 接口地址:https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate
// 请求方式:get
// 请求参数:
// (1)words:需要被翻译的文本(必传)
// (2)lang: 需要被翻译成的语言(可选)默认值-意大利
// -----------------------------------------------
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
obj: {
words: '小黑',
lang: 'italy'
},
result: '', // 翻译结果
},
watch: {
obj: {
deep: true, // 深度监视
immediate: true, // 立刻执行,一进入页面handler就立刻执行一次
handler (newValue) {
clearTimeout(this.timer)
this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
const res = await axios({
url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
params: newValue
})
this.result = res.data.data
console.log(res.data.data)
}, 300)
}
}
// 'obj.words' (newValue) {
// clearTimeout(this.timer)
// this.timer = setTimeout(async () => {
// const res = await axios({
// url: 'https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/api/translate',
// params: {
// words: newValue
// }
// })
// this.result = res.data.data
// console.log(res.data.data)
// }, 300)
// }
}
})
</script>4.总结
watch侦听器的写法有几种?
1.简单写法
watch: {
数据属性名 (newValue, oldValue) {
一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。
},
'对象.属性名' (newValue, oldValue) {
一些业务逻辑 或 异步操作。
}
}2.完整写法
watch: {// watch 完整写法
数据属性名: {
deep: true, // 深度监视(针对复杂类型),因为deep默认监视的是普通类型,若是对象这种复杂类型则无法监视
immediate: true, // 是否立刻执行一次handler
handler (newValue) {
console.log(newValue)
}
}
}综合案例
购物车案例
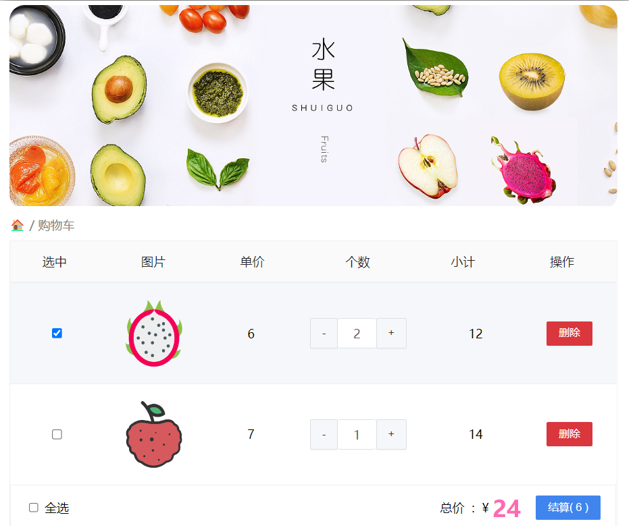
需求说明:
- 渲染功能
- 删除功能
- 修改个数
- 全选反选
- 统计 选中的 总价 和 总数量
- 持久化到本地
实现思路:
1.基本渲染: v-for遍历、:class动态绑定样式
2.删除功能 : v-on 绑定事件,获取当前行的id
3.修改个数 : v-on绑定事件,获取当前行的id,进行筛选出对应的项然后增加或减少
4.全选反选
- 必须所有的小选框都选中,全选按钮才选中 → every
- 如果全选按钮选中,则所有小选框都选中
- 如果全选取消,则所有小选框都取消选中
声明计算属性,判断数组中的每一个checked属性的值,看是否需要全部选
5.统计 选中的 总价 和 总数量 :通过计算属性来计算选中的总价和总数量
6.持久化到本地: 在数据变化时都要更新下本地存储 watch
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/inputnumber.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/index.css" />
<title>购物车</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="app-container" id="app">
<!-- 顶部banner -->
<div class="banner-box"><img src="http://autumnfish.cn/static/fruit.jpg" alt="" /></div>
<!-- 面包屑 -->
<div class="breadcrumb">
<span>🏠</span>
/
<span>购物车</span>
</div>
<!-- 购物车主体 -->
<div class="main" v-if="fruitList.length > 0">
<div class="table">
<!-- 头部 -->
<div class="thead">
<div class="tr">
<div class="th">选中</div>
<div class="th th-pic">图片</div>
<div class="th">单价</div>
<div class="th num-th">个数</div>
<div class="th">小计</div>
<div class="th">操作</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 身体 -->
<div class="tbody">
<div v-for="(item, index) in fruitList" :key="item.id" class="tr" :class="{ active: item.isChecked }">
<div class="td"><input type="checkbox" v-model="item.isChecked" /></div>
<div class="td"><img :src="item.icon" alt="" /></div>
<div class="td">{{ item.price }}</div>
<div class="td">
<div class="my-input-number">
<button :disabled="item.num <= 1" class="decrease" @click="sub(item.id)"> - </button>
<span class="my-input__inner">{{ item.num }}</span>
<button class="increase" @click="add(item.id)"> + </button>
</div>
</div>
<div class="td">{{ item.num * item.price }}</div>
<div class="td"><button @click="del(item.id)">删除</button></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 底部 -->
<div class="bottom">
<!-- 全选 -->
<label class="check-all">
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isAll"/>
全选
</label>
<div class="right-box">
<!-- 所有商品总价 -->
<span class="price-box">总价 : ¥ <span class="price">{{ totalPrice }}</span></span>
<!-- 结算按钮 -->
<button class="pay">结算( {{ totalCount }} )</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 空车 -->
<div class="empty" v-else>🛒空空如也</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const defaultArr = [
{
id: 1,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/火龙果.png',
isChecked: true,
num: 2,
price: 6,
},
{
id: 2,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/荔枝.png',
isChecked: false,
num: 7,
price: 20,
},
{
id: 3,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/榴莲.png',
isChecked: false,
num: 3,
price: 40,
},
{
id: 4,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/鸭梨.png',
isChecked: true,
num: 10,
price: 3,
},
{
id: 5,
icon: 'http://autumnfish.cn/static/樱桃.png',
isChecked: false,
num: 20,
price: 34,
},
]
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
// 水果列表
fruitList: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('list')) || defaultArr,
},
computed: {
// 默认计算属性:只能获取不能设置,要设置需要写完整写法
// isAll () {
// // 必须所有的小选框都选中,全选按钮才选中 → every
// return this.fruitList.every(item => item.isChecked)
// }
// 完整写法 = get + set
isAll: {
get () {
return this.fruitList.every(item => item.isChecked)
},
set (value) {
// 基于拿到的布尔值,要让所有的小选框 同步状态
this.fruitList.forEach(item => item.isChecked = value)
}
},
// 统计选中的总数 reduce
totalCount () {
return this.fruitList.reduce((sum, item) => {
if (item.isChecked) {
// 选中 → 需要累加
return sum + item.num
} else {
// 没选中 → 不需要累加
return sum
}
}, 0)
},
// 总计选中的总价 num * price
totalPrice () {
return this.fruitList.reduce((sum, item) => {
if (item.isChecked) {
return sum + item.num * item.price
} else {
return sum
}
}, 0)
}
},
methods: {
del (id) {
this.fruitList = this.fruitList.filter(item => item.id !== id)
},
add (id) {
// 1. 根据 id 找到数组中的对应项 → find
const fruit = this.fruitList.find(item => item.id === id)
// 2. 操作 num 数量
fruit.num++
},
sub (id) {
// 1. 根据 id 找到数组中的对应项 → find
const fruit = this.fruitList.find(item => item.id === id)
// 2. 操作 num 数量
fruit.num--
}
},
watch: {
fruitList: {
deep: true,
handler (newValue) {
// 需要将变化后的 newValue 存入本地 (转JSON)
localStorage.setItem('list', JSON.stringify(newValue))
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Vue生命周期
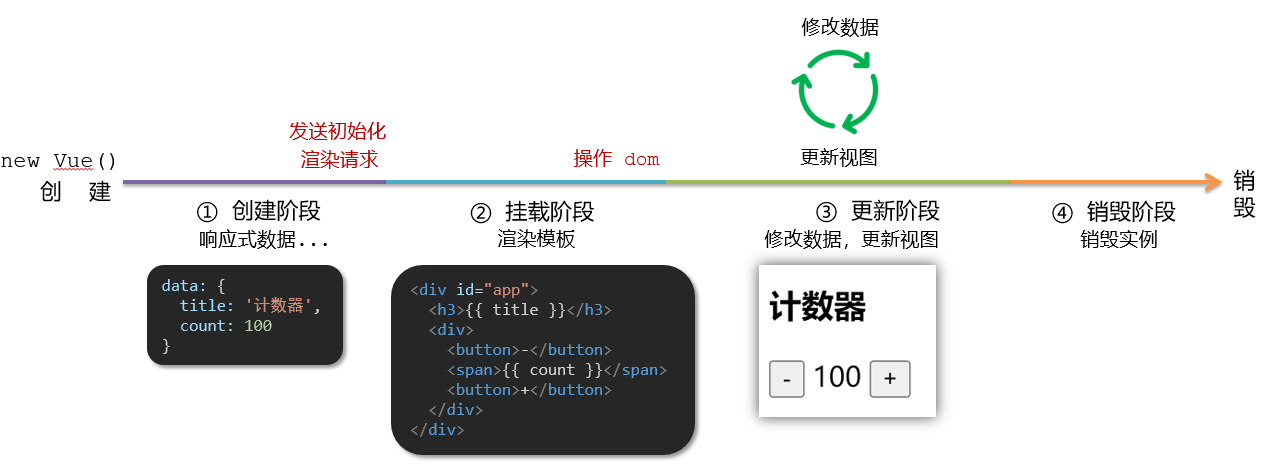
思考:什么时候可以发送初始化渲染请求?(越早越好)什么时候可以开始操作dom?(至少dom得渲染出来)
Vue生命周期:就是一个Vue实例从创建 到 销毁 的整个过程。
生命周期四个阶段:① 创建 ② 挂载 ③ 更新 ④ 销毁
1.创建阶段:创建响应式数据
2.挂载阶段:渲染模板
3.更新阶段:修改数据,更新视图
4.销毁阶段:销毁Vue实例
Vue生命周期钩子
Vue生命周期过程中,会自动运行一些函数,被称为【生命周期钩子】→ 让开发者可以在【特定阶段】运行自己的代码
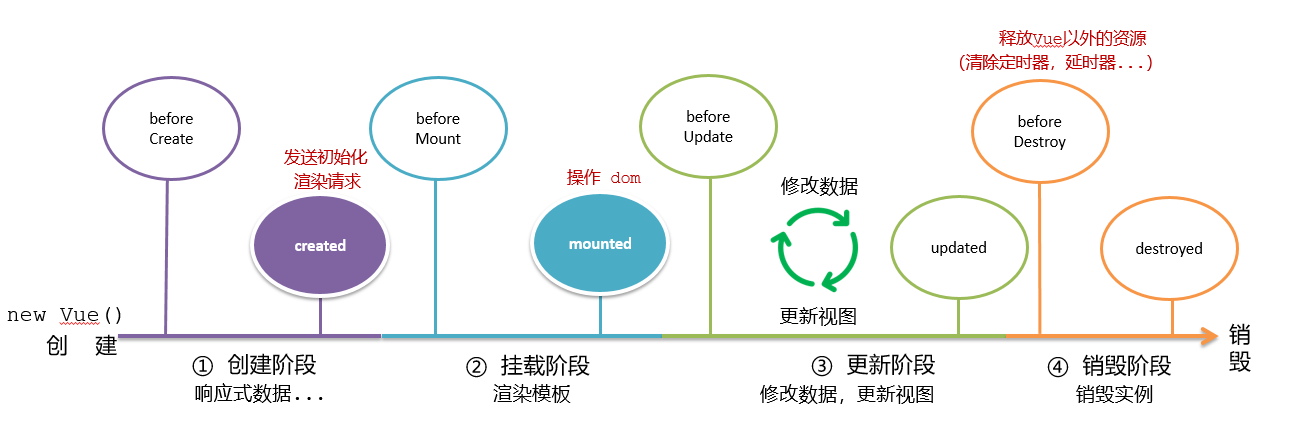
在create之前组件实例this里面是没有数据的(undefined)
<div id="app">
<h3>{{ title }}</h3>
<div>
<button @click="count--">-</button>
<span>{{ count }}</span>
<button @click="count++">+</button>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
count: 100,
title: '计数器'
},
// 1. 创建阶段(准备数据)
beforeCreate () {
console.log('beforeCreate 响应式数据准备好之前', this.count)
},
created () {
console.log('created 响应式数据准备好之后', this.count)
// this.数据名 = 请求回来的数据
// 可以开始发送初始化渲染的请求了
},
// 2. 挂载阶段(渲染模板)
beforeMount () {
console.log('beforeMount 模板渲染之前', document.querySelector('h3').innerHTML)
},
mounted () {
console.log('mounted 模板渲染之后', document.querySelector('h3').innerHTML)
// 可以开始操作dom了
},
// 3. 更新阶段(修改数据 → 更新视图)
beforeUpdate () {
console.log('beforeUpdate 数据修改了,视图还没更新', document.querySelector('span').innerHTML)
},
updated () {
console.log('updated 数据修改了,视图已经更新', document.querySelector('span').innerHTML)
},
// 4. 卸载阶段
beforeDestroy () {
console.log('beforeDestroy, 卸载前')
console.log('清除掉一些Vue以外的资源占用,定时器,延时器...')
},
destroyed () {
console.log('destroyed,卸载后')
}
})
</script>生命周期钩子小案例
1.在created中发送数据
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
}
.news {
display: flex;
height: 120px;
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px 0;
cursor: pointer;
}
.news .left {
flex: 1;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
padding-right: 10px;
}
.news .left .title {
font-size: 20px;
}
.news .left .info {
color: #999999;
}
.news .left .info span {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.news .right {
width: 160px;
height: 120px;
}
.news .right img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
object-fit: cover;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id" class="news">
<div class="left">
<div class="title">{{ item.title }}</div>
<div class="info">
<span>{{ item.source }}</span>
<span>{{ item.time }}</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="right">
<img :src="item.img" alt="">
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
// 接口地址:http://hmajax.itheima.net/api/news
// 请求方式:get
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
list: []
},
async created () {
// 1. 发送请求获取数据
const res = await axios.get('http://hmajax.itheima.net/api/news')
// 2. 更新到 list 中,用于页面渲染 v-for
this.list = res.data.data
}
})
</script>2.在mounted中获取焦点
<style>
html,
body {
height: 100%;
}
.search-container {
position: absolute;
top: 30%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
text-align: center;
}
.search-container .search-box {
display: flex;
}
.search-container img {
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.search-container .search-box input {
width: 512px;
height: 16px;
padding: 12px 16px;
font-size: 16px;
margin: 0;
vertical-align: top;
outline: 0;
box-shadow: none;
border-radius: 10px 0 0 10px;
border: 2px solid #c4c7ce;
background: #fff;
color: #222;
overflow: hidden;
box-sizing: content-box;
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;
}
.search-container .search-box button {
cursor: pointer;
width: 112px;
height: 44px;
line-height: 41px;
line-height: 42px;
background-color: #ad2a27;
border-radius: 0 10px 10px 0;
font-size: 17px;
box-shadow: none;
font-weight: 400;
border: 0;
outline: 0;
letter-spacing: normal;
color: white;
}
body {
background: no-repeat center /cover;
background-color: #edf0f5;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" id="app">
<div class="search-container">
<img src="https://www.itheima.com/images/logo.png" alt="">
<div class="search-box">
<input type="text" v-model="words" id="inp">
<button>搜索一下</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
words: ''
},
// 核心思路:
// 1. 等input框渲染出来 mounted 钩子
// 2. 让input框获取焦点 inp.focus()
mounted () {
document.querySelector('#inp').focus()
}
})
</script>案例-小黑记账清单
1.需求图示:

2.需求分析
1.基本渲染
2.添加功能
3.删除功能
4.饼图渲染
3.思路分析
1.基本渲染
- 立刻发送请求获取数据 created
- 拿到数据,存到data的响应式数据中
- 结合数据,进行渲染 v-for
- 消费统计 —> 计算属性
2.添加功能
- 收集表单数据 v-model,使用指令修饰符处理数据
- 给添加按钮注册点击事件,对输入的内容做非空判断,发送请求
- 请求成功后,对文本框内容进行清空
- 重新渲染列表
3.删除功能
- 注册点击事件,获取当前行的id
- 根据id发送删除请求
- 需要重新渲染
4.饼图渲染
- 初始化一个饼图 echarts.init(dom) mounted钩子中渲染
- 根据数据试试更新饼图
echarts.setOptions({...})
4.代码
<!-- CSS only -->
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.1.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
/>
<style>
.red {
color: red!important;
}
.search {
width: 300px;
margin: 20px 0;
}
.my-form {
display: flex;
margin: 20px 0;
}
.my-form input {
flex: 1;
margin-right: 20px;
}
.table > :not(:first-child) {
border-top: none;
}
.contain {
display: flex;
padding: 10px;
}
.list-box {
flex: 1;
padding: 0 30px;
}
.list-box a {
text-decoration: none;
}
.echarts-box {
width: 600px;
height: 400px;
padding: 30px;
margin: 0 auto;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
tfoot {
font-weight: bold;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 1000px) {
.contain {
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.list-box {
width: 100%;
}
.echarts-box {
margin-top: 30px;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="contain">
<!-- 左侧列表 -->
<div class="list-box">
<!-- 添加资产 -->
<form class="my-form">
<input v-model.trim="name" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="消费名称" />
<input v-model.number="price" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="消费价格" />
<button @click="add" type="button" class="btn btn-primary">添加账单</button>
</form>
<table class="table table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>消费名称</th>
<th>消费价格</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ index + 1 }}</td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td :class="{ red: item.price > 500 }">{{ item.price.toFixed(2) }}</td>
<td><a @click="del(item.id)" href="javascript:;">删除</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="4">消费总计: {{ totalPrice.toFixed(2) }}</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
</div>
<!-- 右侧图表 -->
<div class="echarts-box" id="main"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/echarts@5.4.0/dist/echarts.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
/**
* 接口文档地址:
* https://www.apifox.cn/apidoc/shared-24459455-ebb1-4fdc-8df8-0aff8dc317a8/api-53371058
*
* 功能需求:
* 1. 基本渲染
* (1) 立刻发送请求获取数据 created
* (2) 拿到数据,存到data的响应式数据中
* (3) 结合数据,进行渲染 v-for
* (4) 消费统计 => 计算属性
* 2. 添加功能
* (1) 收集表单数据 v-model
* (2) 给添加按钮注册点击事件,发送添加请求
* (3) 需要重新渲染
* 3. 删除功能
* (1) 注册点击事件,传参传 id
* (2) 根据 id 发送删除请求
* (3) 需要重新渲染
* 4. 饼图渲染
* (1) 初始化一个饼图 echarts.init(dom) mounted钩子实现
* (2) 根据数据实时更新饼图 echarts.setOption({ ... })
*/
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
list: [],
name: '',
price: ''
},
computed: {
totalPrice () {
return this.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.price, 0)
}
},
created () {
// const res = await axios.get('https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/bill', {
// params: {
// creator: '小黑'
// }
// })
// this.list = res.data.data
this.getList()
},
mounted () {
this.myChart = echarts.init(document.querySelector('#main'))
this.myChart.setOption({
// 大标题
title: {
text: '消费账单列表',
left: 'center'
},
// 提示框
tooltip: {
trigger: 'item'
},
// 图例
legend: {
orient: 'vertical',
left: 'left'
},
// 数据项
series: [
{
name: '消费账单',
type: 'pie',
radius: '50%', // 半径
data: [
// { value: 1048, name: '球鞋' },
// { value: 735, name: '防晒霜' }
],
emphasis: {
itemStyle: {
shadowBlur: 10,
shadowOffsetX: 0,
shadowColor: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)'
}
}
}
]
})
},
methods: {
async getList () {
const res = await axios.get('https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/bill', {
params: {
creator: '小黑'
}
})
this.list = res.data.data
// 更新图表
this.myChart.setOption({
// 数据项
series: [
{
// data: [
// { value: 1048, name: '球鞋' },
// { value: 735, name: '防晒霜' }
// ]
data: this.list.map(item => ({ value: item.price, name: item.name}))
}
]
})
},
async add () {
if (!this.name) {
alert('请输入消费名称')
return
}
if (typeof this.price !== 'number') {
alert('请输入正确的消费价格')
return
}
// 发送添加请求
const res = await axios.post('https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/bill', {
creator: '小黑',
name: this.name,
price: this.price
})
// 重新渲染一次
this.getList()
this.name = ''
this.price = ''
},
async del (id) {
// 根据 id 发送删除请求
const res = await axios.delete(`https://applet-base-api-t.itheima.net/bill/${id}`)
// 重新渲染
this.getList()
}
}
})
</script>工程化开发和脚手架
1.开发Vue的两种方式
- 核心包传统开发模式:基于html / css / js 文件,直接引入核心包,开发 Vue。
- 工程化开发模式:基于构建工具(例如:webpack)的环境中开发Vue。
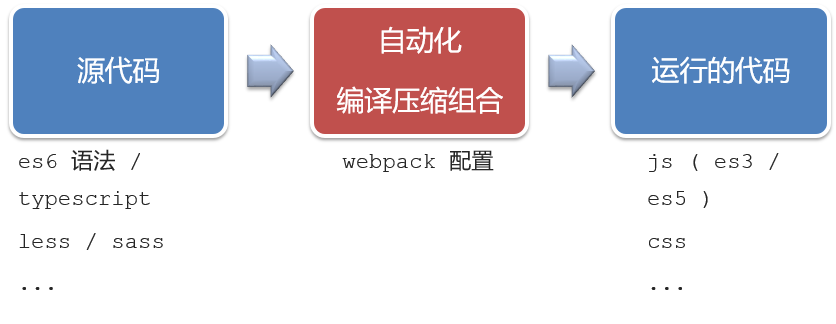
工程化开发模式优点:
提高编码效率,比如使用JS新语法、Less/Sass、Typescript等通过webpack都可以编译成浏览器识别的ES3/ES5/CSS等
工程化开发模式问题:
- webpack配置不简单
- 雷同的基础配置
- 缺乏统一的标准
为了解决以上问题,所以我们需要一个工具,生成标准化的配置
2.脚手架Vue CLI
基本介绍:
Vue CLI 是Vue官方提供的一个全局命令工具
可以帮助我们快速创建一个开发Vue项目的标准化基础架子。【集成了webpack配置】
好处:
- 开箱即用,零配置
- 内置babel等工具
- 标准化的webpack配置
使用步骤:
全局安装(win10下,右键win图标管理员打开Windows PowerShell 只需安装一次即可) yarn global add @vue/cli 或者 npm i @vue/cli -g
查看vue/cli版本: vue --version
创建项目架子:vue create project-name(项目名不能使用中文)
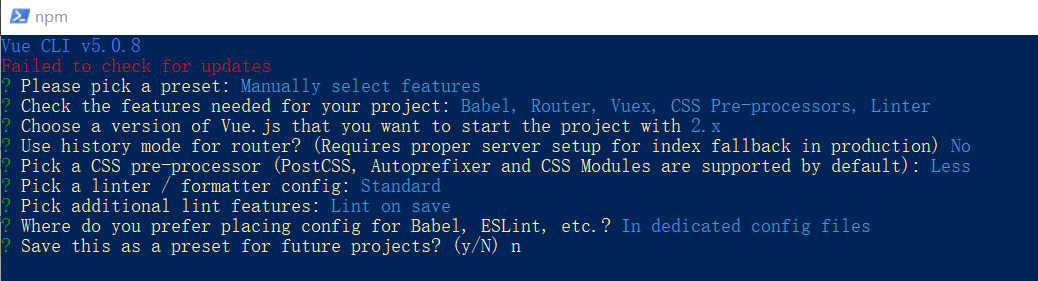
image-20240124212103746 启动项目:yarn serve 或者 npm run serve(命令不固定,找package.json)
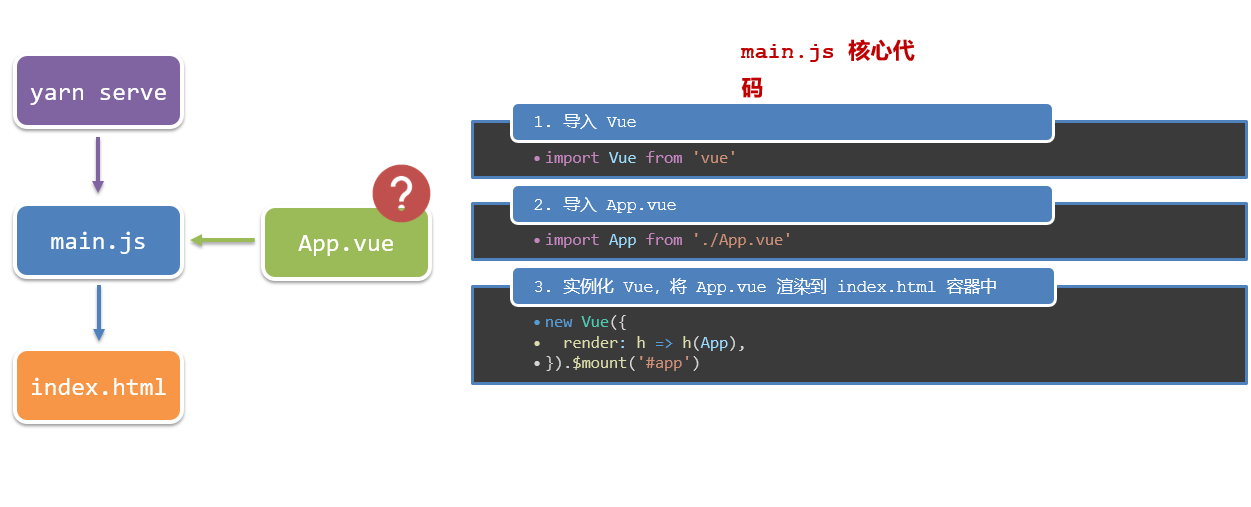
项目目录介绍和运行流程
1.项目目录介绍

虽然脚手架中的文件有很多,目前咱们只需人事三个文件即可
- main.js 入口文件
- App.vue App根组件
- index.html 模板文件
2.运行流程
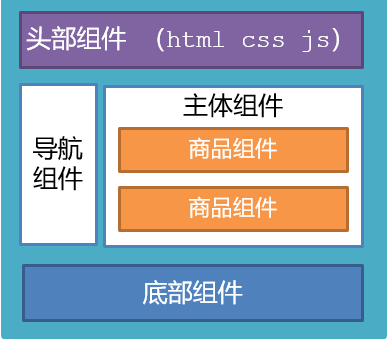
组件化开发
组件化:一个页面可以拆分成一个个组件,每个组件有着自己独立的结构、样式、行为。
好处:便于维护,利于复用 → 提升开发效率。
组件分类:普通组件、根组件。
比如:下面这个页面,可以把所有的代码都写在一个页面中,但是这样显得代码比较混乱,难易维护。咱们可以按模块进行组件划分
根组件 App.vue
1.根组件介绍
整个应用最上层的组件,包裹所有普通小组件
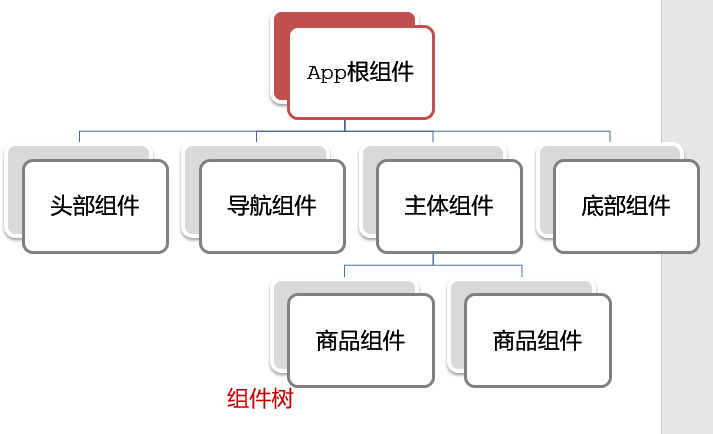
2.组件是由三部分构成
- 语法高亮插件
三部分构成
- template:结构 (有且只能一个根元素)
- script: js逻辑
- style: 样式 (可支持less,需要装包)
让组件支持less
(1) style标签,lang="less" 开启less功能
(2) 装包: yarn add less less-loader -D 或者npm i less less-loader -D
普通组件的注册使用-局部注册
1.特点:
只能在注册的组件内使用
2.步骤:
- 创建.vue文件(三个组成部分)
- 在使用的组件内先导入再注册,最后使用
3.使用方式:
当成html标签使用即可 <组件名></组件名>
4.注意:
组件名规范 —> 大驼峰命名法, 如 HmHeader
5.语法:
// 导入需要注册的组件
import 组件对象 from '.vue文件路径'
import HmHeader from './components/HmHeader'
export default { // 局部注册
components: {
'组件名': 组件对象,
HmHeader:HmHeaer,
HmHeader
}
}6.练习
在App组件中,完成以下练习。在App.vue中使用组件的方式完成下面布局

<template>
<div class="hm-header">
我是hm-header
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
.hm-header {
height: 100px;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 30px;
background-color: #8064a2;
color: white;
}
</style><template>
<div class="hm-main">
我是hm-main
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
.hm-main {
height: 400px;
line-height: 400px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 30px;
background-color: #f79646;
color: white;
margin: 20px 0;
}
</style><template>
<div class="hm-footer">
我是hm-footer
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
.hm-footer {
height: 100px;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 30px;
background-color: #4f81bd;
color: white;
}
</style>普通组件的注册使用-全局注册
1.特点:
全局注册的组件,在项目的任何组件中都能使用
2.步骤
- 创建.vue组件(三个组成部分)
- main.js中进行全局注册
3.使用方式
当成HTML标签直接使用
<组件名></组件名>
4.注意
组件名规范 —> 大驼峰命名法, 如 HmHeader
5.语法
Vue.component('组件名', 组件对象) 要注册多个就写多行
例:
// 导入需要全局注册的组件
import HmButton from './components/HmButton'
Vue.component('HmButton', HmButton)6.练习
在以下3个局部组件中是展示一个通用按钮

<template>
<button class="hm-button">通用按钮</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
.hm-button {
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
padding: 0 20px;
background-color: #3bae56;
border-radius: 5px;
color: white;
border: none;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>综合案例
1.小兔仙首页启动项目演示
2.小兔仙组件拆分示意图
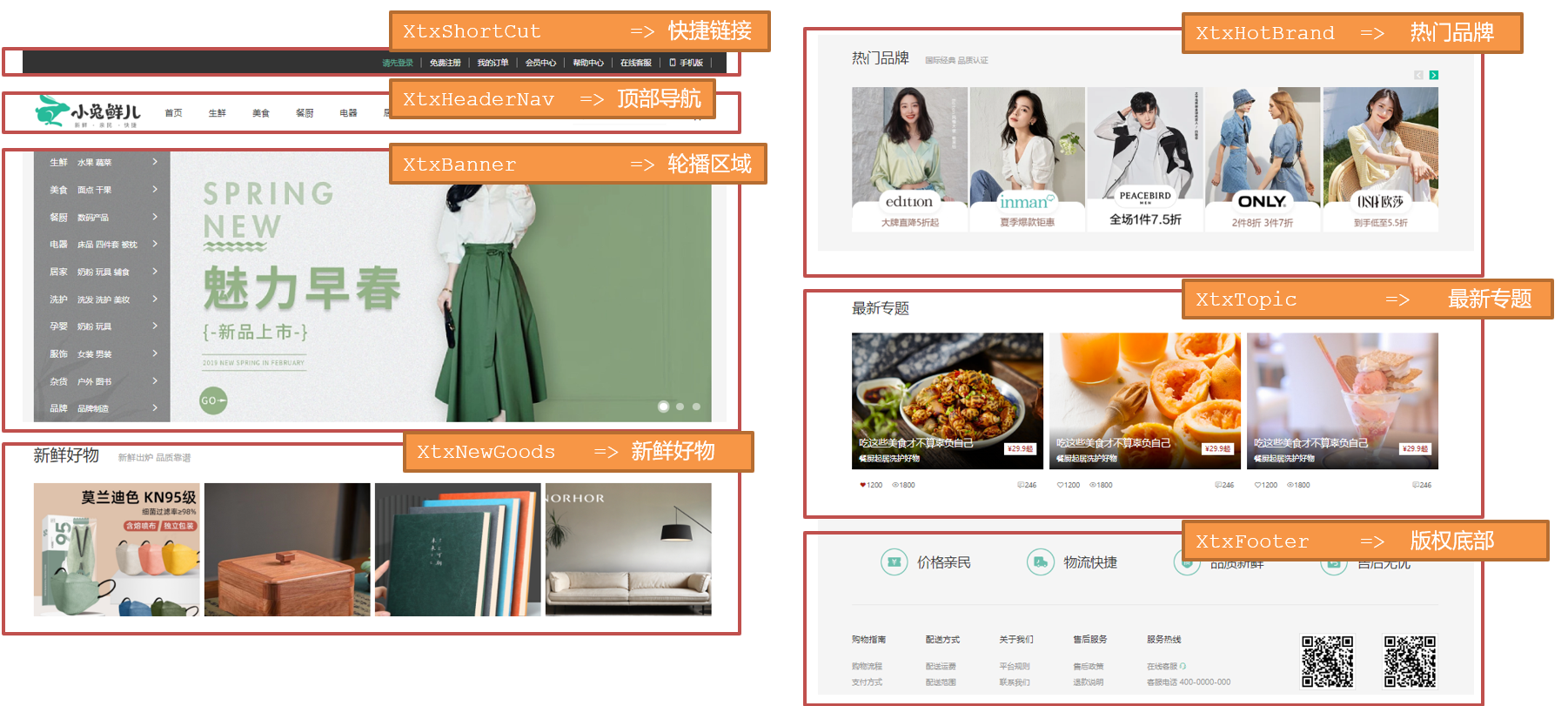
3.开发思路
分析页面,按模块拆分组件,搭架子 (局部或全局注册)
根据设计图,编写组件 html 结构 css 样式 (已准备好)
拆分封装通用小组件 (局部或全局注册)
将来 → 通过 js 动态渲染,实现功能
scoped解决样式冲突
1.默认情况:
写在组件中的样式会 全局生效 → 因此很容易造成多个组件之间的样式冲突问题。
全局样式: 默认组件中的样式会作用到全局,任何一个组件中都会受到此样式的影响
局部样式: 可以给组件加上scoped 属性,可以让样式只作用于当前组件
2.代码演示
BaseOne.vue
<template>
<div class="base-one">
BaseOne
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>BaseTwo.vue
<template>
<div class="base-one">
BaseTwo
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<BaseOne></BaseOne>
<BaseTwo></BaseTwo>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseOne from './components/BaseOne'
import BaseTwo from './components/BaseTwo'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
BaseOne,
BaseTwo
}
}
</script>3.scoped原理
- 当前组件内标签都被添加data-v-hash值 的属性
- css选择器都被添加 [data-v-hash值] 的属性选择器
最终效果: 必须是当前组件的元素, 才会有这个自定义属性, 才会被这个样式作用到

4.总结
- style的默认样式是作用到哪里的?
- scoped的作用是什么?
- style中推不推荐加scoped?
data必须是一个函数
1、data为什么要写成函数
一个组件的 data 选项必须是一个函数。目的是为了:保证每个组件实例,维护独立的一份数据对象。
每次创建新的组件实例,都会新执行一次data 函数,得到一个新对象。
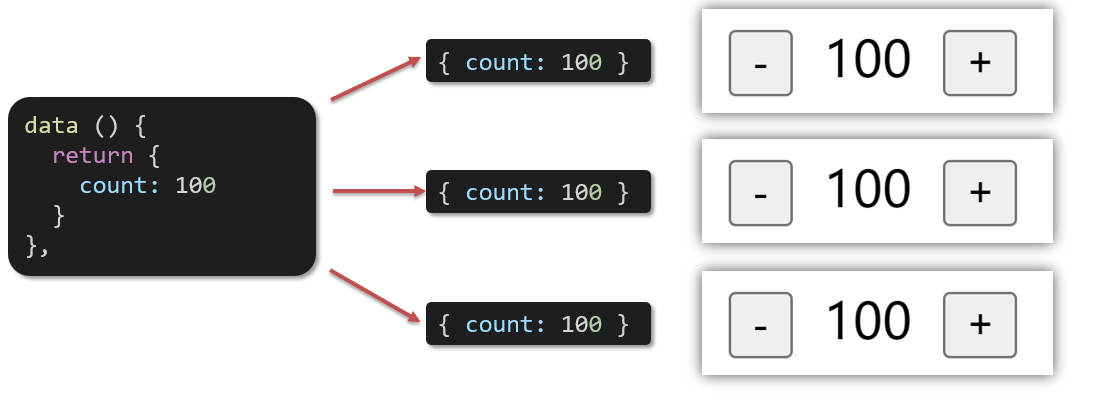
2.代码演示
BaseCount.vue
<template>
<div class="base-count">
<button @click="count--">-</button>
<span>{{ count }}</span>
<button @click="count++">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function () {
return {
count: 100,
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
.base-count {
margin: 20px;
}
</style>App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<BaseCount></BaseCount>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseCount from './components/BaseCount'
export default {
components: {
BaseCount,
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>3.总结
data写成函数的目的是什么?
组件通信
1.什么是组件通信?
组件通信,就是指组件与组件之间的数据传递
- 组件的数据是独立的,无法直接访问其他组件的数据。
- 想使用其他组件的数据,就需要组件通信
2.组件之间如何通信
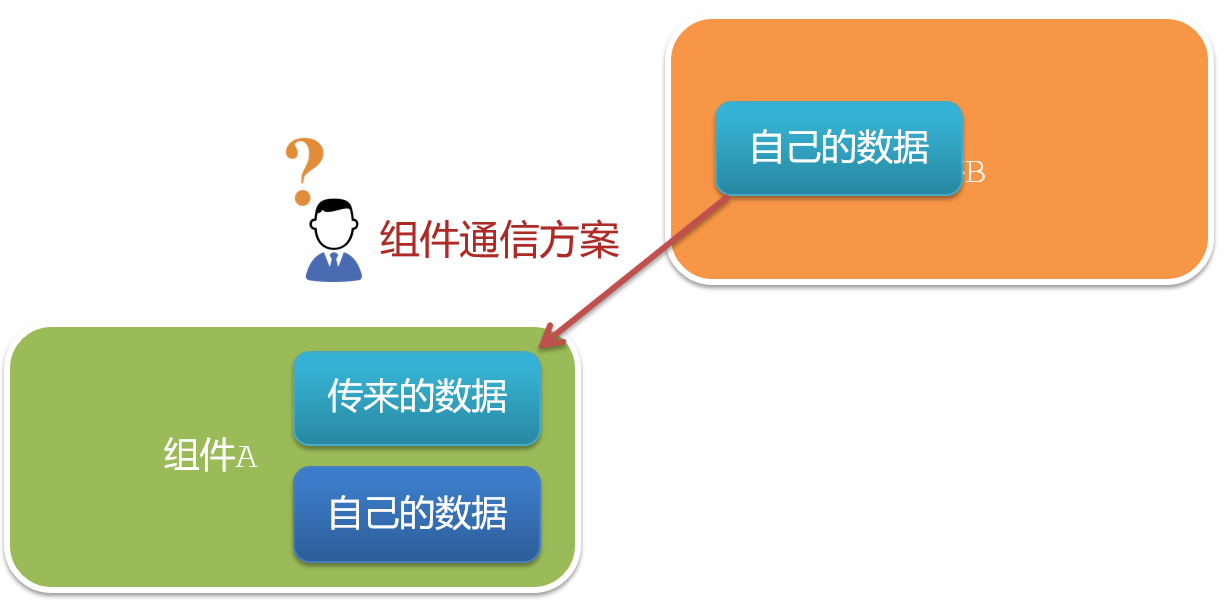
思考:
- 组件之间有哪些关系?
- 对应的组件通信方案有哪几类?
3.组件关系分类
- 父子关系
- 非父子关系
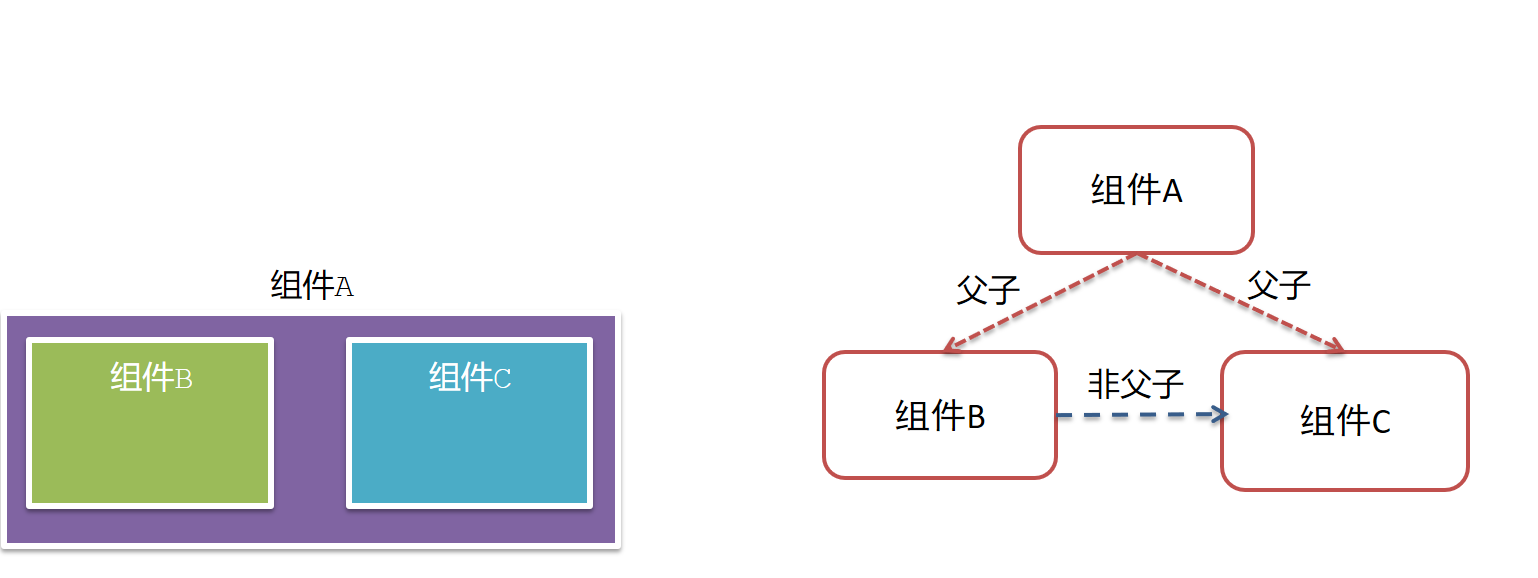
4.通信解决方案
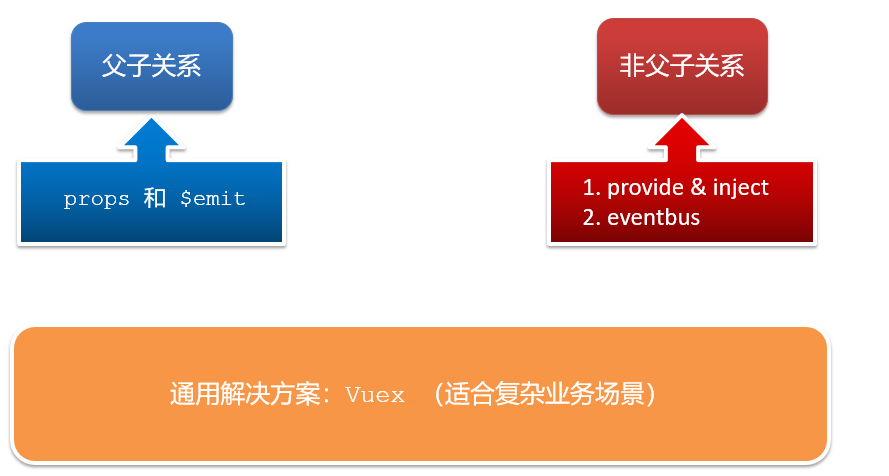
5.父子通信流程
- 父组件通过 props 将数据传递给子组件
- 子组件利用 $emit 通知父组件修改更新
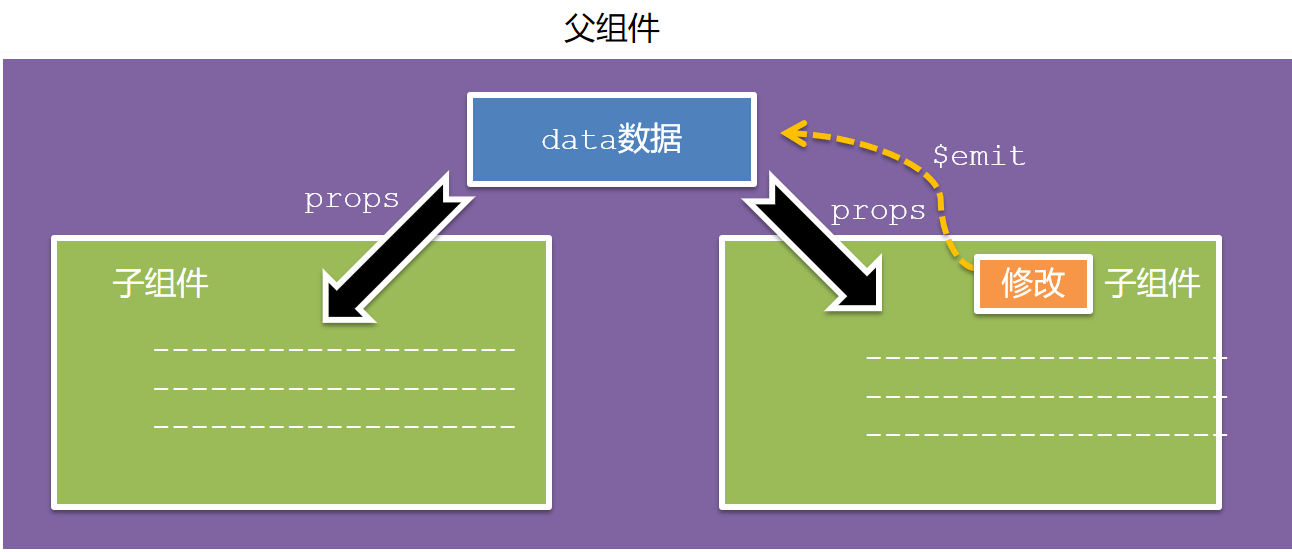
6.父向子通信代码示例
父组件通过props将数据传递给子组件
父组件App.vue
<template>
<div class="app" style="border: 3px solid #000; margin: 10px">
我是APP组件
<!-- 1.给组件标签,添加属性方式 赋值 -->
<Son :title="myTitle"></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from "./components/Son.vue"
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
Son,
},
data() {
return {
myTitle: "学前端,就来黑马程序员",
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>子组件Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son" style="border:3px solid #000;margin:10px">
我是Son组件 {{ titel }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son-Child',
// 2.通过props来接受
props: ['title']
}
</script>
<style>
</style>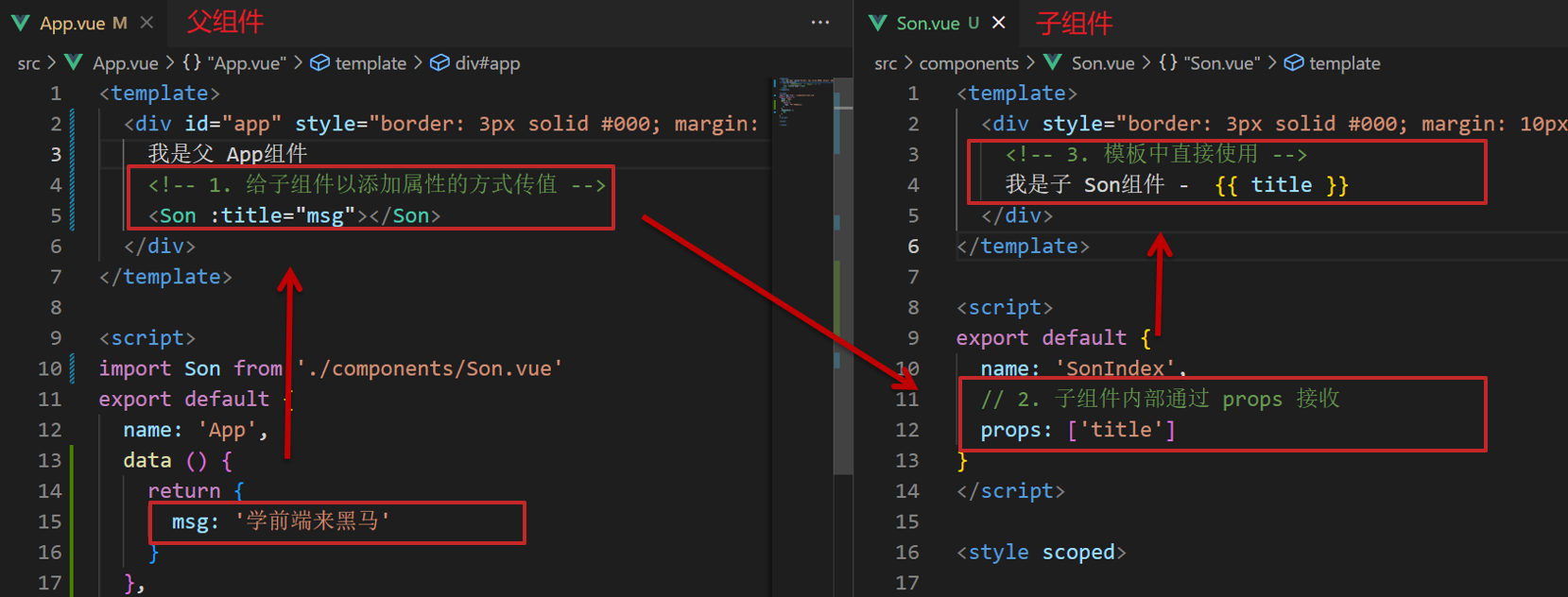
父向子传值步骤
- 给子组件以添加属性的方式传值
- 子组件内部通过props接收
- 模板中直接使用 props接收的值
7.子向父通信代码示例
//子组件语法
this.$emit(事件名, 参数)
//父组件语法
<son :title="msg" @事件名="方法名"></son>子组件利用 $emit 通知父组件,进行修改更新
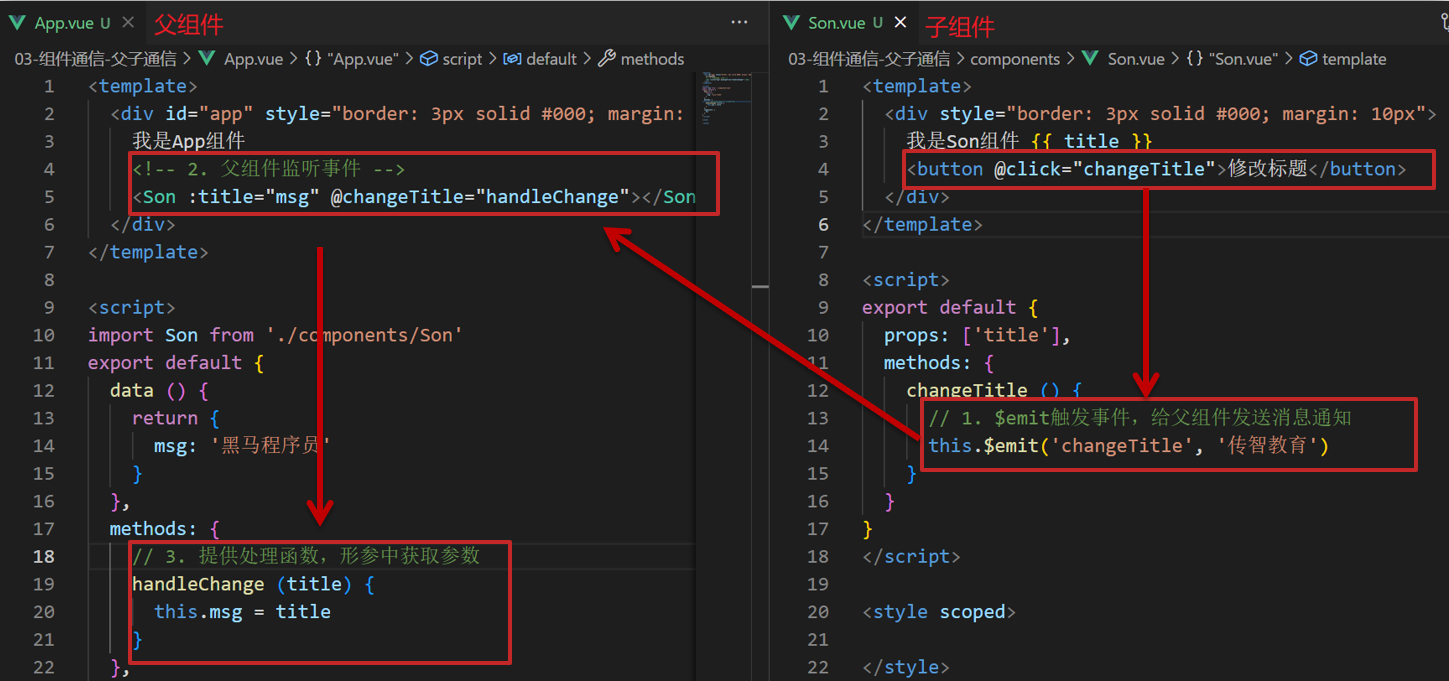
子向父传值步骤
$emit触发事件,给父组件发送消息通知
父组件监听$emit触发的事件
提供处理函数,在函数的性参中获取传过来的参数
什么是props
1.Props 定义
组件上 注册的一些 自定义属性
2.Props 作用
向子组件传递数据
3.特点
- 可以 传递 任意数量 的prop
- 可以 传递 任意类型 的prop
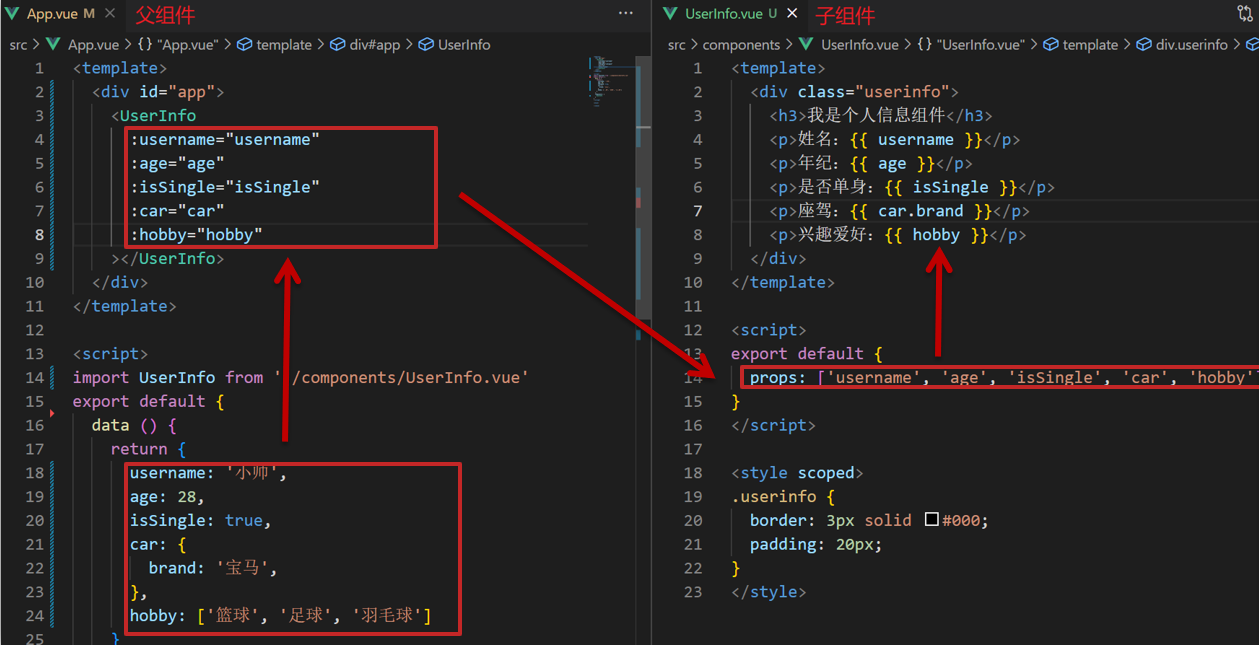
4.代码演示
父组件App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<UserInfo
:username="username"
:age="age"
:isSingle="isSingle"
:car="car"
:hobby="hobby"
></UserInfo>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import UserInfo from './components/UserInfo.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {
username: '小帅',
age: 28,
isSingle: true,
car: {
brand: '宝马',
},
hobby: ['篮球', '足球', '羽毛球'],
}
},
components: {
UserInfo,
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>子组件UserInfo.vue
<template>
<div class="userinfo">
<h3>我是个人信息组件</h3>
<div>姓名:{{username}}</div>
<div>年龄:{{age}}</div>
<div>是否单身:{{isSingle}}</div>
<div>座驾:{{car.brand}}</div>
<div>兴趣爱好:{{hobby.join('、')}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props:['username','age','isSingle','car','hobby']
}
</script>
<style>
.userinfo {
width: 300px;
border: 3px solid #000;
padding: 20px;
}
.userinfo > div {
margin: 20px 10px;
}
</style>props校验
1.思考
组件的props可以乱传吗
2.作用
为组件的 prop 指定验证要求,不符合要求,控制台就会有错误提示 → 帮助开发者,快速发现错误
3.语法
- 类型校验
- 非空校验
- 默认值
- 自定义校验
4.代码演示
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<BaseProgress :w="width"></BaseProgress>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseProgress from './components/BaseProgress.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {
width: 30,
}
},
components: {
BaseProgress,
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>BaseProgress.vue
<template>
<div class="base-progress">
<div
class="inner"
:style="{ width: w + '%' }">
<span>{{ w }}%</span>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
w: Number //Number String Boolean Function
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.base-progress {
height: 26px;
width: 400px;
border-radius: 15px;
background-color: #272425;
border: 3px solid #272425;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.inner {
width: 50%;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
text-align: right;
position: relative;
background-color: #409eff;
background-size: 20px 20px;
box-sizing: border-box;
transition: all 1s;
}
.inner span {
position: absolute;
right: -20px;
bottom: -25px;
}
</style>props校验完整写法
1.语法
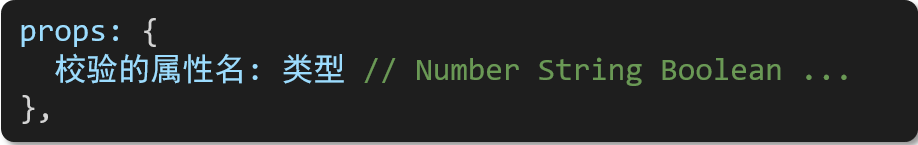
props: {
校验的属性名: {
type: 类型, // Number String Boolean ...
required: true, // 是否必填
default: 默认值, // 默认值
validator (value) {
// 自定义校验逻辑
return 是否通过校验
}
}
},2.代码实例
<script>
export default {
// 完整写法(类型、默认值、非空、自定义校验)
props: {
w: {
type: Number,
//required: true,
default: 0,
validator(val) {
// console.log(val)
if (val >= 100 || val <= 0) {
console.error('传入的范围必须是0-100之间')
return false
} else {
return true
}
},
},
},
}
</script>3.注意
1.default和required一般不同时写(因为当时必填项时,肯定是有值的)
2.default后面如果是简单类型的值,可以直接写默认。如果是复杂类型的值,则需要以函数的形式return一个默认值
props&data、单向数据流
1.共同点
都可以给组件提供数据
2.区别
- data 的数据是自己的 → 随便改
- prop 的数据是外部的 → 不能直接改,要遵循 单向数据流
3.单向数据流:
父级props 的数据更新,会向下流动,影响子组件。这个数据流动是单向的
4.代码演示
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
//<BaseCount :count="count"></BaseCount>
<BaseCount></BaseCount>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseCount from './components/BaseCount.vue'
export default {
components:{
BaseCount
},
data(){
return {
count: 666
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>BaseCount.vue
<template>
<div class="base-count">
<button @click="count--">-</button>
<span>{{ count }}</span>
<button @click="count++">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 1.自己的数据随便修改 (谁的数据 谁负责)
data () {
return {
count: 100,
}
},
// 2.外部传过来的数据 不能直接修改,可以$emit传到父组件进行修改,父组件prop更新,会单向向下流动,子组件自动更新
//props: {
// count: {
// type: Number,
// },
//}
}
</script>
<style>
.base-count {
margin: 20px;
}
</style>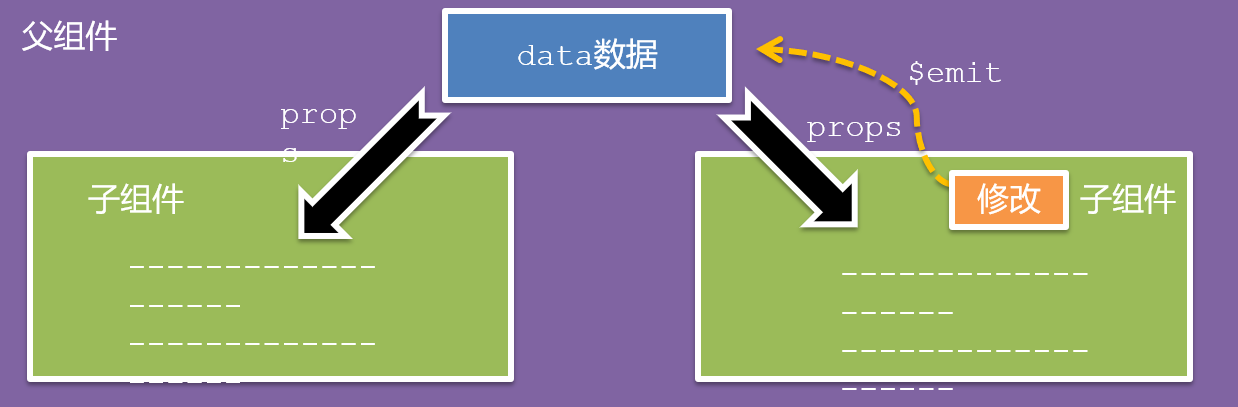
5.口诀
谁的数据谁负责
综合案例-组件拆分
1.需求说明
- 拆分基础组件
- 渲染待办任务
- 添加任务
- 删除任务
- 底部合计 和 清空功能
- 持久化存储
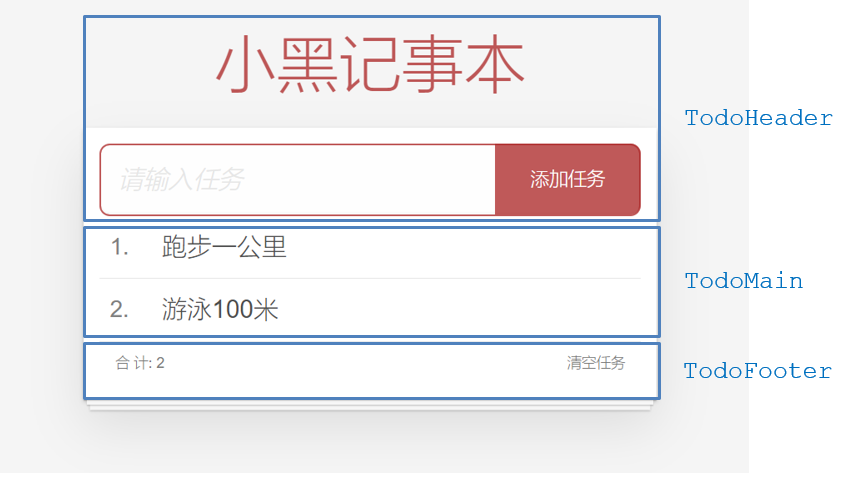
2.拆分基础组件
咱们可以把小黑记事本原有的结构拆成三部分内容:头部(TodoHeader)、列表(TodoMain)、底部(TodoFooter)
综合案例-列表渲染
思路分析:
- 提供数据:提供在公共的父组件 App.vue
- 通过父传子,将数据传递给TodoMain
- 利用v-for进行渲染
综合案例-添加功能
思路分析:
- 收集表单数据 v-model
- 监听时间 (回车+点击 都要进行添加)
- 子传父,将任务名称传递给父组件App.vue
- 父组件接受到数据后 进行添加 unshift(自己的数据自己负责)
综合案例-删除功能
思路分析:
- 监听时间(监听删除的点击)携带id
- 子传父,将删除的id传递给父组件App.vue
- 进行删除 filter (自己的数据自己负责)
综合案例-底部功能及持久化存储
思路分析:
- 底部合计:父组件传递list到底部组件 —>展示合计
- 清空功能:监听事件 —> 子组件通知父组件 —>父组件清空
- 持久化存储:watch监听数据变化,持久化到本地
data () {
return {
//如果查到缓存里面没有数据,则使用默认数据
list: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('list')) || [
{ id: 1, name: '唱歌'},
{ id: 2, name: '打篮球'},
{ id: 3, name: '跳舞'}
]
}
}
watch: {
list: {
deep: true,
handler (newValue) {
console.log('保存到本地')
//将数据缓存到本地
localStorage.setItem('list', JSON.stringify(newValue))
}
}
}非父子通信-event bus 事件总线
1.作用
非父子组件之间,进行简易消息传递。(复杂场景→ Vuex)
2.步骤
创建一个都能访问的事件总线 (空Vue实例)
import Vue from 'vue' const Bus = new Vue() export default BusA/C组件(接受方),监听Bus的 $on事件
created () { Bus.$on('sendMsg', (msg) => { this.msg = msg }) }B组件(发送方),触发Bus的$emit事件
Bus.$emit('sendMsg', '这是一个消息')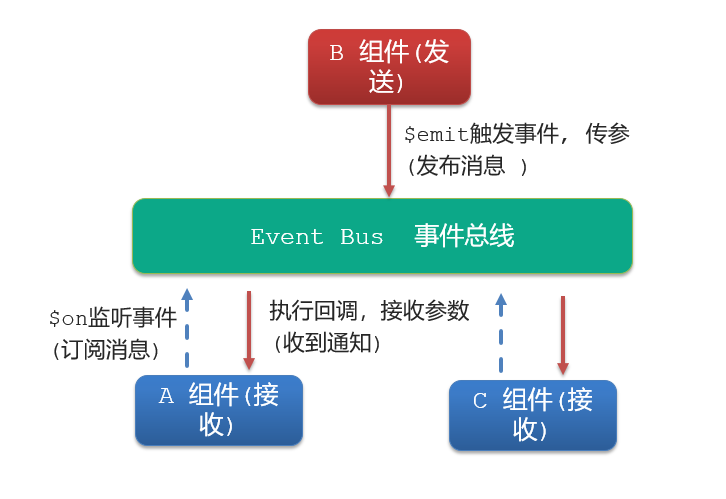
68232839240
3.代码示例
EventBus.js
import Vue from 'vue'
const Bus = new Vue()
export default BusBaseA.vue(接受方)
<template>
<div class="base-a">
我是A组件(接受方)
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Bus from '../utils/EventBus'
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: '',
}
},
created() {
Bus.$on('sendMsg', (msg) => {
// console.log(msg)
this.msg = msg
})
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.base-a {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid #000;
border-radius: 3px;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>BaseB.vue(发送方)
<template>
<div class="base-b">
<div>我是B组件(发布方)</div>
<button @click="sendMsgFn">发送消息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Bus from '../utils/EventBus'
export default {
methods: {
sendMsgFn() {
Bus.$emit('sendMsg', '今天天气不错,适合旅游')
},
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.base-b {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid #000;
border-radius: 3px;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<BaseA></BaseA>
<BaseB></BaseB>
<BaseC></BaseC>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseA from './components/BaseA.vue'
import BaseB from './components/BaseB.vue'
import BaseC from './components/BaseC.vue'
export default {
components:{
BaseA,
BaseB,
BaseC
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>4.总结
1.非父子组件传值借助什么?
2.什么是事件总线
3.发送方应该调用事件总线的哪个方法
4.接收方应该调用事件总线的哪个方法
5.一个组件发送数据,可不可以被多个组件接收
非父子通信-provide&inject
1.作用
跨层级共享数据
2.场景
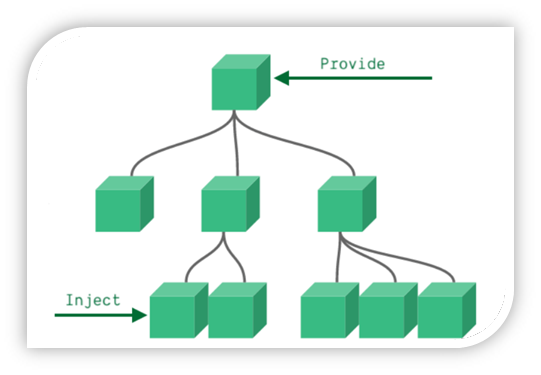
3.语法
- 父组件 provide提供数据
//color: 'pink',
//userInfo: {
// name: 'zs',
// age: 18,
//}
export default {
provide () {
return {
// 普通类型【非响应式】
color: this.color,
// 复杂类型【响应式】
userInfo: this.userInfo,
}
}
}2.子/孙组件 inject获取数据
export default {
inject: ['color','userInfo'],
created () {
console.log(this.color, this.userInfo)
}
}4.注意
- provide提供的简单类型的数据不是响应式的,复杂类型数据是响应式。(推荐提供复杂类型数据)
- 子/孙组件通过inject获取的数据,不能在自身组件内修改
v-model原理
1.原理:
v-model本质上是一个语法糖。例如应用在输入框上,就是value属性 和 input事件 的合写
<template>
<div id="app" >
<input v-model="msg" type="text">
<input :value="msg" @input="msg = $event.target.value" type="text">
</div>
</template>2.作用:
提供数据的双向绑定
- 数据变,视图跟着变 :value
- 视图变,数据跟着变 @input
3.注意
$event 用于在模板中,获取事件的形参
4.v-model使用在其他表单元素上的原理
不同的表单元素, v-model在底层的处理机制是不一样的。比如给checkbox使用v-model
底层处理的是 checked属性和change事件。
不过咱们只需要掌握应用在文本框上的原理即可
表单类组件封装
1.需求目标
实现子组件和父组件数据的双向绑定 (实现App.vue中的selectId和子组件选中的数据进行双向绑定)
2.代码演示
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<BaseSelect
:cityId="selectId"
@changeId="selectId = $event" //$event等价于e.target.value
></BaseSelect>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseSelect from './components/BaseSelect.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {
selectId: '102',
}
},
components: {
BaseSelect,
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>BaseSelect.vue
<template>
<div>
<select :value="cityId" @change="handleChange">
<option value="101">北京</option>
<option value="102">上海</option>
<option value="103">武汉</option>
<option value="104">广州</option>
<option value="105">深圳</option>
</select>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
cityId: String
},
methods: {
handleChange (e) {
this.$emit('changeId',e.target.value)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>v-model简化代码
1.目标:
父组件通过v-model 简化代码,实现子组件和父组件数据 双向绑定
2.如何简化:
v-model其实就是 :value和@input事件的简写
- 子组件:props通过value接收数据,事件触发 input
- 父组件:v-model直接绑定数据
3.代码示例
子组件
<select :value="value" @change="handleChange">...</select>
props: {
//这里必须用value接收
value: String
},
methods: {
handleChange (e) {
//这里必须写input事件触发
this.$emit('input', e.target.value)
}
}父组件
<BaseSelect v-model="selectId"></BaseSelect>.sync修饰符
1.作用
可以实现 子组件 与 父组件数据 的 双向绑定,简化代码
简单理解:子组件可以修改父组件传过来的props值
2.场景
封装弹框类的基础组件, visible属性 true显示 false隐藏
3.本质
.sync修饰符 就是 :属性名 和 @update:属性名 合写
4.语法
父组件
//.sync写法
<BaseDialog :visible.sync="isShow" />
--------------------------------------
//完整写法
<BaseDialog
:visible="isShow"
@update:visible="isShow = $event"
/>子组件
props: {
visible: Boolean
},
this.$emit('update:visible', false)5.代码示例
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<button @click="openDialog">退出按钮</button>
<BaseDialog :isShow="isShow"></BaseDialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseDialog from './components/BaseDialog.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {
isShow: false,
}
},
components: {
BaseDialog,
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>BaseDialog.vue
<template>
<div class="base-dialog-wrap" v-show="isShow">
<div class="base-dialog">
<div class="title">
<h3>温馨提示:</h3>
<button class="close">x</button>
</div>
<div class="content">
<p>你确认要退出本系统么?</p>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<button>确认</button>
<button>取消</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
isShow: Boolean,
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.base-dialog-wrap {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px 2px #ccc;
position: fixed;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
padding: 0 10px;
}
.base-dialog .title {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
border-bottom: 2px solid #000;
}
.base-dialog .content {
margin-top: 38px;
}
.base-dialog .title .close {
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
line-height: 10px;
}
.footer {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
margin-top: 26px;
}
.footer button {
width: 80px;
height: 40px;
}
.footer button:nth-child(1) {
margin-right: 10px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>6.总结
1.父组件如果想让子组件修改传过去的值 必须加什么修饰符?
2.子组件要修改父组件的props值 必须使用什么语法?
ref和$refs
1.作用
利用ref 和 $refs 可以用于 获取 dom 元素 或 组件实例(组件对象里面的方法)
2.特点:
查找范围 → 当前组件内(更精确稳定)
3.语法
1.给要获取的盒子添加ref属性
<div ref="chartRef">我是渲染图表的容器</div>2.获取时通过 $refs获取 this.$refs.chartRef 获取
mounted () {
console.log(this.$refs.chartRef)
}4.注意
之前只用document.querySelect('.box') 获取的是整个页面中的盒子
5.获取dom实例
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<div class="base-chart-box">
这是一个捣乱的盒子
</div>
<BaseChart></BaseChart>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseChart from './components/BaseChart.vue'
export default {
data () {
return {
}
},
components:{
BaseChart
}
}
</script>
<style>BaseChart.vue
<template>
<div ref="mychart" class="base-chart-box"></div>
</template>
<script>
import * as echarts from 'echarts'
export default {
mounted() {
console.log(this.$refs.mychart)
// 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例
const myChart = echarts.init(this.$refs.mychart)
// 绘制图表
myChart.setOption({
title: {
text: 'ECharts 入门示例',
},
tooltip: {},
xAxis: {
data: ['衬衫', '羊毛衫', '雪纺衫', '裤子', '高跟鞋', '袜子'],
},
yAxis: {},
series: [
{
name: '销量',
type: 'bar',
data: [5, 20, 36, 10, 10, 20],
},
],
})
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.base-chart-box {
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 3px solid #000;
border-radius: 6px;
}
</style>6.获取组件实例(组件方法)
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<BaseForm
ref="baseForm"
></BaseForm>
<div>
<button @click="getReset">获取数据</button>
<button @click="handleReset">重置数据</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BaseForm from './components/BaseForm.vue'
export default {
components: {
BaseForm,
},
methods: {
getReset () {
console.log(this.$refs.baseForm.getFormData())
},
handleReset () {
// 如果组件有特殊符号无法识别时,可以使用这个语法
this.$refs["baseForm"].resetFormData()
this.$refs.baseForm.resetFormData()
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>BaseForm.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<div>
账号: <input v-model="username" type="text">
</div>
<div>
密码: <input v-model="password" type="text">
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
username: 'admin',
password: '123456',
}
},
methods: {
getFormData() {
console.log('获取表单数据', this.username, this.password);
},
resetFormData() {
this.username = ''
this.password = ''
console.log('重置表单数据成功');
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.app {
border: 2px solid #ccc;
padding: 10px;
}
.app div{
margin: 10px 0;
}
.app div button{
margin-right: 8px;
}
</style>异步更新 & $nextTick
1.需求
编辑标题, 编辑框自动聚焦
- 点击编辑,显示编辑框
- 让编辑框,立刻获取焦点

2.代码实现
<template>
<div class="app">
<div v-if="isShowEdit">
<input type="text" v-model="editValue" ref="inp" />
<button>确认</button>
</div>
<div v-else>
<span>{{ title }}</span>
<button @click="handleEdit">编辑</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
title: '大标题',
isShowEdit: false,
editValue: '',
}
},
methods: {
handleEdit () {
//显示输入框 (异步dom更新)
this.isShowEdit = true
//让输入框获取焦点 ($nextTick等dom更新完,立刻执行准备的函数体)
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.$refs.inp.focus()
})
//用setTimeout也可,但是时间设置不够准确,浪费了不必要的时间)
// setTimeout(() => {
// this.$refs.inp.focus()
// }, 1000)
}
},
}
</script>3.问题
"显示之后",立刻获取焦点是不能成功的!
原因:Vue 是异步更新DOM (提升性能)
4.解决方案
$nextTick:等 DOM更新后,才会触发执行此方法里的函数体
语法: this.$nextTick(函数体)
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.$refs.inp.focus()
})注意:$nextTick 内的函数体 一定是箭头函数,这样才能让函数内部的this指向Vue实例
自定义指令
1.指令介绍
内置指令:v-html、v-if、v-bind、v-on... 这都是Vue给咱们内置的一些指令,可以直接使用
自定义指令:同时Vue也支持让开发者,自己注册一些指令。这些指令被称为自定义指令
每个指令都有自己各自独立的功能
2.自定义指令
概念:自己定义的指令,可以封装一些DOM操作,扩展额外的功能
3.自定义指令语法
全局注册
//在main.js中 Vue.directive('指令名', { //inserted会在指令所在的元素被插入到页面中时触发 "inserted" (el) { //el就是指令所绑定的元素,可以对 el 标签,扩展额外功能 el.focus() } })局部注册
//在Vue组件的配置项中 directives: { //指令名:指令的配置项 "指令名": { inserted () { // 可以对 el 标签,扩展额外功能 el.focus() } } }使用指令
注意:在使用指令的时候,一定要先注册,再使用,否则会报错 使用指令语法: v-指令名。如:
<input type="text" v-focus/>注册指令时不用加v-前缀,但使用时一定要加v-前缀
4.指令中的配置项介绍
inserted:被绑定元素插入父节点时调用的钩子函数
el:使用指令的那个DOM元素
5.代码示例
需求:当页面加载时,让元素获取焦点(autofocus在safari浏览器有兼容性)
App.vue
<div>
<h1>自定义指令</h1>
<input v-focus ref="inp" type="text">
</div>自定义指令-指令的值
1.需求
实现一个 color 指令 - 传入不同的颜色, 给标签设置文字颜色
2.语法
1.在绑定指令时,可以通过“等号”的形式为指令 绑定 具体的参数值
<div v-color="color">我是内容</div>2.通过 binding.value 可以拿到指令值,指令值修改会 触发 update 函数
directives: {
color: {
inserted (el, binding) {
el.style.color = binding.value
},
update (el, binding) {
el.style.color = binding.value
}
}
}3.代码示例
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<!--显示红色-->
<h2 v-color="color1">指令的值1测试</h2>
<!--显示蓝色-->
<h2 v-color="color2">指令的值2测试</h2>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
color1: 'red',
color2: 'green'
}
},
directives: {
color: {
//inserted 提供的是元素被添加到页面中时的逻辑
inserted (el,binding) {
// console.log(el);
//binding.value 就是指令的值
el.style.color = binding.value
},
// update 指令的值修改的时候触发,提供值变化后,dom更新的逻辑
update (el, binding) {
console.log('指令的值修改了');
el.style.color = binding.value
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>自定义指令-v-loading指令的封装
1.场景
实际开发过程中,发送请求需要时间,在请求的数据未回来时,页面会处于空白状态 => 用户体验不好
2.需求
封装一个 v-loading 指令,实现加载中的效果
3.分析
1.本质 loading效果就是一个蒙层,盖在了盒子上
2.数据请求中,开启loading状态,添加蒙层
3.数据请求完毕,关闭loading状态,移除蒙层
4.实现
1.准备一个 loading类,通过伪元素定位,设置宽高,实现蒙层
2.开启关闭 loading状态(添加移除蒙层),本质只需要添加移除类即可
3.结合自定义指令的语法进行封装复用
.loading:before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: #fff url("./loading.gif") no-repeat center;
}5.准备代码
<template>
<div class="main">
<div class="box" v-loading="isLoading">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in list" :key="item.id" class="news">
<div class="left">
<div class="title">{{ item.title }}</div>
<div class="info">
<span>{{ item.source }}</span>
<span>{{ item.time }}</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="right">
<img :src="item.img" alt="">
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 安装axios => yarn add axios
import axios from 'axios'
// 接口地址:http://hmajax.itheima.net/api/news
// 请求方式:get
export default {
data () {
return {
list: [],
isLoading: true
}
},
async created () {
// 1. 发送请求获取数据
const res = await axios.get('http://hmajax.itheima.net/api/news')
setTimeout(() => {
// 2. 更新到 list 中
this.list = res.data.data
this.isLoading = false
}, 2000)
},
directives: {
loading: {
inserted (el, binding) {
binding.value ? el.classList.add('loading') : el.classList.remove('loading')
},
update (el, binding) {
binding.value ? el.classList.add('loading') : el.classList.remove('loading')
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
/* 伪类 - 蒙层效果 */
.loading:before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: #fff url('./loading.gif') no-repeat center;
}
/* .box2 {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
border: 2px solid #000;
position: relative;
} */
.box {
width: 800px;
min-height: 500px;
border: 3px solid orange;
border-radius: 5px;
position: relative;
}
.news {
display: flex;
height: 120px;
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px 0;
cursor: pointer;
}
.news .left {
flex: 1;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
padding-right: 10px;
}
.news .left .title {
font-size: 20px;
}
.news .left .info {
color: #999999;
}
.news .left .info span {
margin-right: 20px;
}
.news .right {
width: 160px;
height: 120px;
}
.news .right img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
object-fit: cover;
}
</style>插槽-默认插槽
1.作用
让组件内部的一些 结构 支持 自定义
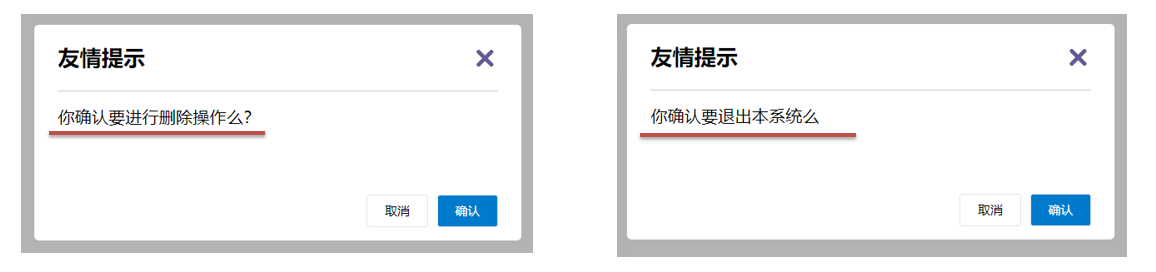
2.需求
将需要多次显示的对话框,封装成一个组件
3.问题
组件的内容部分,不希望写死,希望能使用的时候自定义。怎么办
4.插槽的基本语法
- 组件内需要定制的结构部分,改用**
<slot></slot>**占位 - 使用组件时, **
<MyDialog></MyDialog>**标签内部, 传入结构替换slot - 给插槽传入内容时,可以传入纯文本、html标签、组件
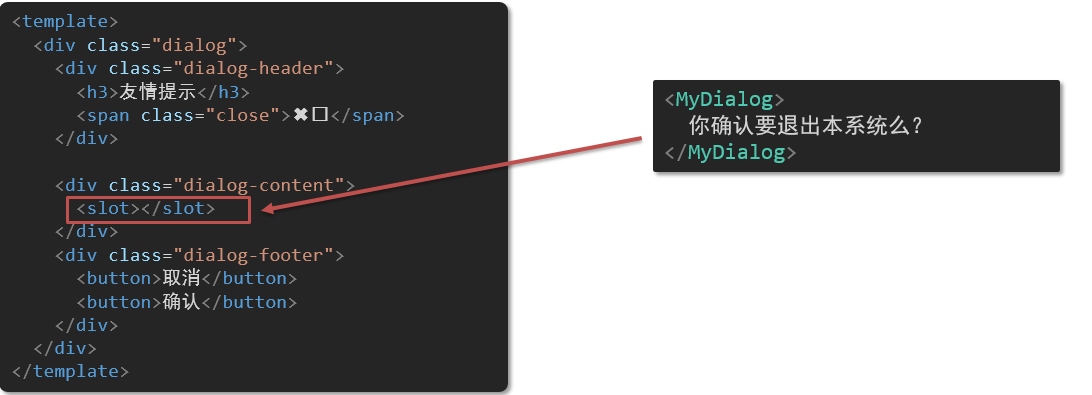
5.代码示例
MyDialog.vue
<template>
<div class="dialog">
<div class="dialog-header">
<h3>友情提示</h3>
<span class="close">✖️</span>
</div>
<div class="dialog-content">
<!-- 在需要定制的位置使用slot占位 -->
<slot></slot>
</div>
<div class="dialog-footer">
<button>取消</button>
<button>确认</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.dialog {
width: 470px;
height: 230px;
padding: 0 25px;
background-color: #ffffff;
margin: 40px auto;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.dialog-header {
height: 70px;
line-height: 70px;
font-size: 20px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc;
position: relative;
}
.dialog-header .close {
position: absolute;
right: 0px;
top: 0px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.dialog-content {
height: 80px;
font-size: 18px;
padding: 15px 0;
}
.dialog-footer {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
}
.dialog-footer button {
width: 65px;
height: 35px;
background-color: #ffffff;
border: 1px solid #e1e3e9;
cursor: pointer;
outline: none;
margin-left: 10px;
border-radius: 3px;
}
.dialog-footer button:last-child {
background-color: #007acc;
color: #fff;
}
</style>App.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 在组件标签内填入内容 -->
<MyDialog>
<div>你确认要删除吗</div>
</MyDialog>
<MyDialog>
<p>你确认要退出吗</p>
</MyDialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyDialog from "./components/MyDialog.vue"
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
components: {
MyDialog,
},
}
</script>
<style>
body {
background-color: #b3b3b3;
}
</style>6.总结
场景:组件内某一部分结构不确定,想要自定义怎么办
使用:插槽的步骤分为哪几步?
插槽-后备内容(默认值)
1.问题
通过插槽完成了内容的定制,传什么显示什么, 但是如果不传,则是空白
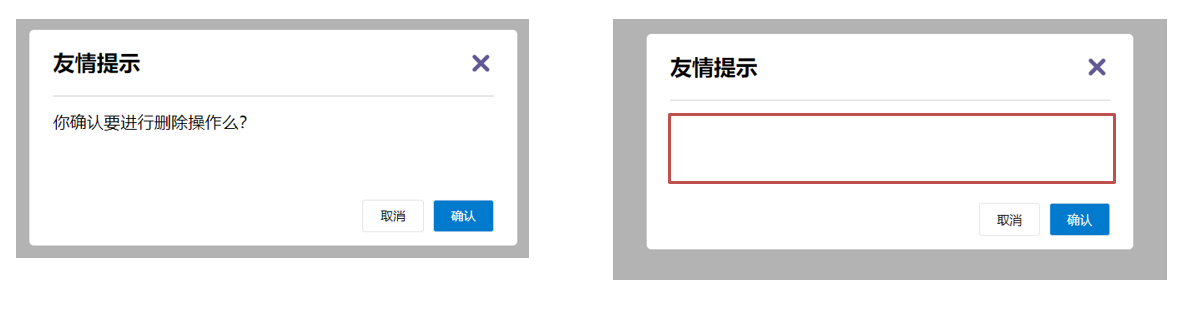
能否给插槽设置 默认显示内容 呢?
2.插槽的后备内容
封装组件时,可以为预留的 <slot> 插槽提供后备内容(默认内容)。
3.语法
在 <slot> 标签内,放置内容, 作为默认显示内容
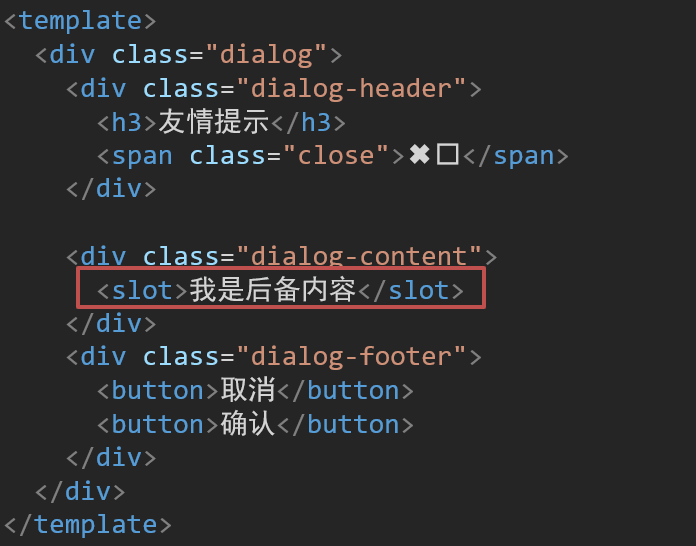
4.效果
外部使用组件时,不传东西,则slot会显示”我是后备内容“

68241243265 外部使用组件时,传东西了,则slot整体会被换掉

68241245902
插槽-具名插槽
1.需求
一个组件内有多处结构,需要外部传入标签,进行定制 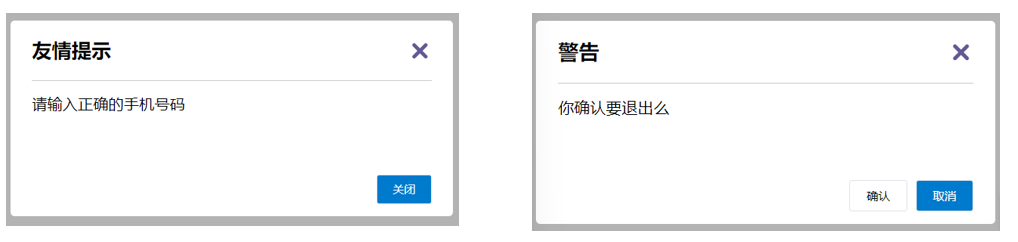
上面的弹框中有三处不同,但是默认插槽只能定制一个位置,这时候怎么办呢?
2.具名插槽语法
多个slot使用name属性区分名字
68241339172 template配合v-slot:名字来分发对应标签

68241341192
3.v-slot的简写
v-slot写起来太长,vue给我们提供一个简单写法 v-slot -> #
4.总结
- 组件内 有多处不确定的结构 怎么办?
- 具名插槽的语法是什么?
- v-slot:插槽名可以简化成什么?
作用域插槽
1.插槽分类
默认插槽
具名插槽
插槽只有两种,作用域插槽不属于插槽的一种分类
2.作用
定义slot 插槽的同时, 是可以传值的。给 插槽 上可以 绑定数据,将来 使用组件时可以用
3.场景
封装表格组件
4.使用步骤
给 slot 标签, 以 添加属性的方式传值
<slot :id="item.id" msg="测试文本"></slot>所有添加的属性, 都会被收集到一个对象中
{ id: 3, msg: '测试文本' }在template中, 通过
#插槽名= "obj"接收,默认插槽名为 default,obj也可直接替换为 { 属性名 } 来直接传属性,不用传递整个对象<MyTable :list="list"> <template #default="obj"> <button @click="del(obj.id)">删除</button> </template> </MyTable>
5.代码示例
MyTable.vue
<template>
<table class="my-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年纪</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in data" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ index + 1 }}</td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.age }}</td>
<td>
<!-- 给slot标签,以添加属性的方式传值 -->
<slot :row="item" msg="测试文本"></slot>
<!-- 将所有的属性添加到一个对象中 -->
<!--
{
row: {id: 2, name: '陈铭鹤', age: 19},
msg; '测试文本'
}
-->
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
data: Array,
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.my-table {
width: 450px;
text-align: center;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
font-size: 24px;
margin: 30px auto;
}
.my-table thead {
background-color: #1f74ff;
color: #fff;
}
.my-table thead th {
font-weight: normal;
}
.my-table thead tr {
line-height: 40px;
}
.my-table th,
.my-table td {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc;
border-right: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.my-table td:last-child {
border-right: none;
}
.my-table tr:last-child td {
border-bottom: none;
}
.my-table button {
width: 65px;
height: 35px;
font-size: 18px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
outline: none;
border-radius: 3px;
cursor: pointer;
background-color: #ffffff;
margin-left: 5px;
}
</style>App.vue
<template>
<div>
<MyTable :data="list">
<template #default="obj">
<button @click="del(obj.row.id)">
删除
</button></template>
</MyTable>
<MyTable :data="list2">
<template #default="{ row }">
<button @click="show(row)">查看</button>
</template>
</MyTable>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyTable from './components/MyTable.vue'
export default {
data () {
return {
list: [
{ id: 1, name: '张小花', age: 18 },
{ id: 2, name: '孙大明', age: 19 },
{ id: 3, name: '刘德忠', age: 17 },
],
list2: [
{ id: 1, name: '赵小云', age: 18 },
{ id: 2, name: '刘蓓蓓', age: 19 },
{ id: 3, name: '姜肖泰', age: 17 },
]
}
},
methods: {
del (id) {
this.list = this.list.filter(item => item.id !== id)
},
show (row) {
console.log(row);
alert('姓名: ${row.name}; 年纪: ${row.age}')
}
},
components: {
MyTable
}
}
</script>6.总结
1.作用域插槽的作用是给插槽上绑定数据,供将来使用组件时使用
2.作用域插槽的使用步骤:
给slot标签,以添加属性的方式传值
所有属性都会被收集到一个对象中
template中,通过 #插槽名="obj" 接收
综合案例 - 商品列表-MyTag组件抽离
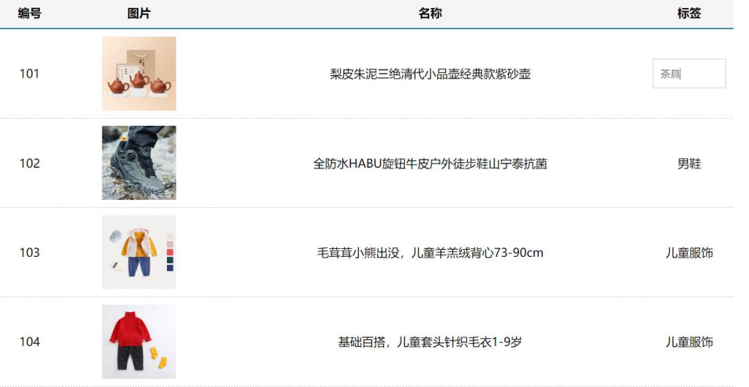
1.需求说明
- my-tag 标签组件封装
(1) 双击显示输入框,输入框获取焦点
(2) 失去焦点,隐藏输入框
(3) 回显标签信息
(4) 内容修改,回车 → 修改标签信息
- my-table 表格组件封装
(1) 动态传递表格数据渲染
(2) 表头支持用户自定义
(3) 主体支持用户自定义
2.代码
App.vue
<template>
<div class="table-case">
<MyTable :data="goods">
<template #head>
<th>编号</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>图片</th>
<th width="100px">标签</th>
</template>
<template #body="{item, index}">
<td>{{ index + 1 }}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>
<img :src="item.picture" />
</td>
<td>
<!-- 标签组件 -->
<MyTag v-model="item.tag"></MyTag>
</td>
</template>
</MyTable>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyTable from './components/MyTable.vue'
import MyTag from './components/MyTag.vue'
export default {
name: 'TableCase',
components: {
MyTag,
MyTable,
},
data() {
return {
//测试组件功能的临时数据
templateText: '茶壶',
templateText2: '钢笔',
goods: [
{
id: 101,
picture:
'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/f8c37ffa41ab1eb84bff499e1f6acfc7.jpg',
name: '梨皮朱泥三绝清代小品壶经典款紫砂壶',
tag: '茶具',
},
{
id: 102,
picture:
'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/221317c85274a188174352474b859d7b.jpg',
name: '全防水HABU旋钮牛皮户外徒步鞋山宁泰抗菌',
tag: '男鞋',
},
{
id: 103,
picture:
'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/cd4b840751ef4f7505c85004f0bebcb5.png',
name: '毛茸茸小熊出没,儿童羊羔绒背心73-90cm',
tag: '儿童服饰',
},
{
id: 104,
picture:
'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/56eb25a38d7a630e76a608a9360eec6b.jpg',
name: '基础百搭,儿童套头针织毛衣1-9岁',
tag: '儿童服饰',
},
],
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.table-case {
width: 1000px;
margin: 50px auto;
img {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
object-fit: contain;
vertical-align: middle;
}
}
</style>my-tag组件封装-创建组件
MyTag.vue
<template>
<div class="my-tag">
<input v-if="isEdit"
ref="inp"
v-focus
class="input"
type="text"
placeholder="输入标签"
:value="value"
@blur="isEdit = false"
@keyup.enter = "handleEnter"
/>
<div v-else @dblclick="handleClick" class="text">
{{ value }}
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
value: String
},
data() {
return {
isEdit: false
}
},
methods: {
handleClick () {
//获取焦点方式: 通过nextTick配合$refs聚焦
//双击后切换到显示状态 (Vue是异步更新)
this.isEdit = true
// 所以显示输入框以后不能直接显示焦点
// this.$refs.inp.focus()
// this.$nextTick(() => {
// //获取焦点
// this.$refs.inp.focus()
// })
},
handleEnter (e) {
if (e.target.value.trim() === '') return alert('标签内容不能为空')
//子传父,将回车时,输入框的内容提交给父组件更新,e.target代表这个标签,value表示里面的内容
//由于父组件是 v-model,触发事件,需要触发 input 事件,父组件接收后将值修改
console.log('回车了')
this.$emit('input', e.target.value)
//提交完成,关闭输入状态
this.isEdit = false
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.my-tag {
cursor: pointer;
.input {
appearance: none;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
width: 100px;
height: 40px;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 10px;
color: #666;
&::placeholder {
color: #666;
}
}
}
</style>main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
//封装全局指令 focus
Vue.directive('focus', {
//指令所在的dom元素,被插入到页面中时触发
inserted (el) {
el.focus()
}
})
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')封装MyTable组件进行动态渲染
MyTable.vue
<template>
<div class="my-tag">
<input
v-if="isEdit"
v-focus
ref="inp"
class="input"
type="text"
placeholder="输入标签"
@blur="isEdit = false"
/>
<div
v-else
@dblclick="handleClick"
class="text">
茶具
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
isEdit: false
}
},
methods: {
handleClick () {
this.isEdit = true
}
}
}
</script>单页应用程序介绍
1.概念
单页应用程序:SPA【Single Page Application】是指所有的功能都在一个html页面上实现
2.具体示例
单页应用网站: 网易云音乐 https://music.163.com/
多页应用网站:京东 https://jd.com/
3.单页应用 VS 多页面应用
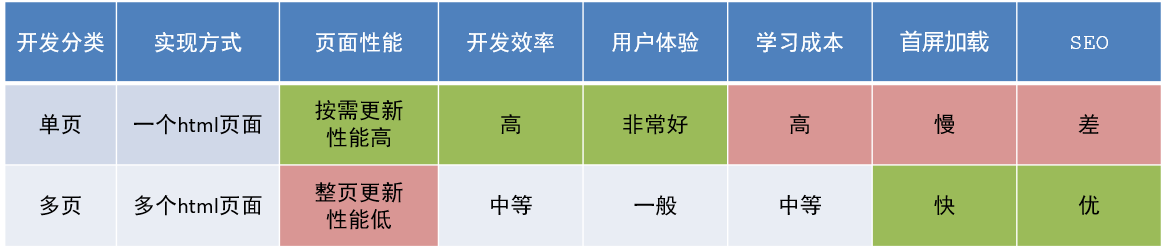
单页应用类网站:系统类网站 / 内部网站 / 文档类网站 / 移动端站点
多页应用类网站:公司官网 / 电商类网站
4.总结
1.什么是单页面应用程序?
2.单页面应用优缺点?
3.单页应用场景?
路由介绍
1.思考
单页面应用程序,之所以开发效率高,性能好,用户体验好
最大的原因就是:页面按需更新
比如当点击【发现音乐】和【关注】时,只是更新下面部分内容,对于头部是不更新的
要按需更新,首先就需要明确:访问路径和 组件的对应关系!
访问路径 和 组件的对应关系如何确定呢? 路由
2.路由的介绍
生活中的路由:设备和ip的映射关系
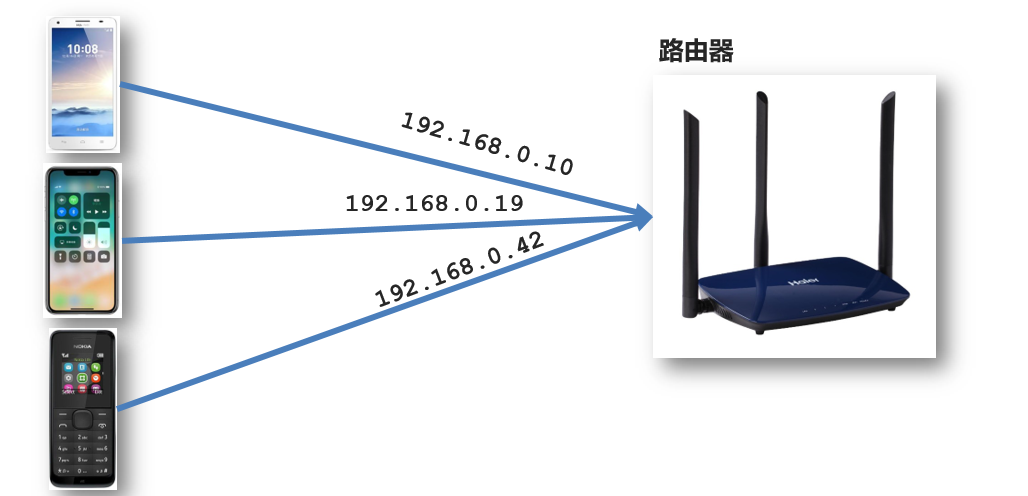
Vue中的路由:路径和组件的映射关系
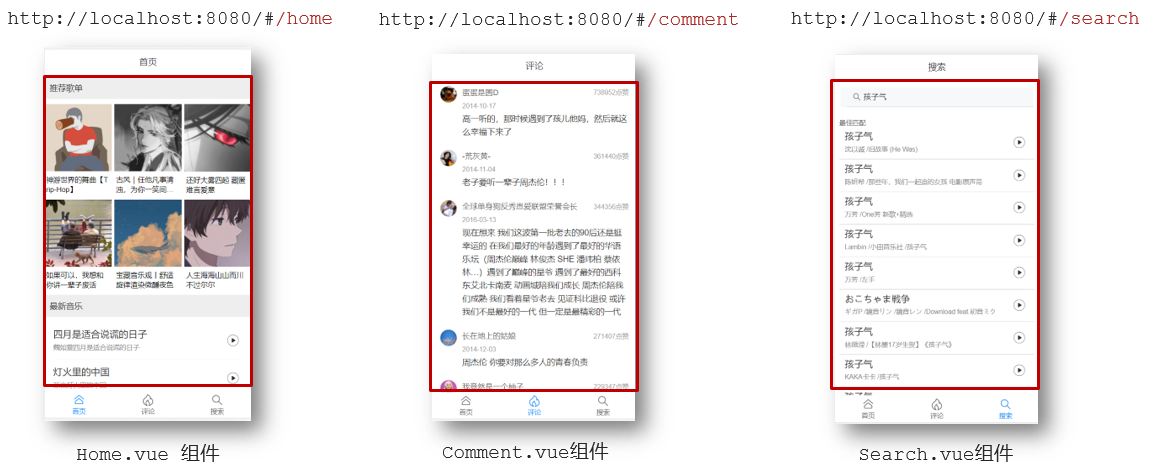
3.总结
- 什么是路由
- Vue中的路由是什么
路由的基本使用
1.目标
认识插件 VueRouter,掌握 VueRouter 的基本使用步骤
2.作用
修改地址栏路径时,切换显示匹配的组件
3.说明
Vue 官方的一个路由插件,是一个第三方包
4.官网
https://v3.router.vuejs.org/zh/
5.VueRouter的使用(5+2)
固定5个固定的步骤(不用死背,熟能生巧)
下载 VueRouter 模块到当前工程,vue2对应版本3.x,vue3对应版本4
yarn add vue-router@3.6.5npm install vue-router@3.6.5 --save-devmain.js中引入VueRouter
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'安装注册
Vue.use(VueRouter)创建路由对象
const router = new VueRouter()注入,将路由对象注入到new Vue实例中,建立关联
new Vue({ render: h => h(App), router:router }).$mount('#app')
当我们配置完以上5步之后 就可以看到浏览器地址栏中的路由 变成了 /#/的形式。表示项目的路由已经被Vue-Router管理了
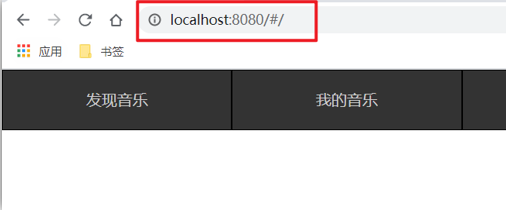
6.代码示例
main.js
// 路由的使用步骤 5 + 2
// 5个基础步骤
// 1. 下载 v3.6.5
// yarn add vue-router@3.6.5
// 2. 引入
// 3. 安装注册 Vue.use(Vue插件)
// 4. 创建路由对象
// 5. 注入到new Vue中,建立关联
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter) // VueRouter插件初始化
const router = new VueRouter()
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
//完整写法
// router: router
//当对象键和值相同时可以简写
router
}).$mount('#app')7.两个核心步骤
创建需要的组件 (views目录),配置路由规则(组件是views目录里面的文件名)
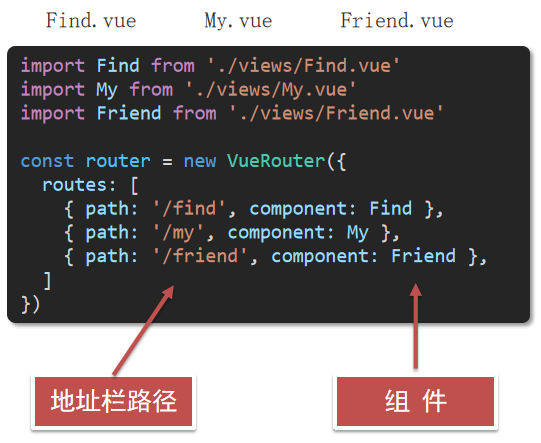
68247963966 配置导航,配置路由出口(路径匹配的组件显示的位置)
App.vue
<div class="footer_wrap"> //配置导航 <a href="#/find">发现音乐</a> <a href="#/my">我的音乐</a> <a href="#/friend">朋友</a> </div> <div class="top"> //配置路由出口,div位置可调 <router-view></router-view> </div> </div>
8.总结
- 如何实现 路径改变,对应组件 切换,应该使用哪个插件?
组件的存放目录问题
注意: .vue文件 本质无区别
1.组件分类
.vue文件分为2类,都是 .vue文件(本质无区别)
- 页面组件 (配置路由规则时使用的组件)
- 复用组件(多个组件中都使用到的组件)
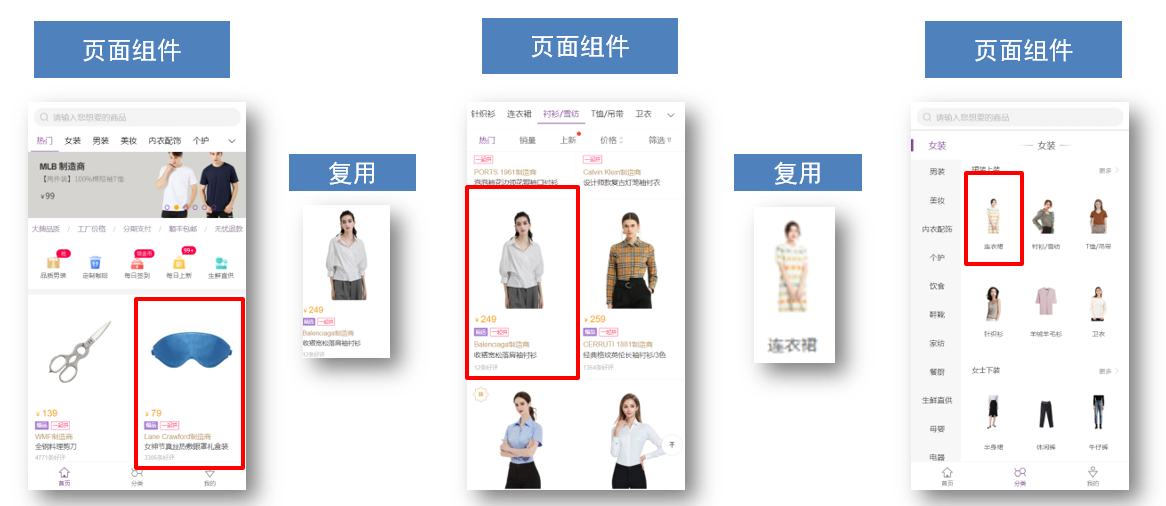
2.存放目录
分类开来的目的就是为了 更易维护
src/views文件夹
页面组件 - 页面展示 - 配合路由用
src/components文件夹
复用组件 - 展示数据 - 常用于复用
路由的封装抽离
问题:所有的路由配置都在main.js中合适吗?
目标:将路由模块抽离出来。 好处:拆分模块,利于维护
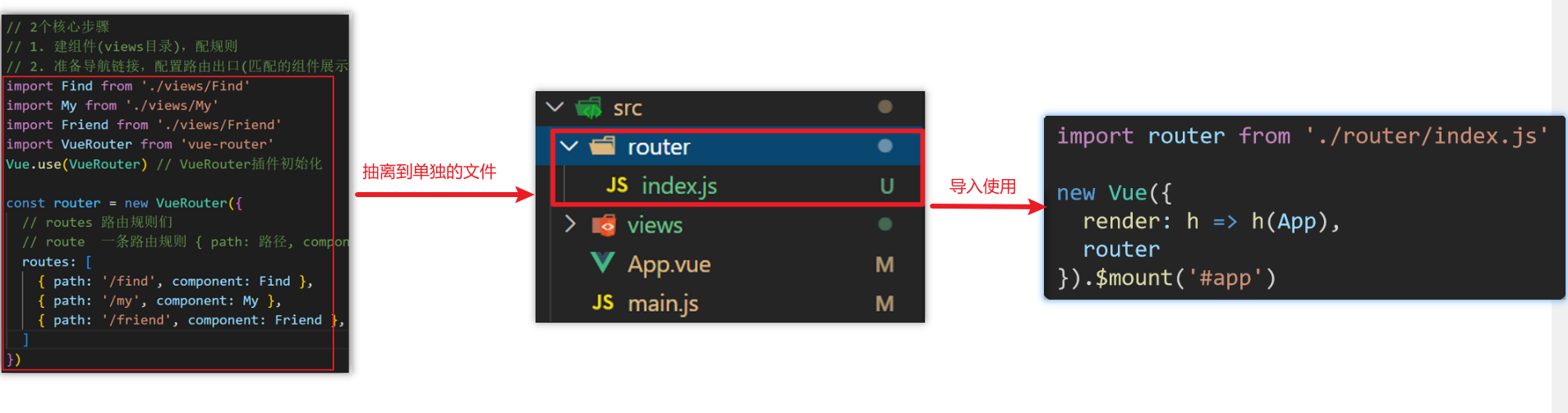
路径简写:
脚手架环境下 @指代src目录,可以用于快速引入组件
声明式导航-导航链接
1.需求
实现导航高亮效果
如果使用a标签进行跳转的话,需要给当前跳转的导航加样式,同时要移除上一个a标签的样式,太麻烦!!!
2.解决方案
vue-router 提供了一个全局组件 router-link (取代 a 标签)
- 能跳转,配置 to 属性指定路径(必须) 。本质还是 a 标签 ,to 无需 #
- 能高亮,默认就会提供高亮类名,可以直接设置高亮样式
语法: <router-link to="path的值">发现音乐</router-link>
<div>
<div class="footer_wrap">
<router-link to="/find">发现音乐</router-link>
<router-link to="/my">我的音乐</router-link>
<router-link to="/friend">朋友</router-link>
</div>
<div class="top">
<!-- 路由出口 → 匹配的组件所展示的位置 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>3.通过router-link自带的两个样式进行高亮
使用router-link跳转后,我们发现。当前点击的链接默认加了两个class的值 router-link-exact-active和router-link-active
我们可以给任意一个class属性添加高亮样式即可实现功能
4.总结
router-link是什么?
vue-router提供的全局组件,用于替换a标签
router-link怎么用?
<router-link to="/路径值"></router> 必须传入to属性,指定路由路径值
router-link的好处是什么?
能跳转,能高亮(自带激活时的类名)
声明式导航-两个类名
当我们使用<router-link></router-link>跳转时,自动给当前导航加了两个类名
1.router-link-active
模糊匹配(用的多)
to="/my" 可以匹配 /my /my/a /my/b ....
只要是以/my开头的路径 都可以和 to="/my"匹配到
2.router-link-exact-active
精确匹配
to="/my" 仅可以匹配 /my
3.在地址栏中输入二级路由查看类名的添加
声明式导航-自定义类名(了解)
1.问题
router-link的两个高亮类名 太长了,我们希望能定制怎么办
2.解决方案
我们可以在创建路由对象时,额外配置两个配置项即可。 linkActiveClass和linkExactActiveClass
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [...],
//link自定义高亮类名
linkActiveClass: "类名1", // 配置模糊匹配
linkExactActiveClass: "类名2" // 配置精确匹配的类名
})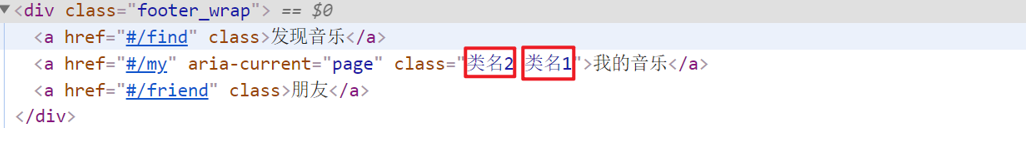
3.代码演示
// 创建了一个路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
...
],
linkActiveClass: 'active', // 配置模糊匹配的类名
linkExactActiveClass: 'exact-active' // 配置精确匹配的类名
})4.总结
如何自定义router-link的两个高亮类名
声明式导航-查询参数传参
1.目标
在跳转路由时,进行传参

比如:现在我们在搜索页点击了热门搜索链接,跳转到详情页,需要把点击的内容带到详情页,改怎么办呢?
2.跳转传参
我们可以通过两种方式,在跳转的时候把所需要的参数传到其他页面中
- 查询参数传参
- 动态路由传参
3.查询参数传参
如何传参?
<router-link to="/path?参数名=值"></router-link>如何接受参数
固定用法:$route.query.参数名
方法内(js文件)接收参数: this.$route.query.参数名
4.代码演示
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<div class="link">
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/search">搜索页</router-link>
</div>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {};
</script>
<style scoped>
.link {
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
background-color: #495150;
display: flex;
margin: -8px -8px 0 -8px;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.link a {
display: block;
text-decoration: none;
background-color: #ad2a26;
width: 100px;
text-align: center;
margin-right: 5px;
color: #fff;
border-radius: 5px;
}
</style>Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<div class="logo-box"></div>
<div class="search-box">
<input type="text">
<button>搜索一下</button>
</div>
<div class="hot-link">
热门搜索:
<router-link to="/search?key=黑马程序员">黑马程序员</router-link>
<router-link to="/search?key=前端培训">前端培训</router-link>
<router-link to="/search?key=如何成为前端大牛">如何成为前端大牛</router-link>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'FindMusic'
}
</script>
<style>
.logo-box {
height: 150px;
background: url('@/assets/logo.jpeg') no-repeat center;
}
.search-box {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.search-box input {
width: 400px;
height: 30px;
line-height: 30px;
border: 2px solid #c4c7ce;
border-radius: 4px 0 0 4px;
outline: none;
}
.search-box input:focus {
border: 2px solid #ad2a26;
}
.search-box button {
width: 100px;
height: 36px;
border: none;
background-color: #ad2a26;
color: #fff;
position: relative;
left: -2px;
border-radius: 0 4px 4px 0;
}
.hot-link {
width: 508px;
height: 60px;
line-height: 60px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.hot-link a {
margin: 0 5px;
}
</style>Search.vue
<template>
<div class="search">
<p>搜索关键字: {{ $route.query.key }}</p>
<p>搜索结果: </p>
<ul>
<li>.............</li>
<li>.............</li>
<li>.............</li>
<li>.............</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'MyFriend',
created (){
//在create中,获取路由参数
//this.$route.query.参数名 获取
console.log(this.$route.query);
}
}
</script>
<style>
.search {
width: 400px;
height: 240px;
padding: 0 20px;
margin: 0 auto;
border: 2px solid #c4c7ce;
border-radius: 5px;
}
</style>router/index.js
import Home from '@/views/Home'
import Search from '@/views/Search'
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter) // VueRouter插件初始化
// 创建了一个路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/home', component: Home },
{ path: '/search', component: Search }
]
})
export default routermain.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router/index'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
router
}).$mount('#app')声明式导航-动态路由传参
1.动态路由传参方式
配置动态路由
动态路由后面的参数可以随便起名,但要有语义
const router = new VueRouter({ routes: [ ..., { // :words代表要传入的值,接受的时候参数名就是words path: '/search/:words', component: Search } ] })配置导航链接
to="/path/参数值"
对应页面组件接受参数
接收参数: $route.params.参数名
方法内(js文件)接收参数: this.$route.params.参数名
params后面的参数名要和动态路由配置的参数保持一致
2.查询参数传参 VS 动态路由传参
查询参数传参 (比较适合传多个参数)
- 跳转:to="/path?参数名=值&参数名2=值"
- 获取:$route.query.参数名
动态路由传参 (优雅简洁,传单个参数比较方便)
- 配置动态路由:path: "/path/:参数名"
- 跳转:to="/path/参数值"
- 获取:$route.params.参数名
注意:动态路由也可以传多个参数,但一般只传一个
3.总结
声明式导航跳转时, 有几种方式传值给路由页面?
- 查询参数传参(多个参数)
- 动态路由传参(一个参数,优雅简洁)
动态路由参数的可选符(了解)
1.问题
配了路由 path:"/search/:words" 为什么按下面步骤操作,会未匹配到组件,显示空白?
2.原因
/search/:words 表示,必须要传参数。如果不传参数,也希望匹配,可以加个可选符"?"
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
...
{ path: '/search/:words?', component: Search }
]
})Vue路由-重定向
1.问题
网页打开时, url 默认是 / 路径,未匹配到组件时,会出现空白
2.解决方案
重定向 → 匹配 / 后, 强制跳转 /home 路径
3.语法
{ path: 匹配路径, redirect: 重定向到的路径 },
比如:
{ path:'/' ,redirect:'/home' }4.代码演示
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', redirect: '/home'},
...
]
})Vue路由-404
1.作用
当路径找不到匹配时,给个提示页面
2.位置
404的路由,虽然配置在任何一个位置都可以,但一般都配置在其他路由规则的最后面
3.语法
path: "*" (任意路径) – 前面不匹配就命中最后这个
import NotFind from '@/views/NotFind'
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
...
{ path: '*', component: NotFind } //最后一个
]
})4.代码示例
NotFound.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>404 Not Found</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
</style>router/index.js
...
import NotFound from '@/views/NotFound'
...
// 创建了一个路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
...
{ path: '*', component: NotFound }
]
})
export default routerVue路由-模式设置
1.问题
路由的路径看起来不自然, 有#,能否切成真正路径形式?
- hash路由(默认) 例如: http://localhost:8080/#/home
- history路由(常用) 例如: http://localhost:8080/home (以后上线需要服务器端支持,开发环境webpack给规避掉了history模式的问题)
2.语法
const router = new VueRouter({
mode:'histroy', //默认是hash
routes:[]
})编程式导航-两种路由跳转方式
1.问题
点击按钮跳转如何实现?
2.方案
编程式导航:用JS代码来进行跳转
3.语法
两种语法:
- path 路径跳转 (简易方便)
- name 命名路由跳转 (适合 path 路径长的场景)
4.path路径跳转语法
特点:简易方便
//简单写法
this.$router.push('路由路径')
//完整写法
this.$router.push({
path: '路由路径'
})5.代码演示 path跳转方式
6.name命名路由跳转
特点:适合 path 路径长的场景
语法:
路由规则,必须配置name配置项
{ name: '路由名', path: '/path/xxx', component: XXX },通过name来进行跳转
this.$router.push({ name: '路由名' })
编程式导航-path路径跳转传参
1.问题
点击搜索按钮,跳转需要把文本框中输入的内容传到下一个页面如何实现?

2.两种传参方式
1.查询参数
2.动态路由传参
3.传参
两种跳转方式,对于两种传参方式都支持:
① path 路径跳转传参
② name 命名路由跳转传参
4.path路径跳转传参(query传参)
//简单写法
this.$router.push('/路径?参数名1=参数值1&参数2=参数值2')
//完整写法
this.$router.push({
path: '/路径',
query: {
参数名1: '参数值1',
参数名2: '参数值2'
}
})接受参数的方式依然是:$route.query.参数名
5.path路径跳转传参(动态路由传参)
//简单写法
this.$router.push('/路径/参数值')
//完整写法
this.$router.push({
path: '/路径/参数值'
})接受参数的方式依然是:$route.params.参数值
**注意:**path不能配合params使用
编程式导航-name命名路由传参
1.name 命名路由跳转传参 (query传参)
this.$router.push({
name: '路由名字',
query: {
参数名1: '参数值1',
参数名2: '参数值2'
}
})2.name 命名路由跳转传参 (动态路由传参)
this.$router.push({
name: '路由名字',
params: {
参数名: '参数值',
}
})3.总结
编程式导航,如何跳转传参?
1.path路径跳转
query传参
this.$router.push('/路径?参数名1=参数值1&参数2=参数值2') //如果参数值过多,写成下面的完整语法 this.$router.push({ path: '/路径', query: { 参数名1: '参数值1', 参数名2: '参数值2' } })动态路由传参
this.$router.push('/路径/参数值') this.$router.push({ path: '/路径/参数值' })
2.name命名路由跳转
query传参
this.$router.push({ name: '路由名字', query: { 参数名1: '参数值1', 参数名2: '参数值2' } })动态路由传参 (需要配动态路由)
this.$router.push({ name: '路由名字', params: { 参数名: '参数值', } })
面经基础版-案例效果分析
1.面经效果演示
2.功能分析
- 通过演示效果发现,主要的功能页面有两个,一个是列表页,一个是详情页,并且在列表页点击时可以跳转到详情页
- 底部导航可以来回切换,并且切换时,只有上面的主题内容在动态渲染
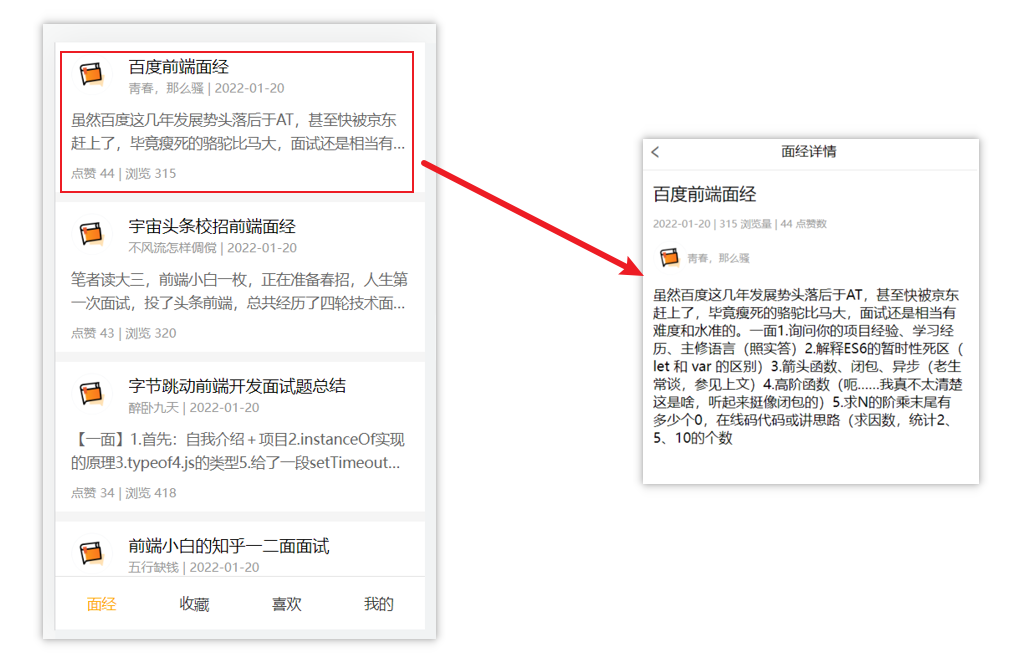
3.实现思路分析:配置路由+功能实现
1.配置路由
- 首页和面经详情页,两个一级路由
- 首页内嵌套4个可切换的页面(嵌套二级路由)
2.实现功能
- 首页请求渲染
- 跳转传参 到 详情页,详情页动态渲染
- 组件缓存,性能优化
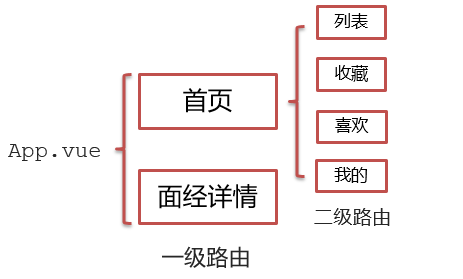
面经基础版-一级路由配置
1.把文档中准备的素材拷贝到项目中
2.针对router/index.js文件 进行一级路由配置
...
import Layout from '@/views/Layout.vue'
import ArticleDetail from '@/views/ArticleDetail.vue'
...
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
component: Layout
},
{
path: '/detail',
component: ArticleDetail
}
]
})面经基础版-二级路由配置
二级路由也叫嵌套路由,当然也可以嵌套三级、四级...
1.使用场景
当在页面中点击链接跳转,只是部分内容切换时,我们可以使用嵌套路由
2.语法
- 在一级路由下,配置children属性即可
- 配置二级路由的出口
1.在一级路由下,配置children属性
注意:一级的路由path 需要加 / 二级路由的path不需要加 /
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
component: Layout,
children:[
//children中的配置项 跟一级路由中的配置项一模一样
{path:'xxxx',component:xxxx.vue},
{path:'xxxx',component:xxxx.vue},
]
}
]
})技巧:二级路由应该配置到哪个一级路由下呢?
这些二级路由对应的组件渲染到哪个一级路由下,children就配置到哪个路由下边
2.配置二级路由的出口 <router-view></router-view>
注意: 配置了嵌套路由,一定配置对应的路由出口,否则不会渲染出对应的组件
Layout.vue
<template>
<div class="h5-wrapper">
<div class="content">
// 配置对应的路由出口
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
....
</div>
</template>3.代码实现
router/index.js
...
import Article from '@/views/Article.vue'
import Collect from '@/views/Collect.vue'
import Like from '@/views/Like.vue'
import User from '@/views/User.vue'
...
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
component: Layout,
redirect: '/article',
children:[
{
path:'/article',
component:Article
},
{
path:'/collect',
component:Collect
},
{
path:'/like',
component:Like
},
{
path:'/user',
component:User
}
]
},
....
]
})Layout.vue
<template>
<div class="h5-wrapper">
<div class="content">
<!-- 内容部分 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<nav class="tabbar">
<a href="#/article">面经</a>
<a href="#/collect">收藏</a>
<a href="#/like">喜欢</a>
<a href="#/user">我的</a>
</nav>
</div>
</template>面经基础版-二级导航高亮
1.实现思路
- 将a标签替换成
<router-link></router-link>组件,配置to属性,不用加 # - 结合高亮类名实现高亮效果 (推荐模糊匹配:router-link-active)
2.代码实现
Layout.vue
....
<nav class="tabbar">
<router-link to="/article">面经</router-link>
<router-link to="/collect">收藏</router-link>
<router-link to="/like">喜欢</router-link>
<router-link to="/user">我的</router-link>
</nav>
<style>
a.router-link-active {
color: orange;
}
</style>面经基础版-首页请求渲染
1.步骤分析
1.安装axios
2.看接口文档,确认请求方式,请求地址,请求参数
3.created中发送请求,获取数据,存储到data中
4.页面动态渲染
2.代码实现
1.安装axios
yarn add axios npm i axios
2.接口文档
请求地址: https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles
请求方式: get3.created中发送请求,获取数据,存储到data中
data() {
return {
articelList: [],
}
},
async created() {
const { data: { result: { rows } }} = await axios.get('https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles')
this.articelList = rows
},4.页面动态渲染
<template>
<div class="article-page">
<div class="article-item" v-for="item in articelList" :key="item.id">
<div class="head">
<img :src="item.creatorAvatar" alt="" />
<div class="con">
<p class="title">{{ item.stem }}</p>
<p class="other">{{ item.creatorName }} | {{ item.createdAt }}</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="body">
{{item.content}}
</div>
<div class="foot">点赞 {{item.likeCount}} | 浏览 {{item.views}}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>面经基础版-查询参数传参
1.说明
跳转详情页需要把当前点击的文章id传给详情页,获取数据
- 查询参数传参 this.$router.push('/detail?参数1=参数值&参数2=参数值')
- 动态路由传参 先改造路由 在传参 this.$router.push('/detail/参数值')
2.查询参数传参实现
Article.vue
<template>
<div class="article-page">
<div class="article-item"
v-for="item in articelList" :key="item.id"
@click="$router.push(`/detail?id=${item.id}`)">
...
</div>
</div>
</template>ArticleDetail.vue
created(){
console.log(this.$route.query.id)
}面经基础版-动态路由传参
1.实现步骤
- 改造路由
- 动态传参
- 在详情页获取参数
2.代码实现
改造路由
router/index.js
...
{
path: '/detail/:id',
component: ArticleDetail
}Article.vue
<div class="article-item"
v-for="item in articelList" :key="item.id"
@click="$router.push(`/detail/${item.id}`)">
....
</div>ArticleDetail.vue
created(){
console.log(this.$route.params.id)
}3.额外优化功能点-点击回退跳转到上一页
ArticleDetail.vue
<template>
<div class="article-detail-page">
<nav class="nav"><span class="back" @click="$router.back()"><</span> 面经详情</nav>
....
</div>
</template>面经基础版-详情页渲染
1.实现步骤分析
- 导入axios
- 查看接口文档
- 在created中发送请求
- 页面动态渲染
2.代码实现
接口文档
请求地址: https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles/:id
请求方式: get在created中发送请求
data() {
return {
articleDetail:{}
}
},
async created() {
const id = this.$route.params.id
const { data } = await axios.get(`https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles/${id}`)
this.article = data.result
console.log(this.article);
)
this.articleDetail = result
},页面动态渲染
<template>
<div class="article-detail-page" v-if="article.id">
<nav class="nav"><span @click="$router.back()" class="back"><</span> 面经详情</nav>
<header class="header">
<h1>{{ article.stem }}</h1>
<p>{{ article.createdAt }} | {{ article.views }} 浏览量 | {{ article.likeCount }} 点赞数</p>
<p>
<img
:src="article.creatorAvatar"
alt=""
/>
<span>{{ article.creatNa }}</span>
</p>
</header>
<main class="body">
{{ article.content }}
</main>
</div>
</template>面经基础版-缓存组件
1.问题
从面经列表 点到 详情页,又点返回,数据重新加载了 → 希望回到原来的位置
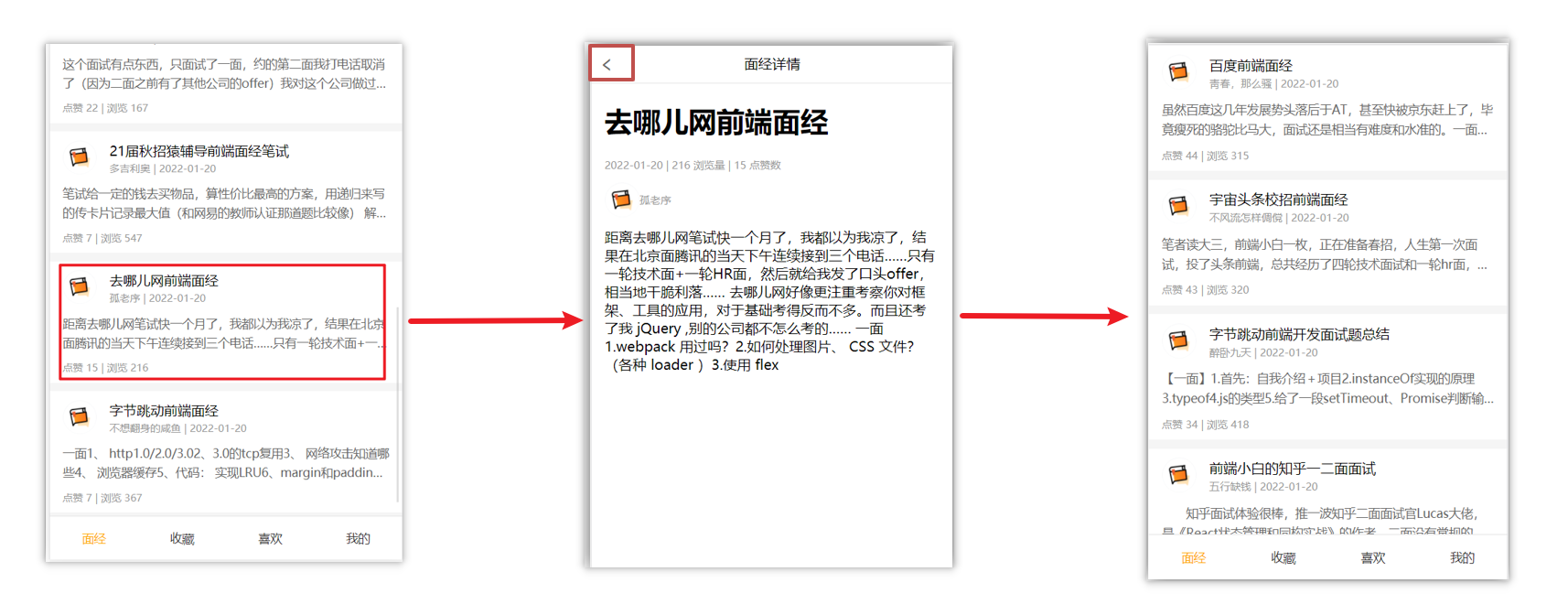
2.原因
当路由被跳转后,原来所看到的组件就被销毁了(会执行组件内的beforeDestroy和destroyed生命周期钩子),重新返回后组件又被重新创建了(会执行组件内的beforeCreate,created,beforeMount,Mounted生命周期钩子),所以数据被加载了
3.解决方案
利用keep-alive把原来的组件给缓存下来
4.什么是keep-alive
keep-alive 是 Vue 的内置组件,当它包裹动态组件时,会缓存不活动的组件实例,而不是销毁它们。
keep-alive 是一个抽象组件:它自身不会渲染成一个 DOM 元素,也不会出现在父组件中。
优点:
在组件切换过程中把切换出去的组件保留在内存中,防止重复渲染DOM,
减少加载时间及性能消耗,提高用户体验性。
App.vue
<template>
<div class="h5-wrapper">
<keep-alive>
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
</div>
</template>问题:
缓存了所有被切换一级路由的组件
5.keep-alive的三个属性
① include : 组件名数组,只有匹配的组件会被缓存
② exclude : 组件名数组,任何匹配的组件都不会被缓存
③ max : 最多可以缓存多少组件实例
App.vue
<template>
<div class="h5-wrapper">
<keep-alive :include="['LayoutPage']">
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
</div>
</template>6.额外的两个生命周期钩子
keep-alive的使用会触发两个生命周期函数
activated 当组件被激活(使用)的时候触发 → 进入这个页面的时候触发
deactivated 当组件不被使用的时候触发 → 离开这个页面的时候触发
组件缓存后就不会执行组件的created, mounted, destroyed 等钩子了
所以其提供了actived 和deactived钩子,帮我们实现业务需求。
VueCli 自定义创建项目
1.安装脚手架 (已安装)
npm i @vue/cli -g2.创建项目
vue create hm-exp-mobile- 选项
Vue CLI v5.0.8
? Please pick a preset:
Default ([Vue 3] babel, eslint)
Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint)
> Manually select features 选自定义- 手动选择功能

- 选择vue的版本
3.x
> 2.x- 是否使用history模式

- 选择css预处理
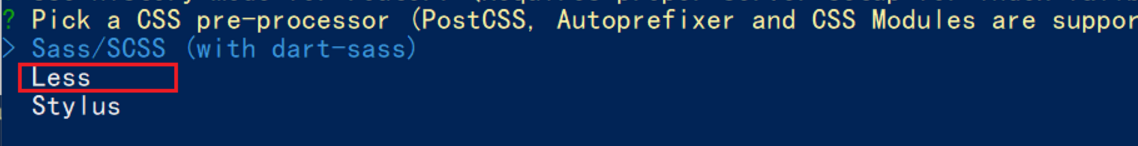
- 选择eslint的风格 (eslint 代码规范的检验工具,检验代码是否符合规范)
- 比如:const age = 18; => 报错!多加了分号!后面有工具,一保存,全部格式化成最规范的样子

- 选择校验的时机 (直接回车)
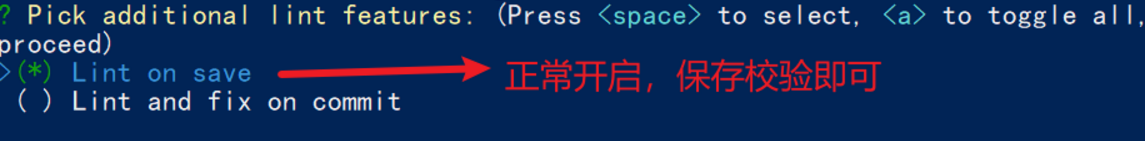
- 选择配置文件的生成方式 (直接回车)
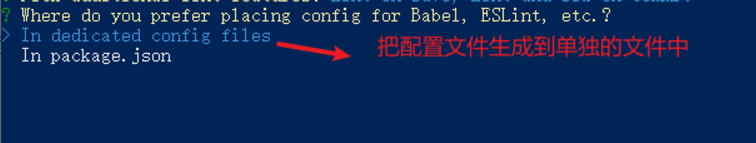
- 是否保存预设,下次直接使用? => 不保存,输入 N
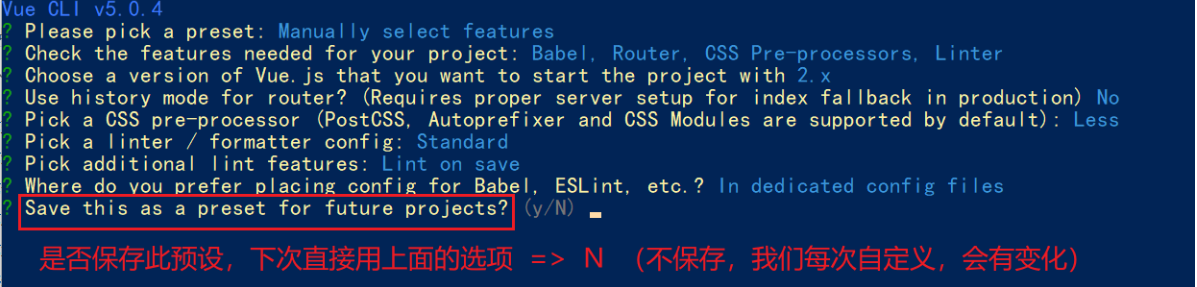
- 等待安装,项目初始化完成
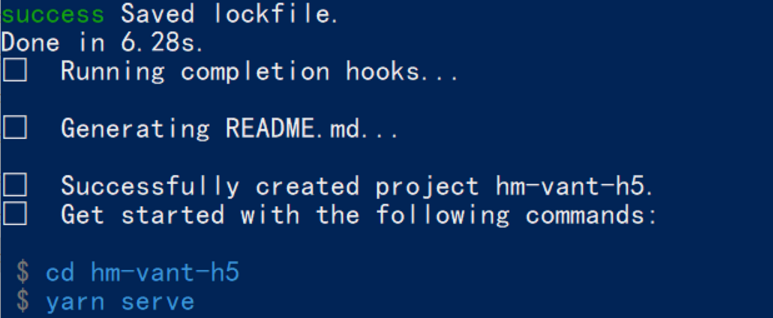
- 启动项目
npm run serveESlint代码规范及手动修复
代码规范:一套写代码的约定规则。例如:赋值符号的左右是否需要空格?一句结束是否是要加?
没有规矩不成方圆
ESLint:是一个代码检查工具,用来检查你的代码是否符合指定的规则(你和你的团队可以自行约定一套规则)。在创建项目时,我们使用的是 JavaScript Standard Style 代码风格的规则。
1.JavaScript Standard Style 规范说明
建议把:https://standardjs.com/rules-zhcn.html 看一遍,然后在写的时候, 遇到错误就查询解决。
下面是这份规则中的一小部分:
- 字符串使用单引号 – 需要转义的地方除外
- 无分号 const name = 'zs'
- 关键字后加空格
if (condition) { ... } - 函数名后加空格
function name (arg) { ... } - 坚持使用全等
===摒弃==一但在需要检查null || undefined时可以使用obj == null - ......
2.代码规范错误
如果你的代码不符合standard的要求,eslint会跳出来提示你。
下面我们在main.js中随意做一些改动:添加一些空行,空格。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import './styles/index.less'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue ( {
render: h => h(App),
router
}).$mount('#app')按下保存代码之后:
你将会看在控制台中输出如下错误:
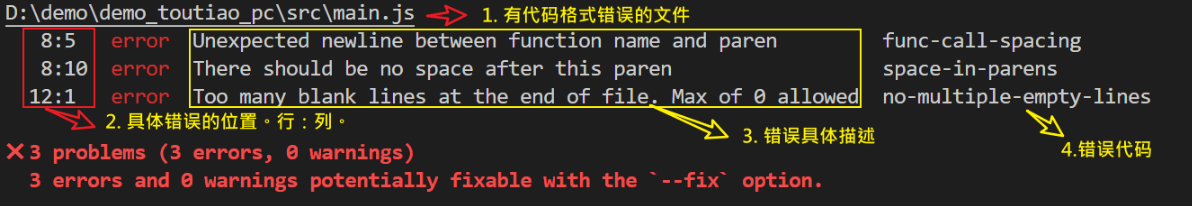
eslint 是来帮助你的。心态要好,有错,就改。
3.手动修正
根据错误提示来一项一项手动修正。
如果你不认识命令行中的语法报错是什么意思,你可以根据错误代码(func-call-spacing, space-in-parens,.....)去 ESLint 规则列表中查找其具体含义。
打开 ESLint 规则表,使用页面搜索(Ctrl + F)这个代码,查找对该规则的一个释义。
通过eslint插件来实现自动修正
- eslint会自动高亮错误显示
- 通过配置,eslint会自动帮助我们修复错误
- 如何安装 (请使用2.4.0,使用新版本可能会出现问题)
- 如何配置
// 当保存的时候,eslint自动帮我们修复错误
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": true
},
// 保存代码,不自动格式化
"editor.formatOnSave": false- 注意:eslint的配置文件必须在根目录下,这个插件才能才能生效。打开项目必须以根目录打开,一次打开一个项目
- 注意:使用了eslint校验之后,把vscode带的那些格式化工具全禁用了 Beatify
settings.json 参考
{
"window.zoomLevel": 2,
"workbench.iconTheme": "vscode-icons",
"editor.tabSize": 2,
"emmet.triggerExpansionOnTab": true,
// 当保存的时候,eslint自动帮我们修复错误
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": true
},
// 保存代码,不自动格式化
"editor.formatOnSave": false
}Vuex 概述
目标:明确Vuex是什么,应用场景以及优势
1.是什么
Vuex 是一个 Vue 的 状态管理工具,状态就是数据。
大白话:Vuex 是一个插件,可以帮我们管理 Vue 通用的数据 (多组件共享的数据)。例如:购物车数据 个人信息数
2.使用场景
某个状态 在 很多个组件 来使用 (个人信息)
多个组件 共同维护 一份数据 (购物车)
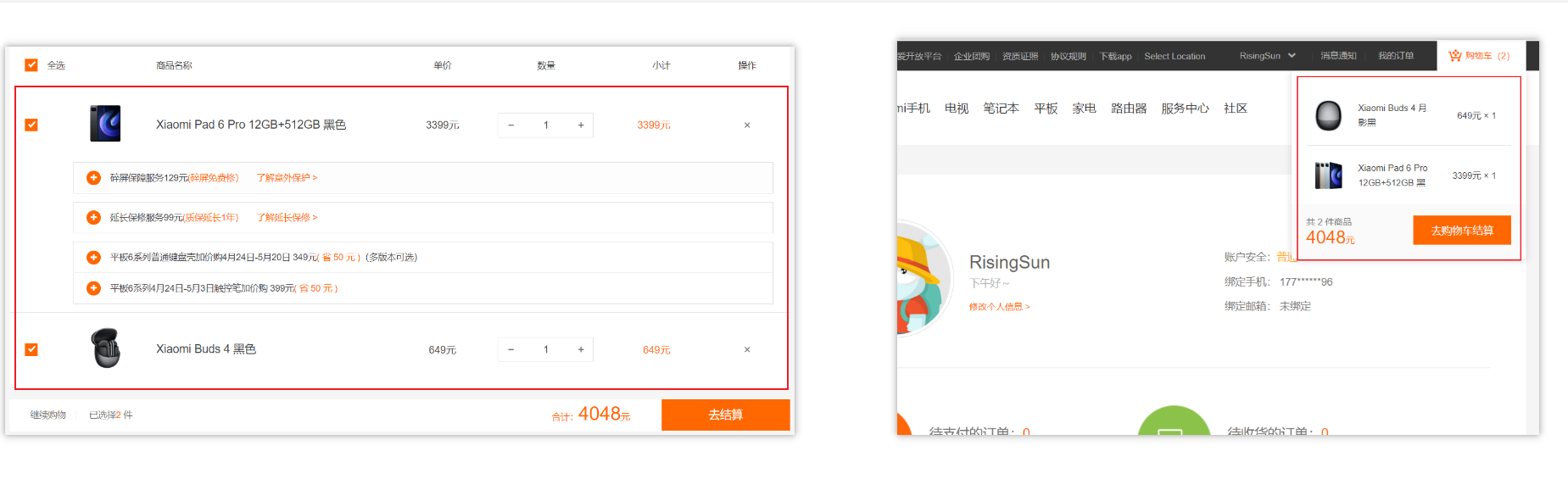
3.优势
- 共同维护一份数据,数据集中化管理
- 响应式变化
- 操作简洁 (vuex提供了一些辅助函数)
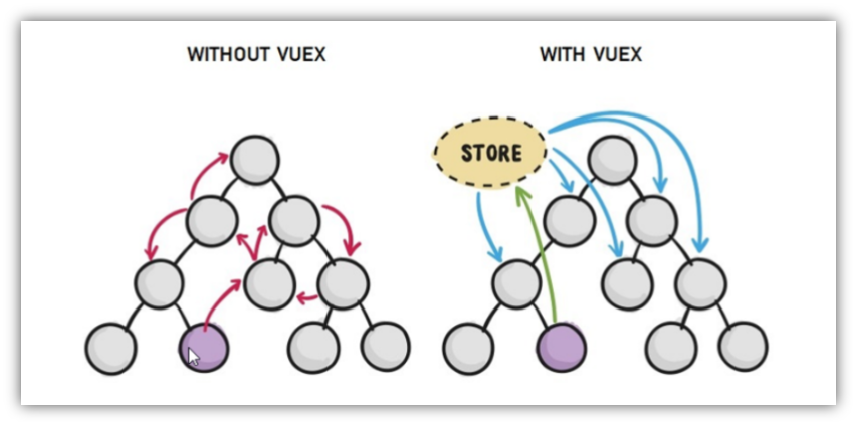
4.注意:
官方原文:
- 不是所有的场景都适用于vuex,只有在必要的时候才使用vuex
- 使用了vuex之后,会附加更多的框架中的概念进来,增加了项目的复杂度 (数据的操作更便捷,数据的流动更清晰)
Vuex就像《近视眼镜》, 你自然会知道什么时候需要用它~
需求: 多组件共享数据
目标:基于脚手架创建项目,构建 vuex 多组件数据共享环境
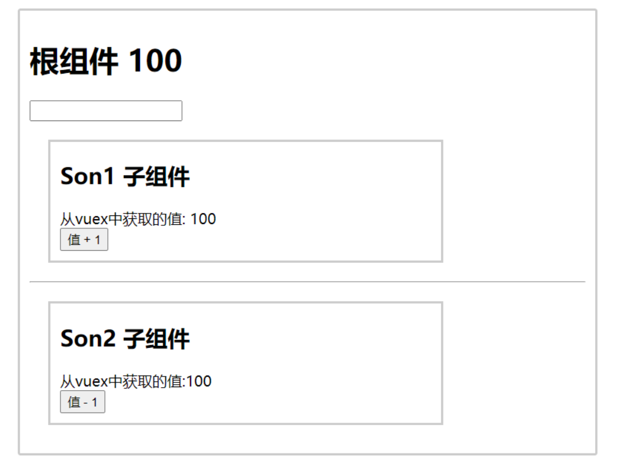
效果是三个组件共享一份数据:
- 任意一个组件都可以修改数据
- 三个组件的数据是同步的
1.创建项目
vue create vuex-demo2.创建三个组件, 目录如下
|-components
|--Son1.vue
|--Son2.vue
|-App.vue3.源代码如下
App.vue在入口组件中引入 Son1 和 Son2 这两个子组件
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件</h1>
<input type="text">
<Son1></Son1>
<hr>
<Son2></Son2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
data: function () {
return {
}
},
components: {
Son1,
Son2
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')Son1.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值: <label></label>
<br>
<button>值 + 1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son1Com'
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box{
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>Son2.vue
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值:<label></label>
<br />
<button>值 - 1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Son2Com'
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>vuex 的使用 - 创建仓库
1.安装 vuex
安装vuex与vue-router类似,vuex是一个独立存在的插件,如果脚手架初始化没有选 vuex,就需要额外安装。
yarn add vuex@3 或者 npm i vuex@32.新建 store/index.js 专门存放 vuex
为了维护项目目录的整洁,在src目录下新建一个store目录其下放置一个index.js文件。 (和 router/index.js 类似)
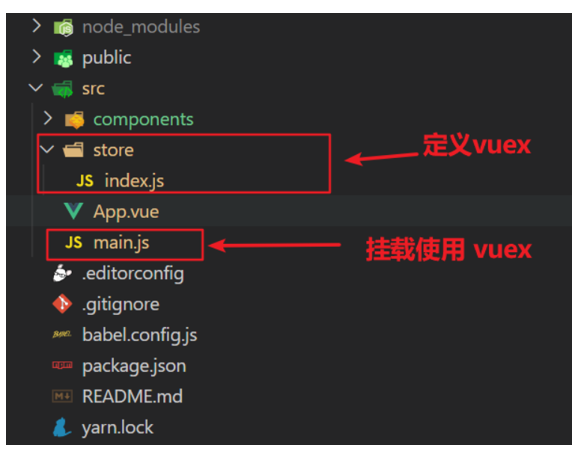
3.创建仓库 store/index.js
// 导入 vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 导入 vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// vuex也是vue的插件, 需要use一下, 进行插件的安装初始化
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库 store
const store = new Vuex.Store()
// 导出仓库
export default store4 在 main.js 中导入挂载到 Vue 实例上
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store/index'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')此刻起, 就成功创建了一个 空仓库!!
5.测试打印Vuex
App.vue
created(){
console.log(this.$store)
}核心概念 - state 状态
1.目标
明确如何给仓库 提供 数据,如何 使用 仓库的数据
2.提供数据
State提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到Store中的State中存储。
打开项目中的store文件夹里面的index.js文件,在state对象中可以添加我们要共享的数据。
// 创建仓库 store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// state 状态, 即数据, 类似于vue组件中的data,
// 区别:
// 1.data 是组件自己的数据,
// 2.state 中的数据整个vue项目的组件都能访问到
state: {
count: 101
}
})3.访问Vuex中的数据
问题: 如何在组件中获取count?
- 通过$store直接访问 —>
{{ $store.state.count }} - 通过辅助函数mapState 映射计算属性 —>
{{ count }}
4.通过$store访问的语法
获取 store:
1.Vue模板中获取 this.$store
2.js文件中获取 import 导入 store
模板中: {{ $store.state.xxx }}
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从vuex中获取的值: <label>{{ $store.state.count }}</label>
<br>
<button>值 + 1</button>
</div>
</template>
组件逻辑中: this.$store.state.xxx
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'app',
created () {
console.log(this.$store.state.count)
},
components: {
Son1,
Son2
}
}
</script>
JS模块中: store.state.xxx
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from '@/store/index'
console.log(store.state.count)
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')5.代码实现
5.1模板中使用
组件中可以使用 $store 获取到vuex中的store对象实例,可通过state属性属性获取count, 如下
<h1>state的数据 - {{ $store.state.count }}</h1>5.2组件逻辑中使用
将state属性定义在计算属性中 https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/state.html
<h1>state的数据 - {{ count }}</h1>
// 把state中数据,定义在组件内的计算属性中
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}5.3 js文件中使用
//main.js
import store from "@/store"
console.log(store.state.count)每次都像这样一个个的提供计算属性, 太麻烦了,我们有没有简单的语法帮我们获取state中的值呢?
通过辅助函数 - mapState获取 state中的数据
mapState是辅助函数,帮助我们把store中的数据映射到 组件的计算属性中, 它属于一种方便的用法
用法 :

1.第一步:导入mapState (mapState是vuex中的一个函数)
import { mapState } from 'vuex'2.第二步:采用数组形式引入state属性
mapState(['count'])上面代码的最终得到的是 类似于
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}3.第三步:利用展开运算符将导出的状态映射给计算属性
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
} <div> state的数据:{{ count }}</div>开启严格模式及Vuex的单项数据流
1.目标
明确 vuex 同样遵循单向数据流,组件中不能直接修改仓库的数据
2.直接在组件中修改Vuex中state的值
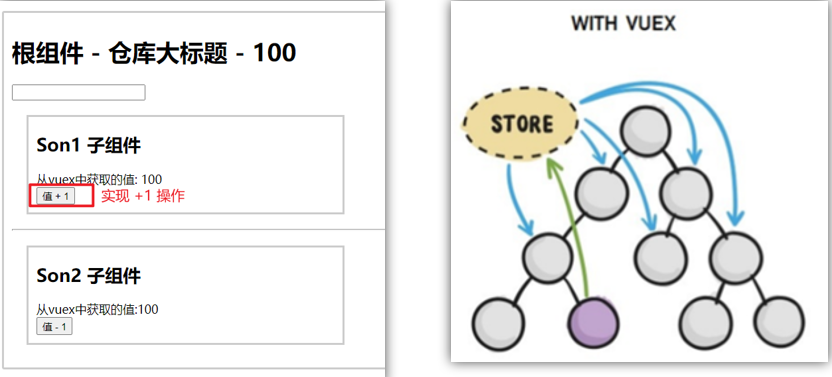
Son1.vue
button @click="handleAdd">值 + 1</button>
methods:{
handleAdd (n) {
// 错误代码(vue默认不会监测,监测需要成本)
this.$store.state.count++
// console.log(this.$store.state.count)
},
}3.开启严格模式
通过 strict: true 可以开启严格模式,开启严格模式后,直接修改state中的值会报错
有利于初学者,检测不规范的代码,但上线时需要关闭,避免消耗多余性能
state数据的修改只能通过mutations,并且mutations必须是同步的
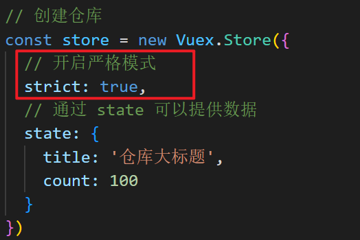
核心概念-mutations
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type)**和一个**回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数
1.定义mutations
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
// 定义mutations
mutations: {
}
})2.格式说明
mutations是一个对象,对象中存放修改state的方法
mutations: {
// 方法里参数 第一个参数是当前store的state属性
// payload 载荷 运输参数 调用mutaiions的时候 可以传递参数 传递载荷
addCount (state) {
state.count += 1
}
},3.组件中提交 mutations
this.$store.commit('addCount')4.练习
1.在mutations中定义个点击按钮进行 +5 的方法
2.在mutations中定义个点击按钮进行 改变title 的方法
3.在组件中调用mutations修改state中的值
5.总结
通过mutations修改state的步骤
1.定义 mutations 对象,对象中存放修改 state 的方法
2.组件中提交调用 mutations(通过$store.commit('mutations的方法名'))
带参数的 mutations
1.目标:
掌握 mutations 传参语法
2.语法
看下面这个案例,每次点击不同的按钮,加的值都不同,每次都要定义不同的mutations处理吗?

提交 mutation 是可以传递参数的 this.$store.commit('xxx', 参数)
2.1 提供mutation函数(带参数)
mutations: {
...
addCount (state, count) {
state.count = count
}
},2.2 提交mutation
handle ( ) {
this.$store.commit('addCount', 10)
}小tips: 提交的参数只能是一个, 如果有多个参数要传, 可以传递一个对象
this.$store.commit('addCount', {
count: 10
})练习-mutations的减法功能
1.步骤

2.代码实现
Son2.vue
<button @click="subCount(1)">值 - 1</button>
<button @click="subCount(5)">值 - 5</button>
<button @click="subCount(10)">值 - 10</button>
export default {
methods:{
subCount (n) {
this.$store.commit('subCount', n)
},
}
}store/index.js
mutations:{
subCount (state, n) {
state.count -= n
},
}练习-Vuex中的值和组件中的input双向绑定
1.目标
实时输入,实时更新,巩固 mutations 传参语法
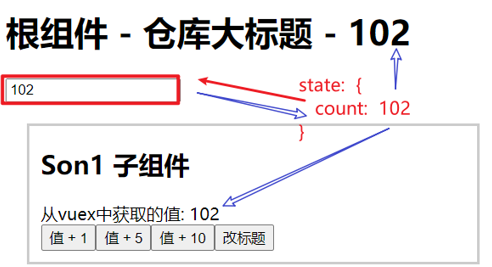
2.实现步骤
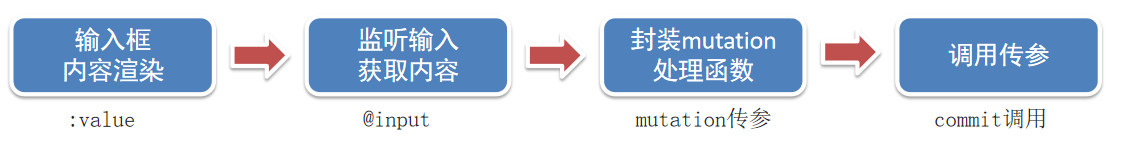
3.代码实现
App.vue
<input :value="count" @input="handleInput" type="text">
export default {
methods: {
handleInput (e) {
// 1. 实时获取输入框的值
const num = +e.target.value
// 2. 提交mutation,调用mutation函数
this.$store.commit('changeCount', num)
}
}
}store/index.js
mutations: {
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
},辅助函数- mapMutations
mapMutations和mapState很像,它把位于index.js的mutations中的方法提取了出来,我们可以将它导入
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapMutations(['addCount'])
}上面代码的含义是将mutations的方法导入了methods中,等价于
methods: {
// commit(方法名, 载荷参数)
addCount () {
this.$store.commit('addCount')
}
}此时,就可以直接通过this.addCount调用了
<button @click="addCount(荷载参数)">值+1</button>但是请注意: Vuex中mutations中要求不能写异步代码,如果有异步的ajax请求,应该放置在actions中
核心概念 - actions
state是存放数据的,mutations是同步更新数据 (便于监测数据的变化, 更新视图等, 方便于调试工具查看变化),
actions则负责进行异步操作
说明:mutations必须是同步的
需求: 一秒钟之后, 要给一个数 去修改state
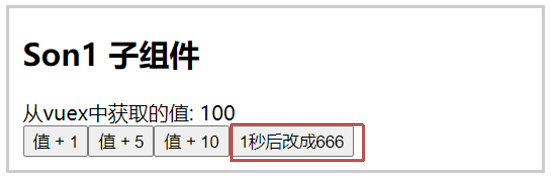
1.定义actions
index.js
mutations: {
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
}
// actions异步处理
// 注意: 不能直接操作 state, 操作 state还是需要 commit mutation方法
actions: {
// context 上下文 (此处未分模块,可以当成store仓库)
// 提交用:context.commit('mutation名字',额外参数)
changeCountAction (context, num) {
// 这里是setTimeout模拟异步,大部分场景是发请求
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
}2.组件中通过dispatch调用
handleChange () {
// 调用action
// this.$store.dispatch('action名字', 额外参数)
this.$store.dispatch('changeCountAction', 666)
}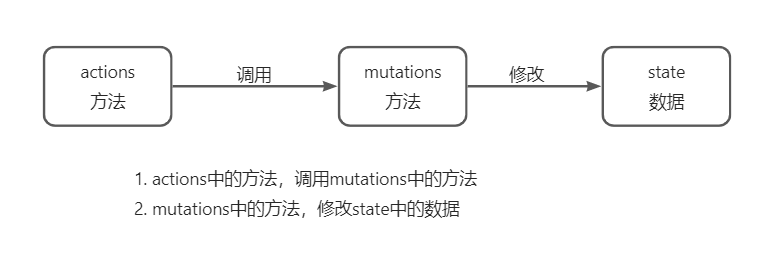
辅助函数 -mapActions
1.目标:掌握辅助函数 mapActions,映射方法
mapActions 是把位于 actions中的方法提取了出来,映射到组件methods中
Son2.vue
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods: {
...mapActions(['changeCountAction'])
}
//mapActions映射的代码 本质上是以下代码的写法
//methods: {
// changeCountAction (n) {
// this.$store.dispatch('changeCountAction', n)
// },
//}index.js
// 定义mutations
mutations: {
// 方法里参数 第一个参数是当前store的state属性
// payload 载荷 运输参数 调用mutaiions的时候 可以传递参数 传递载荷
addCount (state, count) {
state.count += count
},
subCount (state, n) {
state.count -= n
},
changeTitle (state, newTitle) {
state.title = newTitle
},
changeCount (state, newCount) {
state.count = newCount
}
},
// actions异步处理
// 注意: 不能直接操作 state, 操作 state还是需要 commit mutation方法
actions: {
// context 上下文 (此处未分模块,可以当成store仓库)
// 提交用:context.commit('mutation名字',额外参数)
changeCountAction (context, num) {
// 这里是setTimeout模拟异步,大部分场景是发请求
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCount', num)
}, 1000)
}
}直接通过 this.方法 就可以调用
<button @click="changeCountAction(200)">+异步</button>核心概念 - getters
除了state之外,有时我们还需要从state中筛选出符合条件的一些数据,这些数据是依赖state的,此时会用到getters
例如,state中定义了list,为1-10的数组,
state: {
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
}组件中,需要显示所有大于5的数据,正常的方式,是需要list在组件中进行再一步的处理,但是getters可以帮助我们实现它
1.定义getters
getters: {
// getters函数的第一个参数是 state
// 必须要有返回值,返回值就是getters的值
filterList (state) {
return state.list.filter(item => item > 5)
}
}2.使用getters
2.1原始方式-$store
<div>{{ $store.getters.filterList }}</div>2.2辅助函数 - mapGetters
computed: {
...mapGetters(['filterList'])
} <div>{{ filterList }}</div>使用某个模块的getters里的多个方法
computed: {
...mapGetters('模块名', ['filterList', '其他方法名'])
} <div>{{ filterList }}</div>
<div>{{ 其他方法名 }}</div>使用小结

核心概念 - module
1.目标
掌握核心概念 module 模块的创建
2.问题
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
这句话的意思是,如果把所有的状态都放在state中,当项目变得越来越大的时候,Vuex会变得越来越难以维护
由此,又有了Vuex的模块化
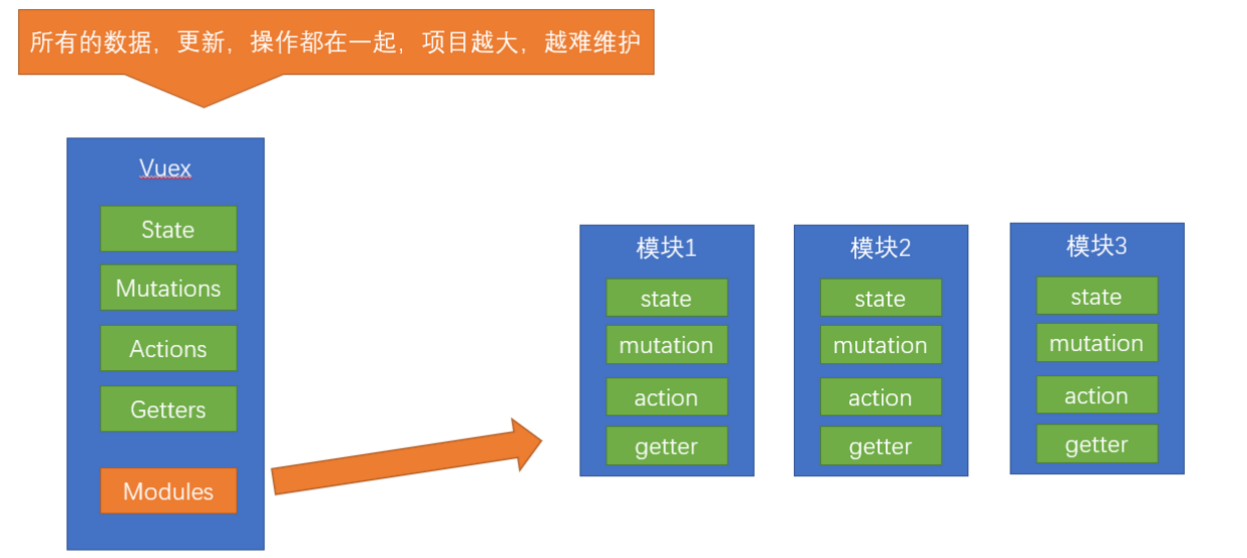
3.模块定义 - 准备 state
定义两个模块 user 和 setting
user中管理用户的信息状态 userInfo modules/user.js
const state = {
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18
}
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}setting中管理项目应用的 主题色 theme,描述 desc, modules/setting.js
const state = {
theme: 'dark'
desc: '描述真呀真不错'
}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}在store/index.js文件中的modules配置项中,注册这两个模块
import user from './modules/user'
import setting from './modules/setting'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
user,
setting
}
})获取模块内的state数据
1.目标:
掌握模块中 state 的访问语法
尽管已经分模块了,但其实子模块的状态,还是会挂到根级别的 state 中,属性名就是模块名
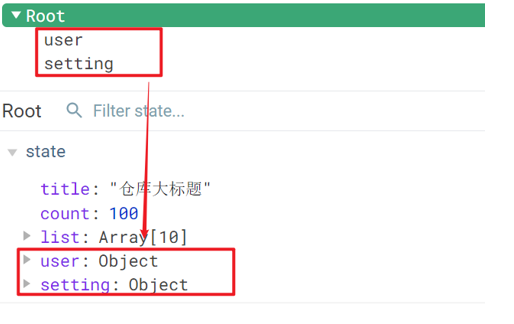
2.使用模块中的数据
- 直接通过模块名访问 $store.state.模块名.xxx
- 通过 mapState 映射:
- 默认根级别的映射 mapState([ 'xxx' ])
- 子模块的映射 :mapState('模块名', ['xxx']) - 需要开启命名空间 namespaced:true
modules/user.js
const state = {
userInfo: {
name: 'zs',
age: 18
},
myMsg: '我的数据'
}
const mutations = {
updateMsg (state, msg) {
state.myMsg = msg
}
}
const actions = {}
const getters = {}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}3.代码示例
访问方式
1.$store直接访问
$store.state.user.userInfo.name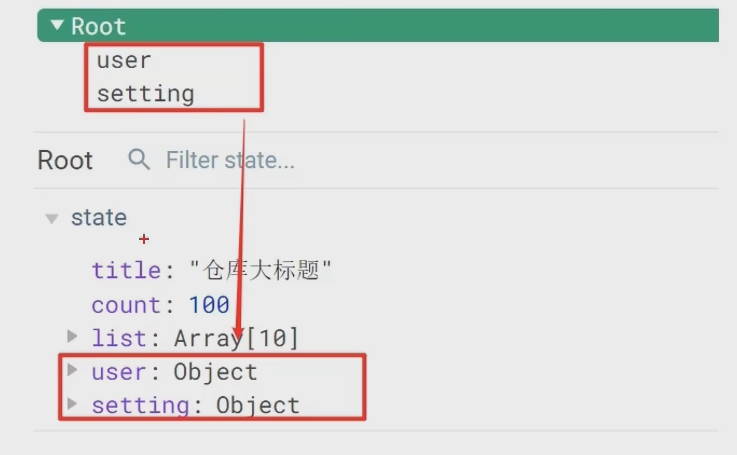
2.mapState辅助函数访问 --需开启命名空间
...mapState('user', ['userInfo']),
...mapState('setting', ['theme', 'desc']),获取模块内的getters数据
1.目标:
掌握模块中 getters 的访问语
2.语法:
使用模块中 getters 中的数据:
- 直接通过模块名访问
$store.getters['模块名/xxx '] - 通过 mapGetters 映射
- 默认根级别的映射
mapGetters([ 'xxx' ]) - 子模块的映射
mapGetters('模块名', ['xxx'])- 需要开启命名空间
- 默认根级别的映射
3.代码演示
modules/user.js
const getters = {
// 分模块后,state指代子模块的state
UpperCaseName (state) {
return state.userInfo.name.toUpperCase()
}
}Son1.vue 直接访问getters
<!-- 测试访问模块中的getters - 原生 -->
<div>{{ $store.getters['user/UpperCaseName'] }}</div>Son2.vue 通过命名空间访问
// 导入辅助函数mapGetters
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed:{
// user:模块名
// UpperCaseName: getters里对应的方法
...mapGetters('user', ['UpperCaseName'])
}获取模块内的mutations方法
1.目标:
掌握模块中 mutation 的调用语法
2.注意:
默认模块中的 mutation 和 actions 会被挂载到全局,需要开启命名空间,才会挂载到子模块。
3.调用方式:
- 直接通过 store 调用 $store.commit('模块名/xxx ', 额外参数)
- 通过 mapMutations 映射
- 默认根级别的映射 mapMutations([ 'xxx' ])
- 子模块的映射 mapMutations('模块名', ['xxx']) - 需要开启命名空间
4.代码实现
modules/user.js
const mutations = {
setUser (state, newUserInfo) {
state.userInfo = newUserInfo
}
}modules/setting.js
const mutations = {
setTheme (state, newTheme) {
state.theme = newTheme
}
}Son1.vue
<button @click="updateUser">更新个人信息</button>
<button @click="updateTheme">更新主题色</button>
export default {
methods: {
updateUser () {
// $store.commit('模块名/mutation名', 额外传参)
this.$store.commit('user/setUser', {
name: 'xiaowang',
age: 25
})
},
updateTheme () {
this.$store.commit('setting/setTheme', 'pink')
}
}
}Son2.vue
<button @click="setUser({ name: 'xiaoli', age: 80 })">更新个人信息</button>
<button @click="setTheme('skyblue')">更新主题</button>
methods:{
// 分模块的映射
...mapMutations('setting', ['setTheme']),
...mapMutations('user', ['setUser']),
}获取模块内的actions方法
1.目标:
掌握模块中 action 的调用语法 (同理 - 直接类比 mutation 即可)
2.注意:
默认模块中的 mutation 和 actions 会被挂载到全局,需要开启命名空间,才会挂载到子模块。
3.调用语法:
- 直接通过 store 调用 $store.dispatch('模块名/xxx ', 额外参数)
- 通过 mapActions 映射
- 默认根级别的映射 mapActions([ 'xxx' ])
- 子模块的映射 mapActions('模块名', ['xxx']) - 需要开启命名空间
4.代码实现
需求:

modules/user.js
const actions = {
setUserSecond (context, newUserInfo) {
// 将异步在action中进行封装
setTimeout(() => {
// 调用mutation context上下文,默认提交的就是自己模块的action和mutation
context.commit('setUser', newUserInfo)
}, 1000)
}
}Son1.vue 直接通过store调用
<button @click="updateUser2">一秒后更新信息</button>
methods:{
updateUser2 () {
// 调用action dispatch
this.$store.dispatch('user/setUserSecond', {
name: 'xiaohong',
age: 28
})
},
}Son2.vue mapActions映射
<button @click="setUserSecond({ name: 'xiaoli', age: 80 })">一秒后更新信息</button>
methods:{
...mapActions('user', ['setUserSecond'])
}Vuex模块化的使用小结
1.直接使用
- state --> $store.state.模块名.数据项名
- getters --> $store.getters['模块名/属性名']
- mutations --> $store.commit('模块名/方法名', 其他参数)
- actions --> $store.dispatch('模块名/方法名', 其他参数)
2.借助辅助方法使用
1.import { mapXxxx, mapXxx } from 'vuex'
computed、methods: {
// ...mapState、...mapGetters放computed中;
// ...mapMutations、...mapActions放methods中;
...mapXxxx('模块名', ['数据项|方法']),
...mapXxxx('模块名', { 新的名字: 原来的名字 }),
}
2.组件中直接使用 属性 {{ age }} 或 方法 @click="updateAge(2)"
综合案例 - 创建项目
脚手架新建项目 (注意:勾选vuex)
版本说明:
vue2 vue-router3 vuex3
vue3 vue-router4 vuex4/pinia
vue create vue-cart-demo- 将原本src内容清空,替换成教学资料的《vuex-cart-准备代码》
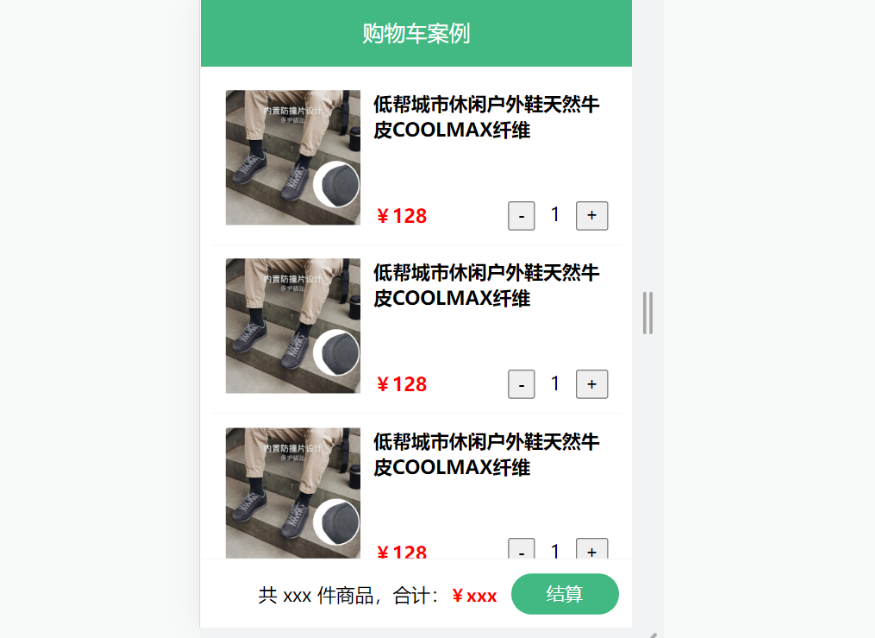
需求:
- 发请求动态渲染购物车,数据存vuex (存cart模块, 将来还会有user模块,article模块...)
- 数字框可以修改数据
- 动态计算总价和总数量
综合案例-构建vuex-cart模块
- 新建
store/modules/cart.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
state () {
return {
list: []
}
},
}- 挂载到 vuex 仓库上
store/cart.js
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import Vue from 'vue'
import cart from './modules/cart'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart
}
})
export default store综合案例-准备后端接口服务环境(了解)
- 安装全局工具 json-server (全局工具仅需要安装一次)
yarn global add json-server 或 npm i json-server -g- 代码根目录新建一个 db 目录
- 将资料 index.json 移入 db 目录
- 进入 db 目录,执行命令,启动后端接口服务 (使用--watch 参数 可以实时监听 json 文件的修改)
json-server --watch index.json综合案例-请求动态渲染数据
1.目标
请求获取数据存入 vuex, 映射渲染

- 安装 axios
yarn add axios- 准备actions 和 mutations
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
namespaced: true,
state () {
return {
list: []
}
},
mutations: {
updateList (state, payload) {
state.list = payload
}
},
actions: {
async getList (ctx) {
// 请求方式:get
// 请求地址:http://localhost:3000/cart
// 2.将数据异步存进List里面
const res = await axios.get('http://localhost:3000/cart')
ctx.commit('updateList', res.data)
}
}
}App.vue页面中调用 action, 获取数据
// 3.通过mapState辅助函数获取state中的数据
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
CartHeader,
CartFooter,
CartItem
},
created () {
// 1.调用请求将结果传给cart仓库的getList方法
this.$store.dispatch('cart/getList')
},
computed: {
// 4.寻找cart模块下的list
...mapState('cart', ['list'])
}
}- 动态渲染
<!-- 商品 Item 项组件 -->
// :item="item" 把整个对象传进去供他渲染
<cart-item v-for="item in list" :key="item.id" :item="item"></cart-item>cart-item.vue
<template>
<div class="goods-container">
<!-- 左侧图片区域 -->
<div class="left">
<img :src="item.thumb" class="avatar" alt="">
</div>
<!-- 右侧商品区域 -->
<div class="right">
<!-- 标题 -->
<div class="title">{{item.name}}</div>
<div class="info">
<!-- 单价 -->
<span class="price">¥{{item.price}}</span>
<div class="btns">
<!-- 按钮区域 -->
<button class="btn btn-light">-</button>
<span class="count">{{item.count}}</span>
<button class="btn btn-light">+</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'CartItem',
props: {
item: Object
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>综合案例-修改数量
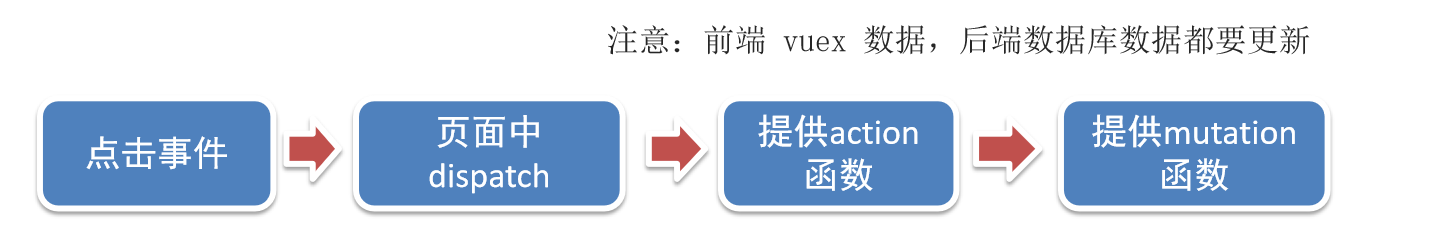
- 注册点击事件
<!-- 按钮区域 -->
<button class="btn btn-light" @click="onBtnClick(-1)">-</button>
<span class="count">{{item.count}}</span>
<button class="btn btn-light" @click="onBtnClick(1)">+</button>- 页面中dispatch action
btnClick (step) {
const newCount = this.item.count + step
const id = this.item.id
// 设置数量不可小于1
if (newCount < 1) return
this.$store.dispatch('cart/updateCountAsync', {
id,
newCount
})
}- 提供action函数
// 请求方式: patch
// 请求地址: http://localhost:3000/cart/:id值
// 请求参数
// name
// price
// count
// thumb
async updateCountAsync (context, obj) {
const res = await axios.patch(`http://localhost:3000/cart/${obj.id}`, {
count: obj.newCount
})
console.log(res)
context.commit('updateCount', {
id: obj.id,
newCount: obj.newCount
})
}- 提供mutation处理函数
mutations: {
...,
updateCount (state, obj) {
console.log(obj)
// 根据id找到对应的对象,更新count属性即可
const goods = state.list.find(item => item.id === obj.id)
goods.count = obj.newCount
}
},综合案例-底部总价展示
- 提供getters
getters: {
// 商品总数量 累加count
total (state) {
return state.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.count, 0)
},
// 商品总价格 累加count * price
totalPrice (state) {
return state.list.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.count * item.price, 0)
}
}- 动态渲染
<template>
<div class="footer-container">
<!-- 中间的合计 -->
<div>
<span>共 {{total}} 件商品,合计:</span>
<span class="price">¥{{totalPrice}}</span>
</div>
<!-- 右侧结算按钮 -->
<button class="btn btn-success btn-settle">结算</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'CartFooter',
computed: {
// cart: 对应模块名
// total,totalPrice 对应的方法
...mapGetters('cart', ['total', 'totalPrice'])
}
}
</script>http://localhost:8086/test-admin/login?redirect=%2F
Vue3
1. Vue2 选项式 API vs Vue3 组合式API
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
count:0
}
},
methods:{
addCount(){
this.count++
}
}
}
</script><script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
const addCount = ()=> count.value++
</script>特点:
- 代码量变少
- 分散式维护变成集中式维护
2. Vue3的优势
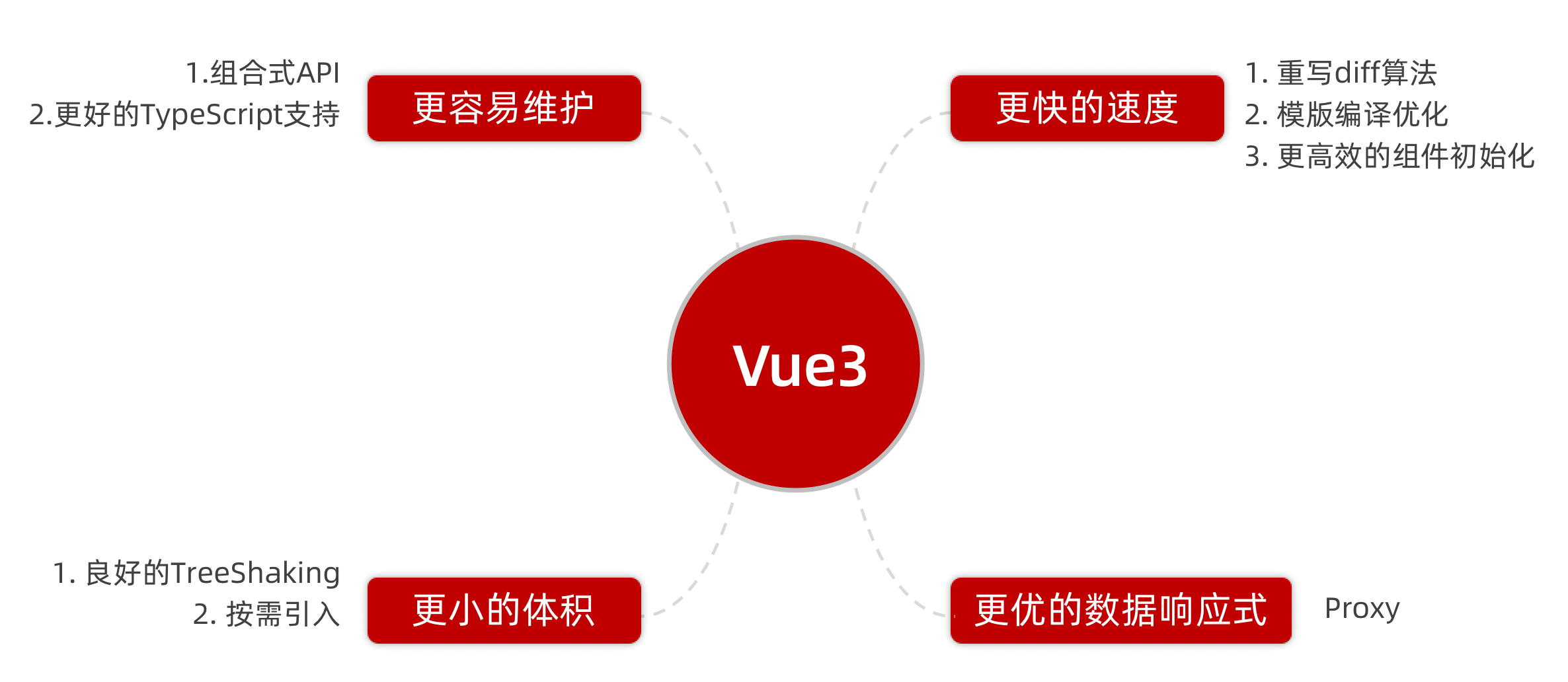
使用create-vue搭建Vue3项目
1. 认识create-vue
create-vue是Vue官方新的脚手架工具,底层切换到了 vite (下一代前端工具链),为开发提供极速响应
2. 使用create-vue创建项目
前置条件 - 已安装16.0或更高版本的Node.js
一些常见的命令
#查看nvm版本
nvm -v
# 查看node版本
node -v
# 查看npm版本
npm -v
#查看已经安装的版本
nvm list
# v10.6.0指版本号
nvm install v10.6.0
# 指定使用该版本的Nodejs
nvm use v10.6.0
#查看指定使用该版本的Nodejs
nvm on v10.6.0
# 禁用node.js版本管理(不卸载任何东西)
nvm off
# 启用node.js版本管理
nvm on
# 卸载node.js是的命令,卸载指定版本的nodejs,当安装失败时卸载使用
nvm uninstall <version>
# 显示可以安装的所有node.js的版本
nvm list available执行如下命令,这一指令将会安装并执行 create-vue
npm init vue@latest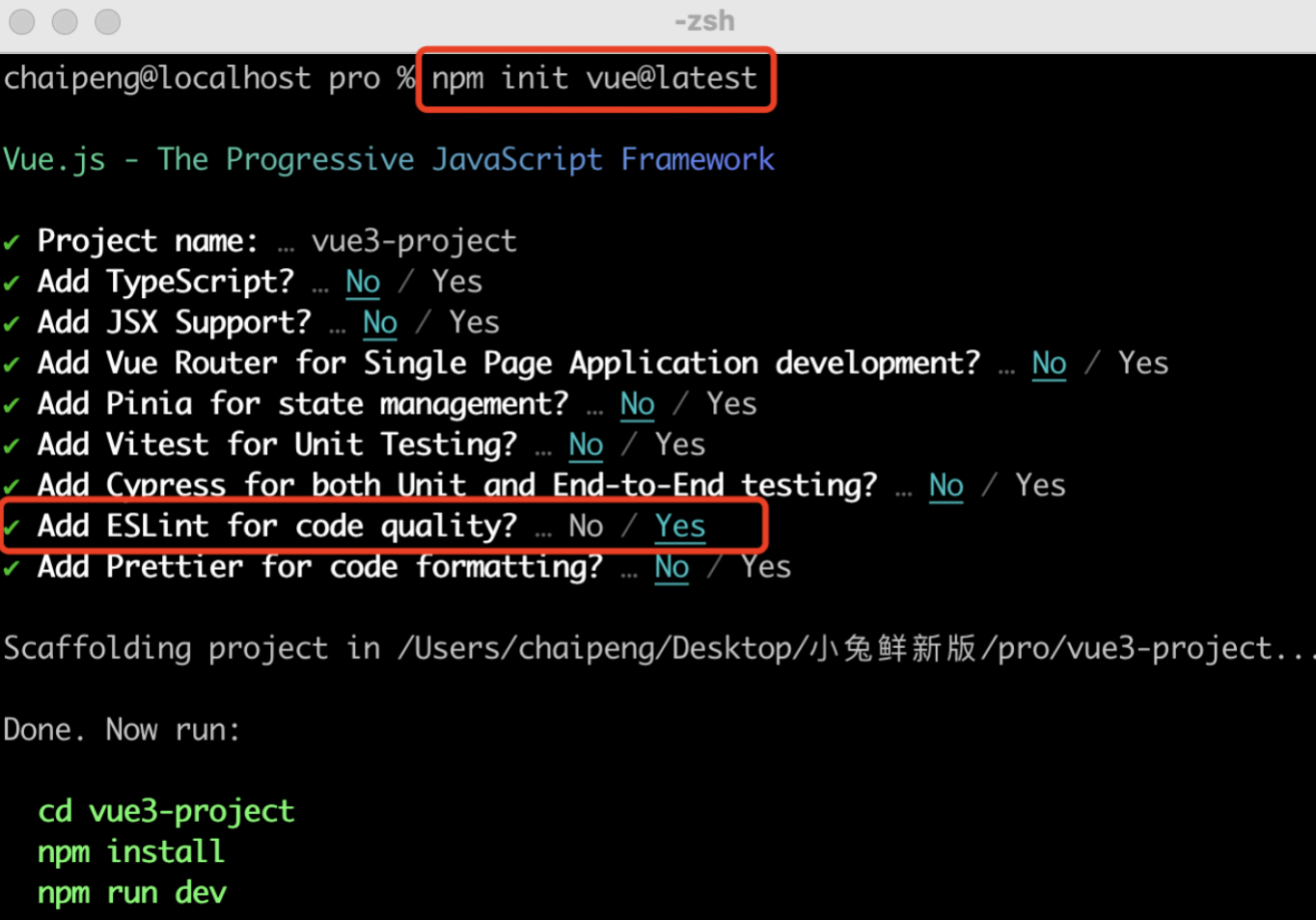
熟悉项目和关键文件

组合式API - setup选项
1. setup选项的写法和执行时机
写法
<script>
export default {
setup(){
},
beforeCreate(){
}
}
</script>执行时机
在beforeCreate钩子之前执行
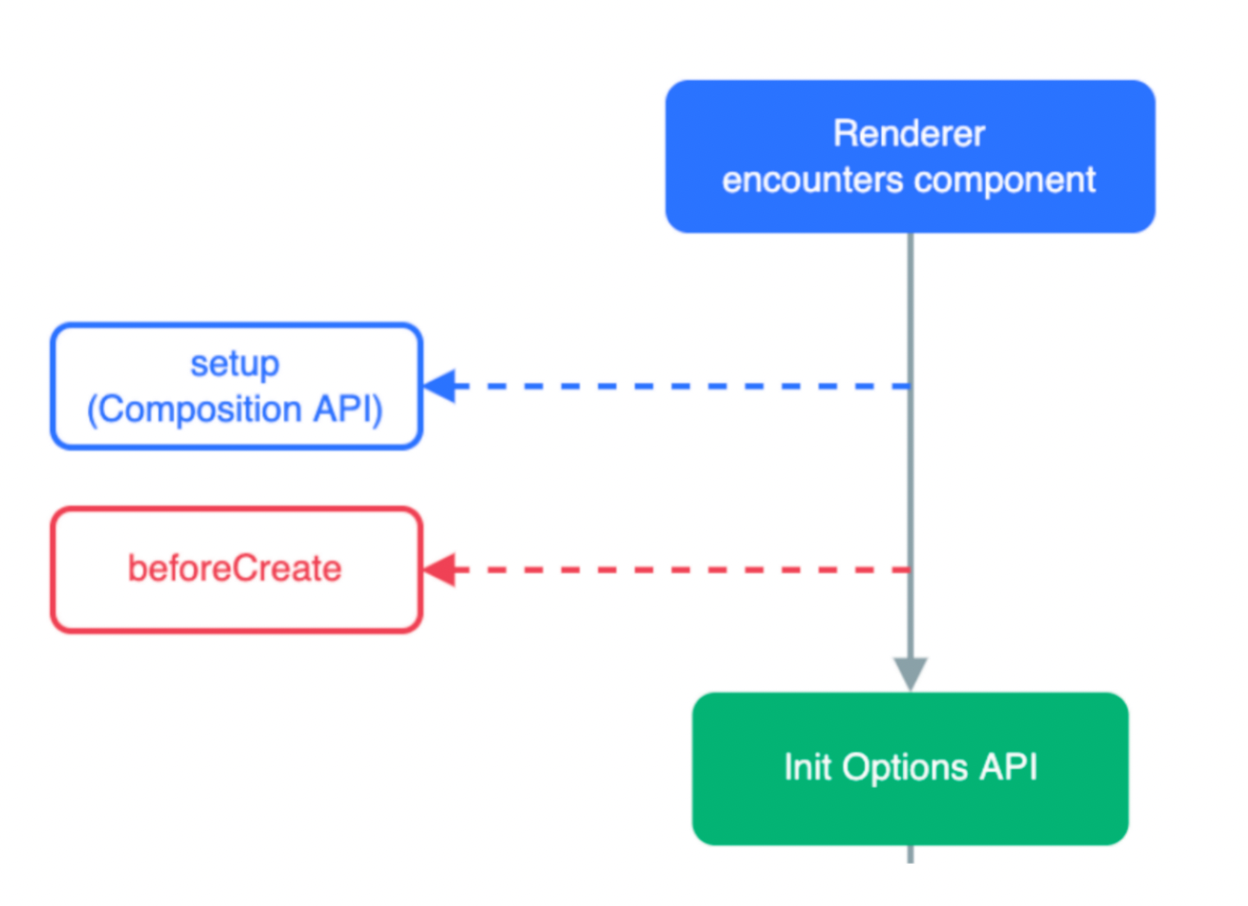
2. setup中写代码的特点
在setup函数中写的数据和方法需要在末尾以对象的方式return,才能给模版使用
<script>
export default {
setup(){
const message = 'this is message'
const logMessage = ()=>{
console.log(message)
}
// 必须return才可以
return {
message,
logMessage
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
{{ message }}
</div>
<button @click="logMessage">
按钮
</button>
</template>3. <script setup>语法糖
script标签添加 setup标记,不需要再写导出语句,默认会添加导出语句
<script setup>
const message = 'this is message'
const logMessage = ()=>{
console.log(message)
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
{{ message }}
</div>
<button @click="logMessage">
按钮
</button>
</template>组合式API - reactive和ref函数
1. reactive
接受对象类型数据的参数传入并返回一个响应式的对象
<script setup>
// 导入
import { reactive } from 'vue'
// 执行函数 传入参数 变量接收
const state = reactive({
msg:'this is msg'
})
const setSate = ()=>{
// 修改数据更新视图
state.msg = 'this is new msg'
}
</script>
<template>
{{ state.msg }}
<button @click="setState">change msg</button>
</template>2. ref
接收简单类型或者对象类型的数据传入并返回一个响应式的对象
<script setup>
// 导入
import { ref } from 'vue'
// 执行函数 传入参数 变量接收
const count = ref(0)
const setCount = ()=>{
// 在脚本(script)中,修改数据更新视图必须加上.value
count.value++
}
</script>
<template>
// template(模板)中,帮我们扒了一层,不用加.value
<button @click="setCount">{{count}}</button>
</template>3. reactive 对比 ref
- 都是用来生成响应式数据
- 不同点
- reactive不能处理简单类型的数据
- ref参数类型支持更好,但是必须通过.value做访问修改
- ref函数内部的实现依赖于reactive函数
- 在实际工作中的推荐
- 推荐使用ref函数,减少记忆负担,小兔鲜项目都使用ref
组合式API - computed
计算属性基本思想和Vue2保持一致,组合式API下的计算属性只是修改了API写法
从list中过滤出大于二的数据

<script setup>
// 导入
import {ref, computed } from 'vue'
// 原始数据
const count = ref(0)
// 计算属性
const doubleCount = computed(()=>count.value * 2)
// 原始数据
const list = ref([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8])
// 计算属性list
const filterList = computed(() => {
return list.value.filter(item => item > 2)
})
</script>
<template>
<div>原始数据: {{ list }}</div>
<div>计算后的数据: {{ filterList }}</div>
</template>组合式API - watch
侦听一个或者多个数据的变化,数据变化时执行回调函数,俩个额外参数 immediate控制立刻执行,deep开启深度侦听
1. 侦听单个数据
<script setup>
// 1. 导入watch
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
// 2. 调用watch 侦听对象变化
watch(count, (newValue, oldValue)=>{
console.log(`count发生了变化,老值为${oldValue},新值为${newValue}`)
})
</script>2. 侦听多个数据
侦听多个数据,第一个参数可以改写成数组的写法
<script setup>
// 1. 导入watch
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
const name = ref('cp')
// 2. 调用watch 侦听对象变化
watch([count, name], ([newCount, newName],[oldCount,oldName])=>{
console.log(`count或者name变化了,[newCount, newName],[oldCount,oldName])
})
</script>3. immediate
在侦听器创建时立即出发回调,响应式数据变化之后继续执行回调
<script setup>
// 1. 导入watch
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
// 2. 调用watch 侦听变化
watch(count, (newValue, oldValue)=>{
console.log(`count发生了变化,老值为${oldValue},新值为${newValue}`)
},{
immediate: true
})
</script>4. deep
通过watch监听的ref对象默认是浅层侦听的,直接修改嵌套的对象属性不会触发回调执行,需要开启deep
<script setup>
// 1. 导入watch
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const state = ref({ count: 0 })
// 2. 监听对象state
watch(state, ()=>{
console.log('数据变化了')
})
const changeStateByCount = ()=>{
// 直接修改不会引发回调执行
state.value.count++
}
</script>
<script setup>
// 1. 导入watch
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const state = ref({ count: 0 })
// 2. 监听对象state 并开启deep
watch(state, ()=>{
console.log('数据变化了')
},{deep:true})
const changeStateByCount = ()=>{
// 此时修改可以触发回调
state.value.count++
}
</script>合并写法
watch([count, name], ([newCount, newName],[oldCount,oldName])=>{
console.log(`count或者name变化了,[newCount, newName],[oldCount,oldName])
},{
immediate: true,
deep:true
})5. 精确侦听某个对象
<script setup>
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'
const userInfo = ref({
name: 'zs',
age: 18
})
const setUserInfo = () => {
// 修改了 userInfo.value 修改了对象的地址,才能监视到
// userInfo.value = { name: 'ls', age: 50 }
userInfo.value.age++
}
// 5. 对于对象中的单个属性,进行监视
watch(() => userInfo.value.age, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
})
</script>
<template>
<button @click="setUserInfo">修改userInfo</button>
</template>组合式API - 生命周期函数
1. 选项式对比组合式
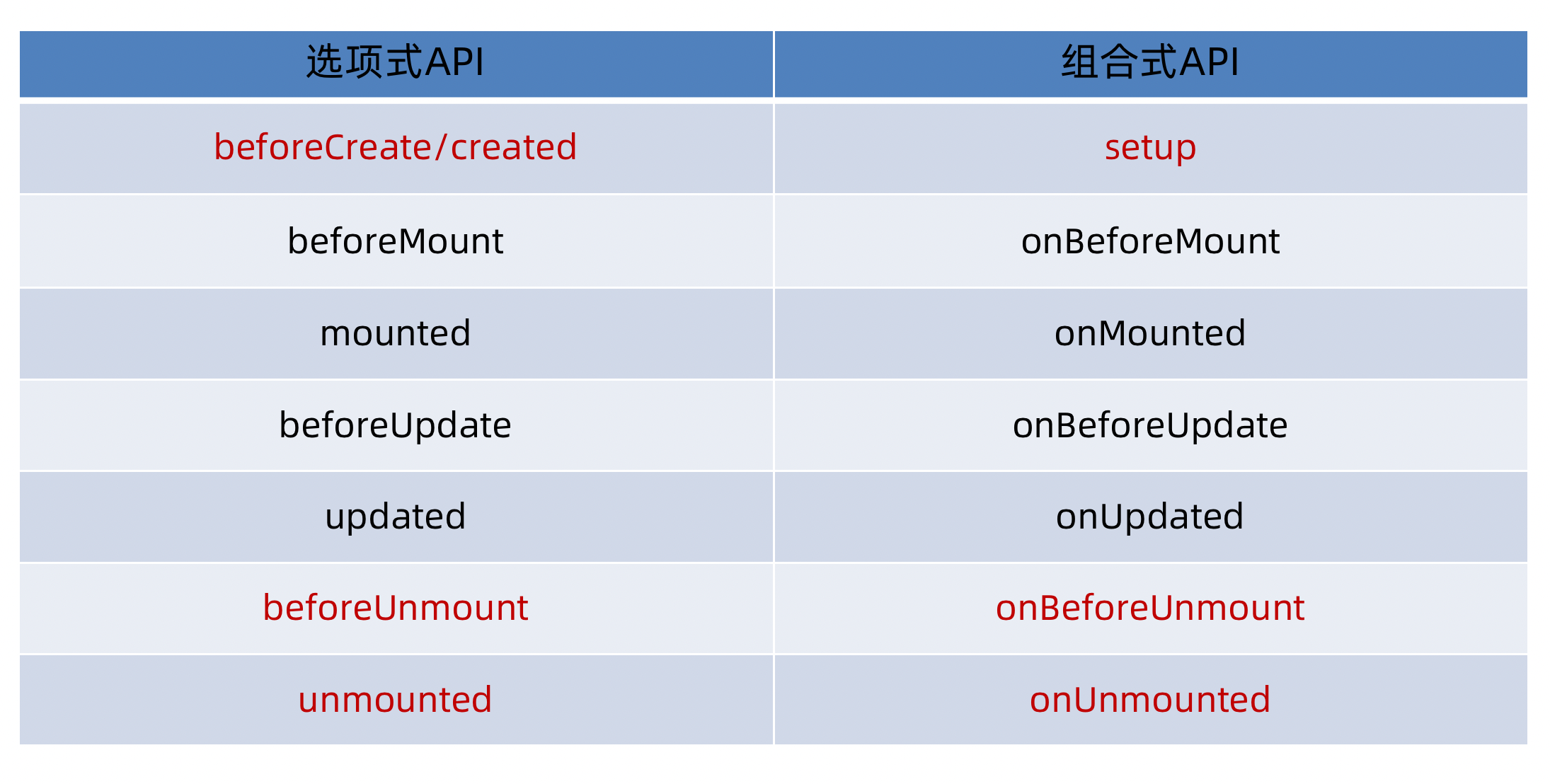
2. 生命周期函数基本使用
- 导入生命周期函数
- 执行生命周期函数,传入回调
<scirpt setup>
import { onMounted } from 'vue';
// beforeCreate 和 created 的相关代码
// 一律放在 setup中执行
const getList = () => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('发送请求,获取数据')
}, 2000 )
}
// 一进页面的请求
getList()
// 如果有些代码需要在mounted的生命周期中执行
onMounted(() => {
console.log('mounted生命周期函数 - 逻辑一')
})
</script>3. 执行多次
生命周期函数执行多次的时候,会按照顺序依次执行
<scirpt setup>
import { onMounted } from 'vue';
// beforeCreate 和 created 的相关代码
// 一律放在 setup中执行
const getList = () => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('发送请求,获取数据')
}, 200)
}
// 一进页面的请求
getList()
// 如果有些代码需要在mounted的生命周期中执行
onMounted(() => {
console.log('mounted生命周期函数 - 逻辑一')
})
// 写成函数的调用方式,可以调用多次,并不会冲突,而是按照顺序依次执行
onMounted(() => {
console.log('mounted生命周期函数 - 逻辑二')
})
</script>组合式API - 父子通信
1. 父传子
基本思想
- 父组件中给子组件绑定属性
- 子组件内部通过props选项接收数据
如果父传子的数据是动态控制的,那么子组件获得的数据也是响应式更新的
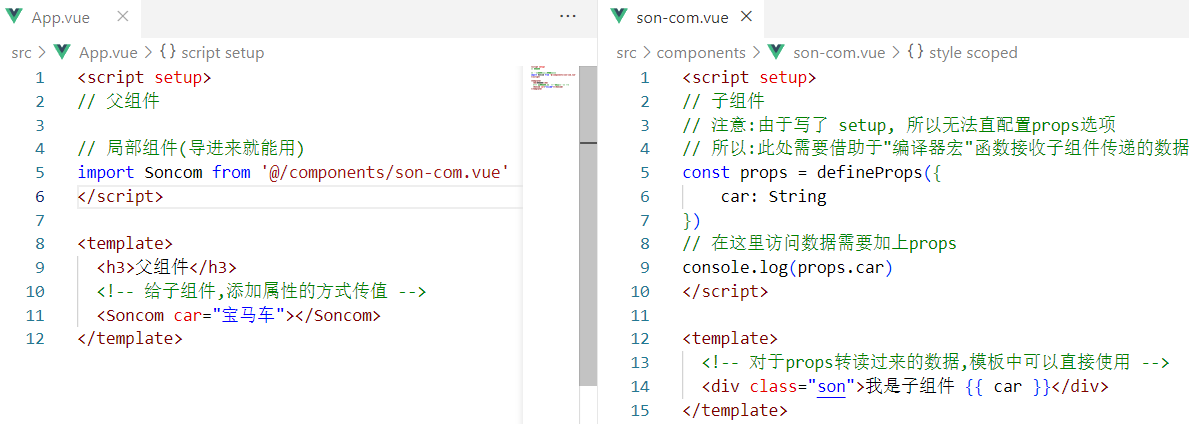
如果父传子的数据是动态控制的,那么子组件获得的数据也是响应式更新的
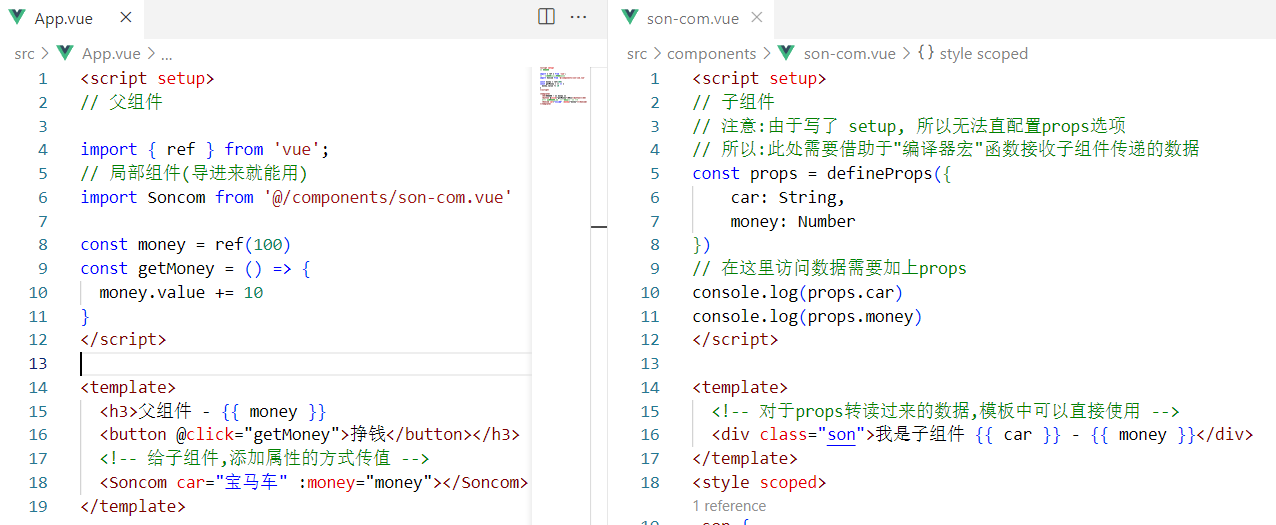
2. 子传父
基本思想
- 父组件中给子组件标签通过@绑定事件
- 子组件内部通过 emit 方法触发事件
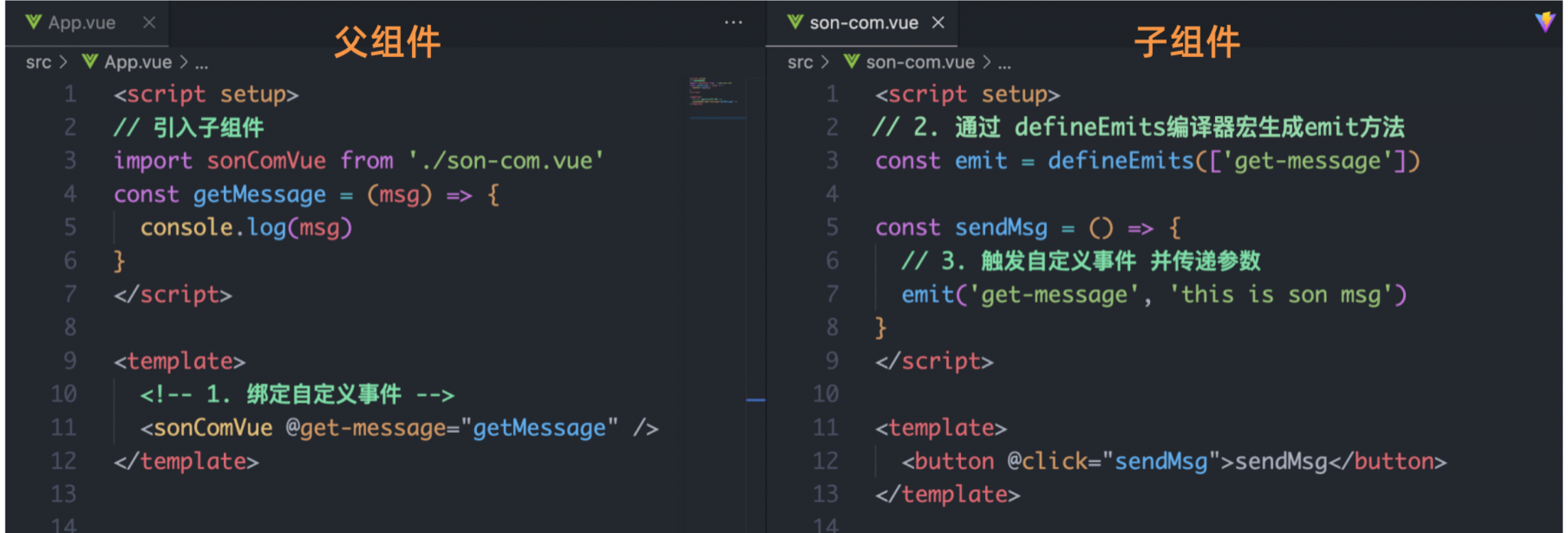
组合式API - 模版引用
概念:通过 ref标识 获取真实的 dom对象或者组件实例对象
1. 基本使用
实现步骤:
- 调用ref函数生成一个ref对象
- 通过ref标识绑定ref对象到标签
<script setup>
import { onMounted, ref } from 'vue';
// 模板引用(可以获取dom元素,也可以获取组件)
// 1.调用ref函数,生成一个ref对象
const inp = ref(null)
// 生命周期钩子 onMounted
onMounted(() => {
// 使引用对象聚焦
// console.log(inp.value);
// 3.通过ref对象.value即可访问到绑定的元素(必须渲染完成后才能拿到)
// inp.value.focus()
})
const clickFn = () => {
// 3.通过ref对象.value即可访问到绑定的元素(必须渲染完成后才能拿到)
inp.value.focus()
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<!-- 2.通过ref标识,进行绑定 -->
<input ref="inp" type="text">
<button @click="clickFn">让点击框聚焦</button>
</div>
</template>2. defineExpose
默认情况下在
<script setup>语法糖下组件内部的属性和方法是不开放给父组件访问的,可以通过defineExpose编译宏指定哪些属性和方法容许访问 说明:指定testMessage属性可以被访问到
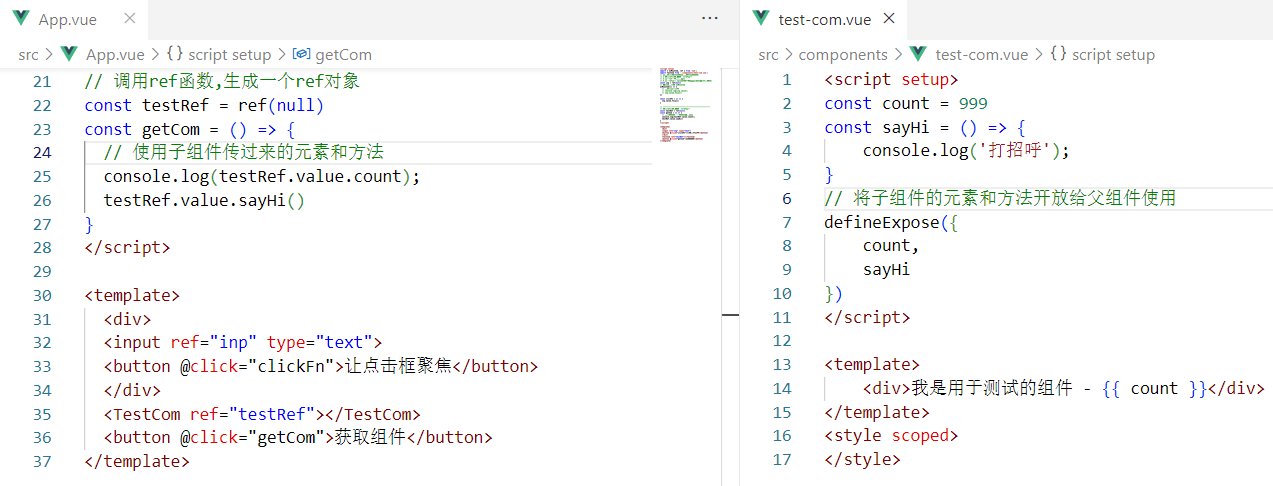
组合式API - provide和inject
1. 作用和场景
顶层组件向任意的底层组件传递数据和方法,实现跨层组件通信
2. 跨层传递普通数据
实现步骤
- 顶层组件通过
provide函数提供数据- 底层组件通过
inject函数提供数据
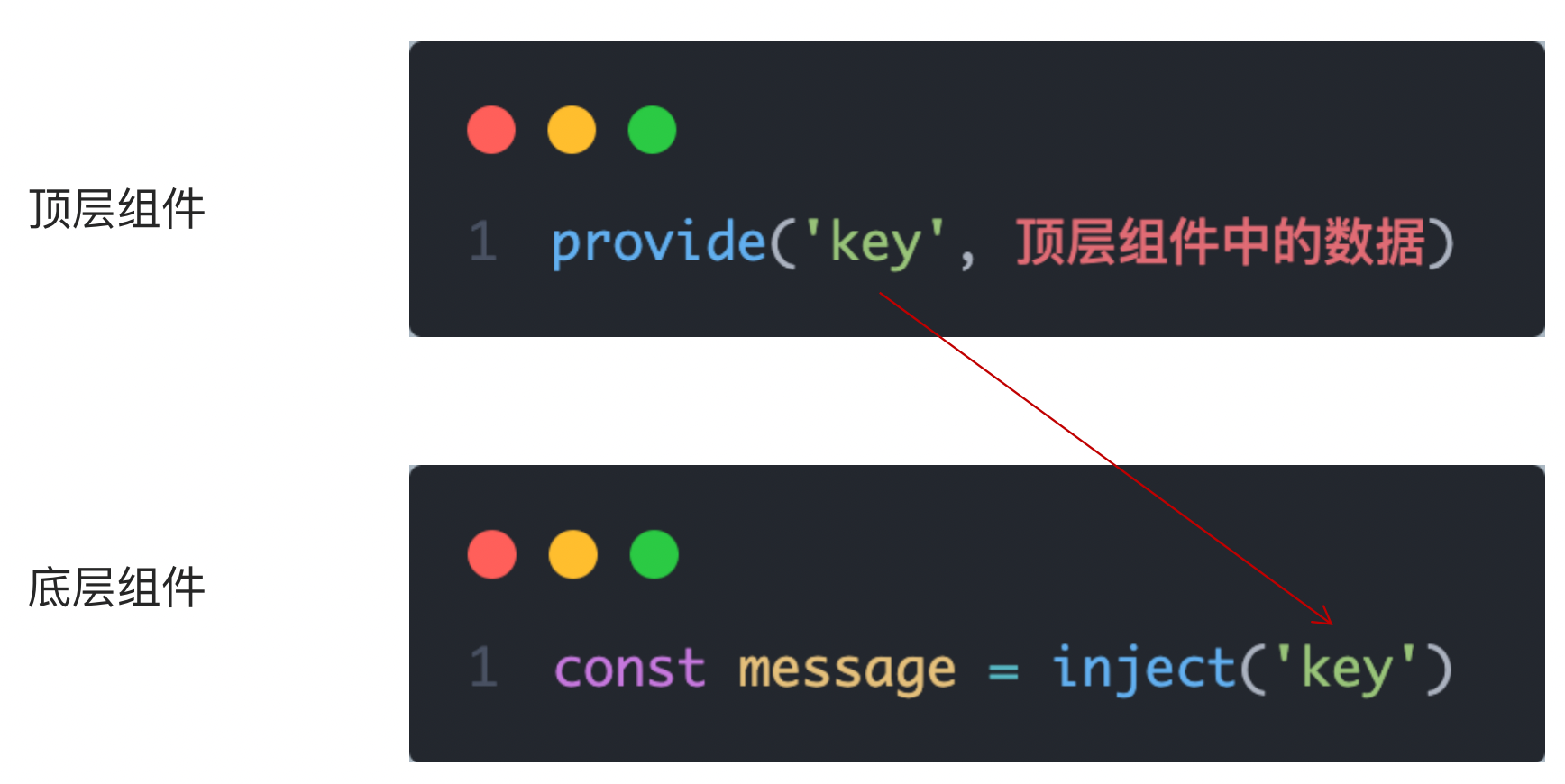
3. 跨层传递响应式数据
在调用provide函数时,第二个参数设置为ref对象

4. 跨层传递方法
顶层组件可以向底层组件传递方法,底层组件调用方法修改顶层组件的数据

然后底层组件调用setCount方法即可,括号里面也可传值
const changeCount = () => {
setCount()
}Vue3.3新特性-defineModel
在Vue3中,自定义组件上使用v-model, 相当于传递一个modelValue属性,同时触发 update:modelValue 事件
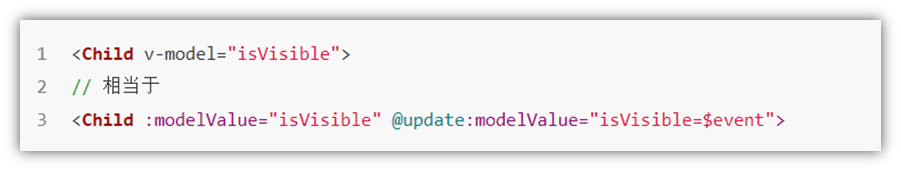
我们需要先定义 props,再定义 emits 。其中有许多重复的代码。如果需要修改此值,还需要手动调用 emit 函数。
于是乎 defineModel 诞生了。
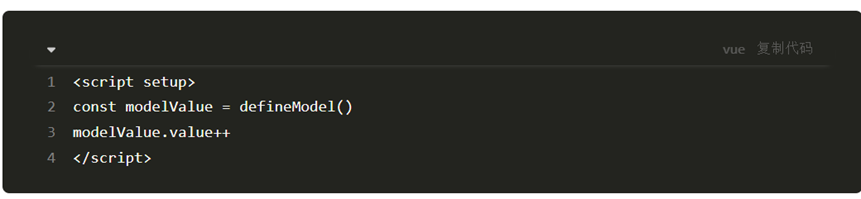
生效需要配置 vite.config.js然后重启应用
import { fileURLToPath, URL } from 'node:url'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
vue({
script: {
// 修改这里
defineModel: true
}
}),
],
resolve: {
alias: {
'@': fileURLToPath(new URL('./src', import.meta.url))
}
}
})Vue3 状态管理 - Pinia
1. 什么是Pinia
Pinia 是 Vue 的专属的最新状态管理库 ,是 Vuex 状态管理工具的替代品 
2. 手动添加Pinia到Vue项目
后面在实际开发项目的时候,Pinia可以在项目创建时自动添加,现在我们初次学习,从零开始:
- 使用 Vite 创建一个空的 Vue3项目
npm init vite@latest- 按照官方文档安装 pinia 到项目中
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
const pinia = createPinia() // 创建Pinia实例
// createApp(App).use(pinia).mount('#app') //支持链式
const app = createApp(App) // 创建根实例
app.use(pinia) // pinia插件的安装配置
app.mount('#app') // 视图的挂载3. Pinia基础使用
- 定义store
- 组件使用store
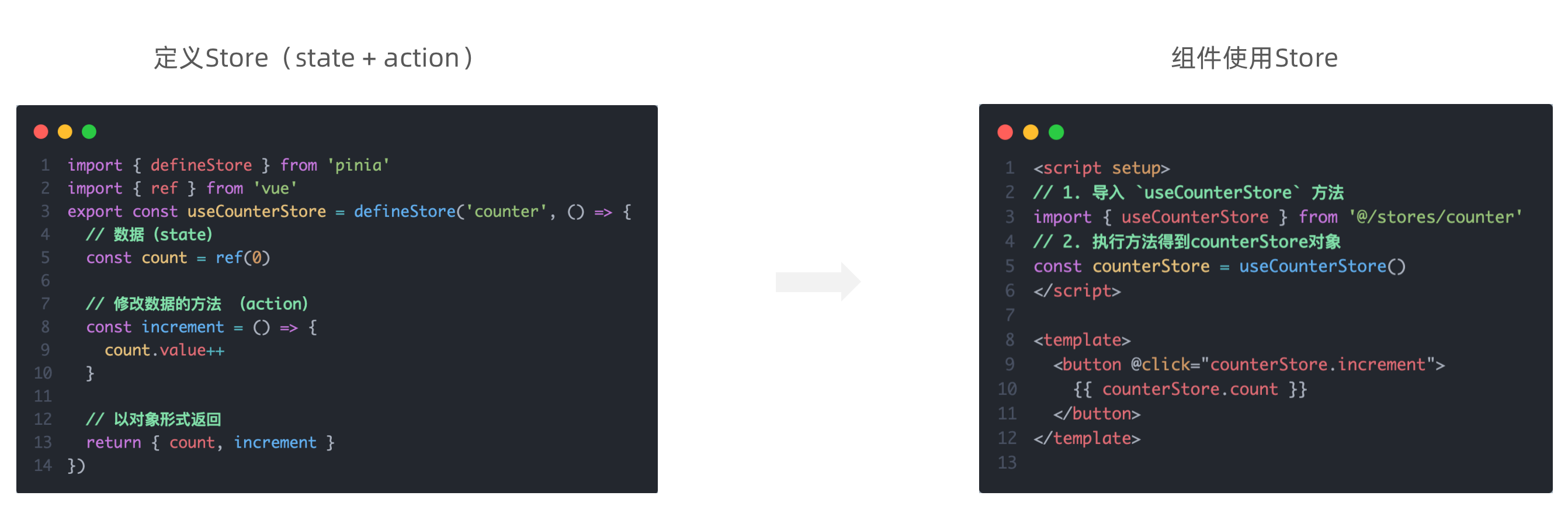
4. getters实现
Pinia中的 getters 直接使用 computed函数 进行模拟, 组件中需要使用需要把 getters return出去

代码
counter.js
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { computed, ref } from "vue";
// 定义store
// defineStore(仓库的唯一标识, () => {...})
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('conter', () => {
// 声明数据 state - count
const count = ref(100)
// 声明操作数据的方法 action (普通函数)
const addCount = () => count.value++
const subCount = () => count.value--
// 声明基于数据派生的计算属性 getters (computed)
const double = computed(() => count.value * 2)
// 声明数据 state - msg
const msg = ref('hello pinia')
// 声明数据
return {
count,
msg,
addCount,
subCount,
double
}
})Son1Com.vue
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from '@/store/counter'
const counterStore = useCounterStore()
</script>
<template>
<div>
我是Son1 - {{ counterStore.count }} - {{ counterStore.double }}<button @click="counterStore.addCount">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>Son2Com.vue
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from '@/store/counter'
const counterStore = useCounterStore()
</script>
<template>
<div>
我是Son2 - {{ counterStore.count }} - <button @click="counterStore.subCount">-</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>5. action异步实现
方式:异步action函数的写法和组件中获取异步数据的写法完全一致
接口地址:http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels
请求方式:get
请求参数:无

需求:在Pinia中获取频道列表数据并把数据渲染App组件的模板中 
代码:
App.vue
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from '@/store/counter'
import { useChannelStore } from './store/channel'
const counterStore = useCounterStore()
const channelStore = useChannelStore()
console.log(counterStore);
</script>
<template>
<div>
<button @click="channelStore.getList">获取频道数据</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in channelStore.channelList" :key="item.id">{{item.name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
</style>仓库文件channel.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref } from 'vue'
import axios from 'axios'
export const useChannelStore = defineStore('channel', () => {
// 声明数据
const channelList = ref([])
// 声明操作数据的方法
const getList = async () => {
// 支持异步
const { data: { data }} = await axios.get('http://geek.itheima.net/v1_0/channels')
console.log(data);
channelList.value = data.channels
}
// 声明getters相关
// 导出数据和方法
return {
channelList,
getList
}
})6. storeToRefs工具函数
使用storeToRefs函数可以辅助保持数据(state + getter)的响应式解构
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
注意:
如果解析的是数据,需要storeToRefs函数,如果解析的是方法就不用storeToRefs也是响应式的
7. Pinia的调试
Vue官方的 dev-tools 调试工具 对 Pinia直接支持,可以直接进行调试 
8. Pinia持久化插件
官方文档:https://prazdevs.github.io/pinia-plugin-persistedstate/zh/
- 安装插件 pinia-plugin-persistedstate
npm i pinia-plugin-persistedstate- 使用 main.js
// 导入持久化插件
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
const pinia = createPinia()
pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)例:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
// 导入持久化的插件
import piniaPluginPersistedstate from 'pinia-plugin-persistedstate'
const pinia = createPinia() // 创建Pinia实例
const app = createApp(App) // 创建跟实例
app.mount('#app') // 视图的挂载
app.use(pinia.use(piniaPluginPersistedstate)) // pinia插件的安装配置- 配置 store/counter.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
...
return {
count,
doubleCount,
increment
}
}, {
// 配置持久化配置保存
persist: true
})- 其他配置,看官网文档即可